Abstract
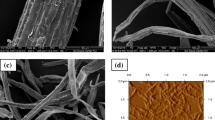
In this study, we have successfully synthesized cellulose nanocrystal/hydroxyapatite nanostructure (CN/HAP) hybrids using Phoenix dactylifera lignocellulosic biomass and eggshell as bio-precursors. CN/HAP nanohybrids were synthesized via ultrasonication. The prepared nanohybrids were characterized via Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction (XRD), thermogravimetric analysis, scanning electron microscopy, and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). XRD and FTIR results indicate CN/HAP hybrid formation. TEM images displayed ~10 to 50 nm HAP nanoparticles decorated on 100 to 200 nm CN matrix. Cell viability assay and acridine orange/ethidium bromide staining results revealed that CN/HAP nanohybrids do not alter cell viability and morphology, indicating that nanohybrids are non-toxic and biocompatible. CN/HAP nanohybrids increased alkaline phosphatase (ALP) activity and calcium nodule formation with upregulation of osteogenic marker (BMP-2, BMP-4, ALP, and BGLAP) gene expression in hMSCs. Overall, the findings suggest that agro-waste-derived CN/HAP hybrids can be suitable for bone tissue engineering applications.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Hadi AM, Periasamy VS, Athinarayanan J, Alshatwi AA (2016) The presence of carbon nanostructures in bakery products induces metabolic stress in human mesenchymal stem cells through CYP1A and p53 gene expression. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 41:103–112
Al-Khalifah NS, Askari E, Khan AS (2012) Molecular and morphological identification of some elite varieties of date palms grown in Saudi Arabia. Emirates J Food Agric 24(5):456
Alshatwi AA, Athinarayanan J, Periasamy VS (2015a) Biocompatibility assessment of rice husk-derived biogenic silica nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Mater Sci Eng C 47:8–16
Alshatwi AA, Athinarayanan J, Periasamy VS (2015b) Green synthesis of bimetallic Au@Pt nanostructures and their application for proliferation inhibition and apoptosis induction in human cervical cancer cell. J Mater Sci Mater Med 26(3):148
Alshatwi AA, Athinarayanan J, Subbarayan PV (2015c) Green synthesis of platinum nanoparticles that induce cell death and G2/M-phase cell cycle arrest in human cervical cancer cells. J Mater Sci Mater Med 26:7
Apalangya VA, Rangari VK, Tiimob BJ, Jeelani S, Samuel T (2019) Eggshell based nano-engineered hydroxyapatite and poly(lactic) acid electrospun fibers as potential tissue scaffold. Int J Biomater 2019:6762575
Athinarayanan J, Periasamy VS, Alshatwi AA (2014) Biogenic silica-metal phosphate (metal = Ca, Fe or Zn) nanocomposites: fabrication from rice husk and their biomedical applications. J Mater Sci Mater Med 25(7):1637–1644
Athinarayanan J, Periasamy VS, Alhazmi M, Alatiah KA, Alshatwi AA (2015) Synthesis of biogenic silica nanoparticles from rice husks for biomedical applications. Ceram Int 41(1):275–281
Athinarayanan J, Periasamy VS, Alshatwi AA (2018a) Fabrication and cytotoxicity assessment of cellulose nanofibrils using Bassia eriophora biomass. Int J Biol Macromol 117:911–918
Athinarayanan J, Periasamy VS, Krishnamoorthy R, Alshatwi AA (2018b) Evaluation of antibacterial and cytotoxic properties of green synthesized Cu2O/graphene nanosheets. Mater Sci Eng C 93:242–253
Athinarayanan J, Periasamy VS, Alshatwi AA (2019a) Phoenix dactylifera lignocellulosic biomass as precursor for nanostructure fabrication using integrated process. Int J Biol Macromol 134:1179–1186
Athinarayanan J, Periasamy VS, Qasem AA, Al-Shagrawi RA, Alshatwi AA (2019b) Synthesis of SiO2 nanostructures from Pennisetum glaucum and their effect on osteogenic differentiation for bone tissue engineering applications. J Mater Sci Mater Med 30(2):1–10
Athinarayanan J, Periasamy VS, Alshatwi AA (2020a) Simultaneous fabrication of carbon nanodots and hydroxyapatite nanoparticles from fish scale for biomedical applications. Mater Sci Eng C 117:111313
Athinarayanan J, Alshatwi AA, Periasamy VS (2020b) Biocompatibility analysis of Borassus flabellifer biomass-derived nanofibrillated cellulose. Carbohydr Polym 235:115961
Ben-Nissan B (2003) Natural bioceramics: From coral to bone and beyond. Curr Opin Solid State Mater Sci 7:283–288
Bhattacharya D, Germinario LT, Winter WT (2008) Isolation, preparation and characterization of cellulose microfibers obtained from bagasse. Carbohydr Polym 73(3):371–377
Carvalho J, Araújo J, Castro F (2011) Alternative low-cost adsorbent for water and wastewater decontamination derived from eggshell waste: an overview. Waste Biomass Valoriz 2(2):157–167
Chandrasekaran M, Bahkali AH (2013) Valorization of date palm (Phoenix dactylifera) fruit processing by-products and wastes using bioprocess technology—review. Saudi J Biol Sci 20(2):105–120
Duran N, Paula Lemes A, Seabra AB (2012) Review of cellulose nanocrystals patents: preparation, composites and general applications. Recent Pat Nanotechnol 6(1):16–28
Gutiérrez-Prieto SJ, Fonseca LF, Sequeda-Castañeda LG, Díaz KJ, Castañeda LY, Leyva-Rojas JA, Salcedo-Reyes JC, Acosta AP (2019) Elaboration and biocompatibility of an eggshell-derived hydroxyapatite material modified with Si/PLGA for bone regeneration in dentistry. Int J Dentist 2019:5949232
