Abstract
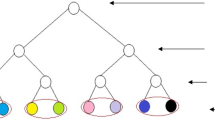
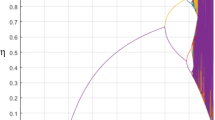
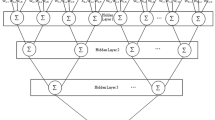
In this paper, a chaos-based triple-layer tree parity machine (TLTPM)-guided neural synchronization has been proposed for the development of the public key exchange protocol. A special neural network structure called tree parity machine (TPM) is used for neural synchronization. Two TPMs accept the common input and different weight vectors and update the weights using the neural learning rule by exchanging their output. In some steps, it results in complete synchronization, and the weights of the two TPMs become identical. These identical weights serve as a secret key. There is, however, hardly any investigation to investigate the randomness of the common input vector used in the synchronization process. In this paper, logistic chaos system-based TLTPM is proposed. For faster synchronization, this proposed TLTPM model uses logistic chaos-generated random common input vector. This proposed TLTPM model is faster and has better security than TPM with the same input, output, and hidden neurons. This proposed technique has been passed through a series of parametric tests. The results have been compared with some recent techniques. The results of the proposed technique have shown effective and robust potential.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bauer, F.L.: Cryptology. In: van Tilborg, H.C.A., Jajodia, S. (eds.) Encyclopedia of Cryptography and Security, pp. 283–284. Springer, Boston, MA (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4419-5906-5
Rana, S.; Mishra, D.: Secure and ubiquitous authenticated content distribution framework for IoT enabled DRM system. Multimedia Tools Appl. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-020-08683-2
Elashry, I.F.; El-Shafai, W.; Hasan, E.S.: Efficient chaotic-based image cryptosystem with different modes of operation. Multimedia Tools Appl. 79, 20665–20687 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-019-08322-5
Kamrani, A.; Zenkouar, K.; Najah, S.: A new set of image encryption algorithms based on discrete orthogonal moments and Chaos theory. Multimedia Tools Appl. 79, 20263–20279 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-020-08879-6
Lindell, Y.; Katz, J.: Introduction to Modern Cryptography. Chapman and Hall/CRC, London (2014)
Diffie, W.; Hellman, M.: New directions in cryptography. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 22(6), 644–654 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1109/tit.1976.1055638
Steiner, M.; Tsudik, G.; Waidner, M.: Diffie–Hellman key distribution extended to group communication. In: Proceedings of the 3rd ACM Conferecne, pp. 31–37 (1996)
Balasubramaniam, P.; Muthukumar, P.: Synchronization of chaotic systems using feedback controller: an application to Diffie-Hellman key exchange protocol and ElGamal public key cryptosystem. J. Egypt. Math. Soc. 22(3), 365–372 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joems.2013.10.003
Eftekhari, M.: A Diffie-Hellman key exchange protocol using matrices over noncommutative rings. Groups Complex. Cryptol. 4(1), 167–176 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1515/gcc-2012-0001
Zhou, X.; Tang, X.: Research and implementation of RSA algorithm for encryption and decryption. In Proceedings of 2011 6th International Forum on Strategic Technology, vol 2, pp. 1118–1121. IEEE (2011). https://doi.org/10.1109/IFOST.2011.6021216
Meneses, F.; Fuertes, W.; Sancho, J.: RSA encryption algorithm optimization to improve performance and security level of network messages. IJCSNS 16(8), 55 (2016)
Chen, H.; Shi, P.; Lim, C.C.: Cluster synchronization for neutral stochastic delay networks via intermittent adaptive control. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 30(11), 3246–3259 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/tnnls.2018.2890269
Liu, P.; Zeng, Z.; Wang, J.: Global synchronization of coupled fractional-order recurrent neural networks. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 30(8), 2358–2368 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/TNNLS.2018.2884620
