Abstract—
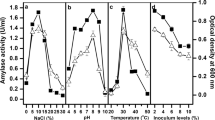
From a technogenic soda sludge storage, 58 cultures of alkalitolerant bacteria with amylase, lipase, protease, and cellulase activities were isolated and identified using a medium with selective substrates in the absence of extreme conditions (pH 8) and a rich medium with pH 11 without selective substrates. The effect of pH and NaCl concentration on the growth and hydrolytic activity of Pseudomonas peli, Paenarthrobacter nitroquajacolicus, and Microbacterium kitamiense with lipase and amylase activities was studied. Amylases of the cultures isolated on media with pH 11 and 8 were shown to exhibit the highest activity at pH 10 and 6, respectively, while the specific activity of extracellular lipase of P. peli isolated at pH 8 reached its maximum at pH 11. On the medium with pH 11, Bacillus aequororis, Brevibacterium pityocampae, Microbacterium kitamiense, Microcella putealis, Oerskovia paurometabola, O. enterophila, and O. jenensis with alkaline amylase activity were isolated.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Ali, S.S., Habib, I., and Riaz, T., Screening and characterization of alkaliphilic bacteria from industrial effluents, Punjab Univ. J. Zool., 2009, vol. 24, pp. 49–60.
Anish, R., Rahman, M.S., and Rao, M., Application of cellulases from an alkalothermophilic Thermomonospora sp. in biopolishing of denims, Biotechnol. Bioeng., 2007, vol. 96, pp. 48–56.
Atlas, R.M., Handbook of Microbiological Media, Parks, L.C., Ed., Boca Raton: CRC press, 1993.
Bezborodov, A.M. and Zagustina, N.A., Lipases in catalytic reactions of organic chemistry, Appl. Biochem. Microbiol., 2014, vol. 50, pp. 313–337.
Blinov, S.M., Maksimovich, N.G., Naidanova, N.F., Shlykov, V.G., and Potapov, S.S., Mineralogical basis of waste treatment in the Berezniki Soda Plant, Mineralogiya Tekhnogeneza, 2003, vol. 4, pp. 51–55.
Borzenko, S.V. and Zamana, L.V., Sulfate reduction as a factor of soda water formation in Lake Doroninskoe (Eastern Transbaikalia), Vestn. Tomsk State Univ., 2008, no. 312, pp. 188–193.
Febriani Rayyana, Ulya, M., Oesman, F., Akhmaloka, and Iqbalsyah, T.M., Low molecular weight alkaline thermostable α-amylase from Geobacillus sp. nov., Heliyon, 2019, vol. 5, e02171.
Grant, W.D. and Sorokin, D.Yu., Distribution and diversity of soda lake alkaliphiles, in Extremophiles Handbook, Horikoshi, K., Antranikian, G., Bull, A., Robb, F., and Stetler, K., Eds., Tokyo: Springer-Verlag, 2011, pp. 27–54.
Gupta, R., Beg, Q.K., and Lorenz, P., Bacterial alkaline proteases: molecular approaches and industrial applications, Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 2002, vol. 59, pp. 15–32.
Hasan, F., Shah, A.A., Javed, S., and Hameed, A., Enzymes used in detergents: lipases, Afr. J. Biotechnol., 2010, vol. 9, pp. 4836–4844.
Horikoshi, K., Alkaliphiles: some applications of their products for biotechnology, Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev., 1999, vol. 63, pp. 735–750.
Jagtap, S. and Rao, M., Purification and properties of a low molecular weight 1,4-β-D-glucan glucohydrolase having one active site for carboxymethyl cellulose and xylan from an alkalothermophilic Thermomonospora sp., Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 2005, vol. 329, pp. 111–116.
Kalwasińska, A., Felföldi, T., Szab, A.J., Deja-Sikora, E., Kosobucki, P., and Walczak, M., Microbial communities associated with the anthropogenic, highly alkaline environment of a saline soda lime, Antonie van Leeuwenhoek, 2017, vol. 110, pp. 945–962.
Kevbrin, V.V., Isolation and cultivation of alkaliphiles, in Alkaliphiles in Biotechnology, Mamo, G. and Mattiasson, B., Eds., Cham: Springer, 2019, Advances in Biochemical Engineering/Biotechnology, vol. 172, pp. 53–84.