Haafiz MM, Hassan A, Zakaria Z, Inuwa IM (2014) Isolation and characterization of cellulose nanowhiskers from oil palm biomass microcrystalline cellulose. Carbohydr Polym 103:119–125
Habte L, Shiferaw N, Mulatu D, Thenepalli T, Chilakala R, Ahn JW (2019) Synthesis of nano-calcium oxide from waste eggshell by sol-gel method. Sustainability 11(11):3196
Herranen K, Lohman M (2015) U.S. Patent No. 9,018,189. U.S. Patent and Trademark Office, Washington, DC
Ingole VH, Vuherer T, Maver U, Vinchurkar A, Ghule AV, Kokol V (2020) Mechanical properties and cytotoxicity of differently structured nanocellulose-hydroxyapatite based composites for bone regeneration application. Nanomaterials 10(1):25
Jaafari SAAH, Athinarayanan J, Periasamy VS, Alshatwi AA (2020) Biogenic silica nanostructures derived from Sorghum bicolor induced osteogenic differentiation through BSP, BMP-2 and BMP-4 gene expression. Process Biochem 91:231–240
Jie W, Yubao L (2004) Tissue engineering scaffold material of nano-apatite crystals and polyamide composite. Eur Polym J 40(3):509–515
Johar N, Ahmad I, Dufresne A (2012) Extraction, preparation and characterization of cellulose fibres and nanocrystals from rice husk. Ind Crop Prod 37(1):93–99
Jorfi M, Foster EJ (2015) Recent advances in nanocellulose for biomedical applications. J Appl Polym Sci 132(14):41719
Kumar P, Joshi L (2013) Pollution caused by agricultural waste burning and possible alternate uses of crop stubble: a case study of Punjab. In: Knowledge systems of societies for adaptation and mitigation of impacts of climate change. Springer, Berlin/Heidelberg, pp 367–385
Laschke MW, Strohe A, Scheuer C, Eglin D, Verrier S, Alini M, Pohlemann T, Menger MD (2009) In vivo biocompatibility and vascularization of biodegradable porous polyurethane scaffolds for tissue engineering. Acta Biomater 5(6):1991–2001
Laufenberg G, Kunz B, Nystroem M (2003) Transformation of vegetable waste into value added products: (A) the upgrading concept; (B) practical implementations. Bioresour Technol 87(2):167–198
Liu X, Smith LA, Hu J, Ma PX (2009) Biomimetic nanofibrous gelatin/apatite composite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Biomaterials 30(12):2252–2258
Lu P, Hsieh YL (2012) Cellulose isolation and core-shell nanostructures of cellulose nanocrystals from chardonnay grape skins. Carbohydr Polym 87(4):2546–2553
Mallaki M, Fatehi R (2014) Design of a biomass power plant for burning date palm waste to cogenerate electricity and distilled water. Renew Energy 63:286–291
Mueller S, Weder C, Foster EJ (2014) Isolation of cellulose nanocrystals from pseudostems of banana plants. RSC Adv 4(2):907–915
Murugan R, Sampath Kumar TS, Panduranga Rao K (2002) Fluorinated bovine hydroxyapatite: preparation and characterization. Mater Lett 57:429–433
Oushabi A, Sair S, Abboud Y, Tanane O, El Bouari A (2015) Natural thermal-insulation materials composed of renewable resources: characterization of local date palm fibers (LDPF). J Mater Environ Sci 6(12):3395–3402
Periasamy VS, Athinarayanan J, Al-Hadi AM, Al Juhaimi F, Mahmoud MH, Alshatwi AA (2015) Identification of titanium dioxide nanoparticles in food products: induce intracellular oxidative stress mediated by TNF and CYP1A genes in human lung fibroblast cells. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 39(1):176–186
Periasamy VS, Athinarayanan J, Alshatwi AA (2016) Anticancer activity of an ultrasonic nanoemulsion formulation of Nigella sativa L. essential oil on human breast cancer cells. Ultrason Sonochem 31:449–455
Ravindran R, Jaiswal AK (2016) Exploitation of food industry waste for high-value products. Trends Biotechnol 34(1):58–69
Rebouillat S, Pla F (2013) State of the art manufacturing and engineering of nanocellulose: a review of available data and industrial applications. J Biomater Nanobiotechnol 4(02):165–188
Saini JK, Saini R, Tewari L (2015) Lignocellulosic agriculture wastes as biomass feedstocks for second-generation bioethanol production: concepts and recent developments. 3 Biotech 5(4):337–353
Sait HH, Hussain A, Salema AA, Ani FN (2012) Pyrolysis and combustion kinetics of date palm biomass using thermogravimetric analysis. Bioresour Technol 118:382–389
Siddharthan A, Kumar TS, Seshadri SK (2009) Synthesis and characterization of nanocrystalline apatites from eggshells at different Ca/P ratios. Biomed Mater 4(4):045010
Tuck CO, Pérez E, Horváth IT, Sheldon RA, Poliakoff M (2012) Valorization of biomass: deriving more value from waste. Science 337(6095):695–699
Wei H, Rodriguez K, Renneckar S, Vikesland PJ (2014) Environmental science and engineering applications of nanocellulose-based nanocomposites. Environ Sci Nano 1(4):302–316
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge the financial support of the National Plan of Science, Technology and Innovation (MAARIFAH), King Abdulaziz City for Science and Technology, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Award Number : 15-NAN5012-02.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to publish
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Athinarayanan, J., Periasamy, V.S. & Alshatwi, A.A. Fabrication of cellulose nanocrystal-decorated hydroxyapatite nanostructures using ultrasonication for biomedical applications. Biomass Conv. Bioref. 13, 5861–5874 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-021-01481-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-021-01481-2