Chen, H.; Shi, P.; Lim, C.C.: Exponential synchronization for Markovian stochastic coupled neural networks of neutral-type via adaptive feedback control. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 28(7), 1618–1632 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/TNNLS.2016.2546962
Wang, J.; Cheng, L.M.; Su, T.: Multivariate cryptography based on clipped hopfield neural network. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 29(2), 353–363 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/tnnls.2016.2626466
Wang, J.L.; Qin, Z.; Wu, H.N.; Huang, T.: Passivity and synchronization of coupled uncertain reaction-diffusion neural networks with multiple time delays. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 30(8), 2434–2448 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/TNNLS.2018.2884954
Xiao, Q.; Huang, T.; Zeng, Z.: Global exponential stability and synchronization for discrete-time inertial neural networks with time delays: a timescale approach. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 30(6), 1854–1866 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/TNNLS.2018.2874982
Zhang, Z.; Cao, J.: Novel finite-time synchronization criteria for inertial neural networks with time delays via integral inequality method. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 30(5), 1476–1485 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/TNNLS.2018.2868800
Wang, A.; Dong, T.; Liao, X.: Event-triggered synchronization strategy for complex dynamical networks with the Markovian switching topologies. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 74, 52–57 (2016)
Dong, T.; Wang, A.; Zhu, H.; Liao, X.: Event-triggered synchronization for reaction-diffusion complex networks via random sampling. Physica A Stat. Mech. Appl. 495, 454–462 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physa.2017.12.008
Rosen-Zvi, M.; Kanter, I.; Kinzel, W.: Cryptography based on neural networks analytical results. J. Phys. A Math. Gen. 35(47), L707–L713 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1088/0305-4470/35/47/104
Lakshmanan, S.; Prakash, M.; Lim, C.P.; Rakkiyappan, R.; Balasubramaniam, P.; Nahavandi, S.: Synchronization of an inertial neural network with time-varying delays and its application to secure communication. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 29(1), 195–207 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/tnnls.2016.2619345
Ni, Z.; Paul, S.: A multistage game in smart grid security: a reinforcement learning solution. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 30(9), 2684–2695 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/tnnls.2018.2885530
Kinzel, W.; Kanter, I.: Interacting neural networks and cryptography. In: Advances in Solid State Physics, pp. 383–391 (2002)
Ruttor, A.; Kinzel, W.; Naeh, R.; Kanter, I.: Genetic attack on neural cryptography. Phys. Rev. E (2006). https://doi.org/10.1103/physreve.73.036121
Sarkar, A.; Mandal, J.K.: Artificial Neural Network Guided Secured Communication Techniques: A Practical Approach. LAP LAMBERT Academic Publishing, Berlin (2012)
Sarkar, A.; Dey, J.; Chatterjee, M.; Bhowmik, A.; Karforma, S.: Neural soft computing based secured transmission of intraoral gingivitis image in e-health care. Indones. J. Electr. Eng. Comput. Sci. 14(1), 178 (2019). https://doi.org/10.11591/ijeecs.v14.i1.pp178-184
Sarkar, A.; Dey, J.; Bhowmik, A.: Multilayer neural network synchronized secured session key based encryption in wireless communication. Indones. J. Electr. Eng. Comput. Sci. 14(1), 169 (2019). https://doi.org/10.11591/ijeecs.v14.i1.pp169-177
Sarkar, A.; Mandal, J.K.: Key generation and certification using multilayer perceptron in wireless communication (KGCMLP). Int. J. Secur. Priv. Trust Manag. (IJSPTM) 1(5), 2319–4103 (2012)
Sarkar, A., Dey, J., Bhowmik, A., Mandal, J.K., Karforma, S.: Computational intelligence based neural session key generation on e-health system for ischemic heart disease information sharing. In: Mandal, J.K., Sinha, D. (eds.) Contemporary. Advances in Innovative and Applicable Information Technology Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing, vol. 812. Springer, Berlin (2019)