Kubrak, O.I., Storey, J.M., Storey, K.B., and Lushchak, V.I., Production and properties of α-amylase from Bacillus sp. BKL20, Can. J. Microbiol., 2010, vol. 56, pp. 279–288.
Margesin, R., Feller, G., Hämmerle, M., Stegner, U., and Schinner, F., A colorimetric method for the determination of lipase activity in soil, Biotechnol. Lett., 2002, vol. 24, pp. 27–33.
Mc Tigue, M.A., Kelly, C.T., Doyle, E.M., and Fogarty, W.M., The alkaline amylase of the alkalophilic Bacillus sp. IMD 370, Enzyme Microb. Technol., 1995, vol. 17, pp. 570–573.
Novozhilov, E.V. and Poshina, D.N., Biotechnologies in cellulose production for chemical treatment (a review), Kh-imiya rastitel’nogo syr’ya, 2011, no. 3, pp. 15–32.
Oren, A., Industrial and environmental applications of halophilic microorganisms, Environ. Technol., 2010, vol. 31, pp. 825–834.
Randagurueva, A.A. and Lavrent’eva, E.V., Extracellular protease activity in natural samples of thermal springs of the Baikal region, Izv. Irkutsk State Univ., Ser. Nauki o Zemle, 2009, vol. 2, no. 2, pp. 162–166.
Ren, L., Han, Y., Yang, S., Tan, X., Wang, J., Zhao, X., Fan, J., Dong, T., and Zhou, Z., Isolation, identification and primary application of bacteria from putrid alkaline silica sol, Front. Chem. Sci. Eng., 2014, vol. 8, pp. 330–339.
Rios, N.S., Pinheiro, B.B., Pinheiro, M.P., Bezerra, R.M., Sousa dos Santos, J.C., and Gonçalves, L.R.B., Biotechnological potential of lipases from Pseudomonas: Sources, properties and applications, Process Biochem., 2018, vol. 75, pp. 99–120.
Roadcap, G.S., Sanford, R.A., Jin, Q., Pardinas, J.R., and Bethke, C.M., Extremely alkaline (pH > 12) ground water hosts diverse microbial community, Ground Water, 2006, vol. 44, pp. 511–517.
Sarethy, I.P., Saxena, Y., Kapoor, A., Sharma, M., Sharma, S.K., Gupta, V., and Gupta, S., Alkaliphilic bacteria: applications in industrial biotechnology, J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 2011, vol. 38, pp. 769–790.
Saxena, R.K., Dutt, K., Agarwal, L., and Nayyar, P., A highly thermostable and alkaline amylase from a Bacillus sp. PN5, Biores. Technol., 2007, vol. 98, pp. 260–265.
Sharma, K.M., Kumar, R., Panwar, S., and Kuma, A., Microbial alkaline proteases: optimization of production parameters and their properties, J. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol., 2017, vol. 15, pp. 115–126.
Shilova, A.V., Maksimov, A.Yu., and Maksimova, Yu.G., Metagenomic analysis of the genus-level composition of bacterial communities of the soil, water, and sediments of the new and old sludge storage of the OAO Soda (Berezniki, Perm krai), Biomika, 2018, vol. 10, no. 1, pp. 24–27.
Shilova, A.V., Maksimov, A.Yu., and Maksimova, Yu.G., Microbiome changes as a marker of environmental remediation in the soda sludge storage of the Berezniki Soda Plant, Voda Ekologiya: Problemy Resheniya, 2020, no. 1(81), pp. 81–94.
Sorokin, D.Y., Banciu, H.L., and Muyzer, G., Functional microbiology of soda lakes, Curr. Opin. Microbiol., 2015, vol. 25, pp. 88–96.
Zavarzin, G.A. and Zhilina, T.N., Soda lakes: a natural model of the ancient biosphere of the continent, Priroda, 2000, no. 2, pp. 45–55.
Funding
This study was supported by the Russian Foundation for Basic Research, project no. 19-34-90103.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests. The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Statement on the welfare of animals. This article does not contain any studies involving animals or human participants performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Translated by A. Panyushkina
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shilova, A.V., Maksimov, A.Y. & Maksimova, Y.G. Isolation and Identification of Alkalitolerant Bacteria with Hydrolytic Activity from a Soda Sludge Storage. Microbiology 90, 166–175 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026261721020120
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026261721020120