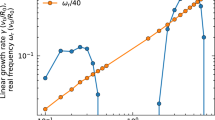
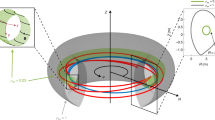
Abstract
Avoiding the accumulation of helium ash in the plasma core is a critical issue for future fusion reactors such as International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor and China Fusion Engineering Test Reactor. The effects of micro-turbulence, including ion temperature gradient (ITG), parallel velocity shear (PVS) and collisionless trapped electron mode (CTEM) turbulence, on the removal of helium ash are briefly reviewed. We study how helium ash affects ITG and PVS instabilities based on our previous theoretical works, and compare the corresponding results with CTEM instability. The parametric dependence of ash flux is illustrated by calculating the turbulent flux and the corresponding transport coefficients. It indicates that long wavelength electrostatic micro-turbulence is favorable for removing helium ash, especially when its density profile is steeper than that of electrons. The outward flux of helium ash becomes larger for the temperature of helium ash being slightly higher than that of background plasmas (\({T}_{z}>{T}_{e}={T}_{i}\)). Isotopic effects are favorable (unfavorable) for exhausting helium ash through PVS and CTEM (ITG) turbulence. In addition, the ambipolarity of turbulent transport fluxes between electrons, ions and helium ash is self-consistently verified, and its implication on the simultaneous transport of both helium ash and D–T ions is discussed.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
ITER Physics Basis 1999 (Chapter 2: Plasma confinement and transport) Nucl. Fusion 39 2175.
E.J. Synakowski, R.E. Bell et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 75, 3689 (1995)
W. Horton, Rev. Mod. Phys. 71, 735 (1999)
T. Fülöp, S. Braun et al., Phys. Plasmas 17, 062501 (2010)
A. Mollén, I. Pusztai et al., Phys. Plasmas 20, 032310 (2013)
T. Hein, C. Angioni, Phys. Plasmas 17, 012307 (2010)
T. Fülöp, J. Weiland, Phys. Plasmas 13, 112504 (2006)
C. Angioni, A.G. Peeters, Phys. Rev. Lett. 96, 095003 (2006)
S.S. Henderson, L. Garzotti et al., Nucl. Fusion 54, 093013 (2014)
C. Angioni, A.G. Peeters et al., Nucl. Fusion 49, 055013 (2009)
J.Q. Dong, W. Horton et al., Phys. Plasmas 1, 3250 (1994)
D.R. McCarthy, S. Maurer, Phys. Rev. Lett. 81, 3399 (1998)
D.R. McCarthy, A.E. Booth et al., Phys. Plasmas 4, 300 (1997)
A. Dimits, B. Cohen et al., Nucl. Fusion 40, 1725 (2001)
Y. Kosuga, S.I. Itoh et al., Plasma Fusion Res. 10, 3401024 (2015)
N. D’Angelo, Phys. Fluids 8, 1748 (1965)
P.J. Catto, Phys. Fluids 16, 1719 (1973)
G. Wang, L. Wang et al., Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 40, 429 (1998)
W.X. Wang, S. Ethier et al., Nucl. Fusion 55, 122001 (2015)
J.Q. Dong, W.B. Xu et al., Phys. Plasmas 5, 4328 (1998)
X. Garbet, Y. Sarazin et al., Phys. Plasmas 9, 3893 (2002)
S.S. Kim, H. Jhang et al., Nucl. Fusion 51, 073021 (2011)
W. Guo, L. Wang et al., Phys. Plasmas 23, 112301 (2016)
W. Guo, L. Wang et al., Nucl. Fusion 59, 076012 (2019)
W. Guo, M. Zhang et al., Nucl. Fusion 61, 016020 (2021)
W. Guo, L. Wang et al., Nucl. Fusion 57, 126052 (2017)
J.C. Adam, W.M. Tang et al., Phys. Fluids 19, 561 (1976)
M.R. Wade, D.L. Hillis et al., Phys. Plasmas 2, 2357 (1995)
O. Schmitz, K. Ida et al., Nucl. Fusion 56, 106011 (2016)
S. Moradi, I. Pusztai et al., Phys. Plasmas 19, 032301 (2012)
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful for the many discussions during the 1st CFEC in Leshan, China. We also acknowledge Profs. Xiaogang Wang, Vincent Chan, P. H. Diamond and K. Ida for useful and interesting discussions. This work is supported by the National Key R&D Program of China under Grant No. 2017YFE0302000, the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant Nos.11905079 and 11675059, 51821005, and the Initiative Postdocs Supporting Program of China under Grant No. BX20180105 and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, HUST: 2021XXJS007.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, W., Zhang, M. Effects of Micro-turbulence on the Removal of Helium Ash in Deuterium–Tritium Plasmas. J Fusion Energ 40, 8 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10894-021-00303-7
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10894-021-00303-7