Allam, A.M.; Abbas, H.M.; El-Kharashi, M.W.: Authenticated key exchange protocol using neural cryptography with secret boundaries. In: Proceedings of the 2013 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, IJCNN 2013, pp. 1–8 (2013)
Ruttor, A.: Neural synchronization and cryptography (2007). arXiv:0711.2411
Klimov, A.; Mityagin, A.; Shamir, A.: Analysis of neural cryptography. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on the Theory and Application of Cryptology and information security, pp. 288–298 (2002)
Dolecki, M.; Kozera, R.: Threshold method of detecting longtime TPM synchronization. In: Computer Information Systems and Industrial Management, vol. 8104, pp. 241–252. Springer (2013)
Santhanalakshmi, S.; Sangeeta, K.; Patra, G.K.: Analysis of neural synchronization using genetic approach for secure key generation. Commun. Comput. Inf. Sci. 536, 207–216 (2015)
Dolecki, M.; Kozera, R.: The impact of the TPM weights distribution on network synchronization time. In: Computer Information Systems and Industrial Management, vol 9339, pp. 451–460. Springer International Publishing (2015)
Dolecki, M.; Kozera, R.: Distribution of the tree parity machine synchronization time. Adv. Sci. Technol. Res. J. 7(18), 20–27 (2013). https://doi.org/10.5604/20804075.1049490
Pu, X.; Tian, X.J.; Zhang, J.; Liu, C.Y.; Yin, J.: Chaotic multimedia stream cipher scheme based on true random sequence combined with tree parity machine. Multimedia Tools Appl. 76(19), 19881–19885 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-016-3728-0
Mu, N., Liao, X.: An approach for designing neural cryptography. In: Guo, C., Hou, Z.-G., Zeng, Z. (eds.) Advances in Neural Networks. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 7951, pp. 99–108. Springer, Heidelberg (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-39065-4_13
Mu, N.; Liao, X.; Huang, T.: Approach to design neural cryptography: a generalized architecture and a heuristic rule. Phys. Rev. E (2013). https://doi.org/10.1103/physreve.87.062804
Gomez, H.; Reyes, Ó.; Roa, E.: A 65 nm CMOS key establishment core based on tree parity machines. Integration 58, 430–437 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vlsi.2017.01.010
Niemiec, M.: Error correction in quantum cryptography based on artificial neural networks. Quantum Inf. Process 174, 1 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-019-2296-4
Dong, T.; Huang, T.: Neural cryptography based on complex-valued neural network. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 31(11), 4999–5004 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/TNNLS.2019.2955165
Engel, A., den Broeck, C.V.: Statistical Mechanics of Learning. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2012). https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9781139164542
Cover, T.M., Thomas, J.A.: Elements of Information Theory. Wiley Series in Telecommunications and Signal Processing, 2nd edn. Wiley-Interscience, New York (2006)
NIST: NIST Statistical Test (2020). http://csrc.nist.gov/groups/ST/toolkit/rng/stats_tests.html
Karakaya, B.; Gülten, A.; Frasca, M.: A true random bit generator based on a memristive chaotic circuit: analysis, design and FPGA implementation. Chaos Solitons Fract. 119, 143–149 (2019)
Patidar, V.; Sud, K.K.; Pareek, N.K.: A pseudo random bit generator based on chaotic logistic map and its statistical testing. Informatica 33, 441–452 (2009)
Liu, L.; Miao, S.; Hu, H.; Deng, Y.: Pseudo-random bit generator based on non-stationary logistic maps. IET Inf. Secur. 2(10), 87–94 (2016)
Acknowledgements
The author expressed deep gratitude for the moral and congenial atmosphere support provided by Ramakrishna Mission Vidyamandira, Belur Math, India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Conflicts of Interest
No conflict of Interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sarkar, A. Chaos-Based Mutual Synchronization of Three-Layer Tree Parity Machine: A Session Key Exchange Protocol Over Public Channel. Arab J Sci Eng 46, 8565–8584 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-021-05387-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-021-05387-z