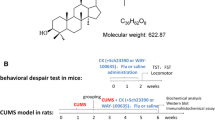
Abstract
Background
Depression causes significant debilitating symptoms and economic burden. Current management is challenged by slow onset of action and modest efficacies of antidepressants; thus, the search for newer antidepressants remains relevant. We evaluated the antidepressant effects of a kaurene diterpene, xylopic acid (XA), in zebrafish and mouse models.
Methods
The chronic unpredictable stress (CUS) protocol in zebrafish and the tail suspension test (TST), forced swim test (FST), lipopolysaccharide-induced depression-like behaviour test (LID) and repeated open space swimming test (OSST) in mice were used. We further examined the impact of depleting monoamines on XA’s antidepressant effects. The contribution of glutamatergic and nitrergic pathways on the antidepressant effect of XA in mice and XA’s effects on 5-HT receptors and monoamine oxidase (MAO) enzymes were also evaluated. Finally, XA’s influence on neuroprotection was evaluated by measuring BDNF and oxidative stress enzymes in whole brain. XA doses (1–10 μM) in zebrafish and (10, 30, 100 mg kg−1) in mice exerted potent antidepressant-like potential in FST, TST, LID and showed fast-onset antidepressant-like property in the OSST.
Results
The antidepressant-like properties in mice were reversed by blocking synthesis/release of serotonin but not noradrenaline using p-chlorophenylalanine and α-methyl-p-tyrosine, respectively. This antidepressant-like effect was potentiated by d-cycloserine and Nω-Nitro-l-arginine methyl ester (l-NAME) but not by d-serine and L-arginine. XA also evoked partial agonist-like effects on 5-hydroxytrptamine receptors on the rat fundus but it did not have MAO inhibition effect. It also increased BDNF, glutathione and antioxidant enzymes.
Conclusion
Therefore, xylopic acid possesses antidepressant-like effects largely mediated by serotonergic and neuroprotective mechanisms.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adaramoye OA, Adedara IA, Popoola B, Farombi EO (2010) Extract of Xylopia aethiopica (Annonaceae) protects against gamma-radiation-induced testicular damage in Wistar rats. J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol 21(4):295–314
Adeoluwa AO, Aderibigbe OA, Agboola IO, Olonode TE, Ben-Azu B (2019) Butanol fraction of Olax subscorpioidea produces antidepressant effect: evidence for the involvement of monoaminergic neurotransmission. Drug Res 69(01):53–60
Allison DJ, Ditor DS (2014) The common inflammatory etiology of depression and cognitive impairment: a therapeutic target. J Neuroinflammation 11(1):151
Ameyaw EO, Woode E, Boakye-Gyasi E, Abotsi WK, Kyekyeku JO, Adosraku RK (2014) Anti-allodynic and anti-hyperalgesic effects of an ethanolic extract and xylopic acid from the fruits of Xylopia aethiopica in murine models of neuropathic pain. Pharm Res 6(2):172–179
Amodeo G, Trusso MA, Fagiolini A (2017) Depression and inflammation: disentangling a clear yet complex and multifaceted link. Neuropsychiatry 7(4):448–457
Association AP (2015) Depressive disorders: DSM-5® Selections. edn. American Psychiatric Pub
Autry AE, Monteggia LM (2012) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor and neuropsychiatric disorders. Pharmacol Rev 64(2):238–258
Barlow R (1961) Effects on amine oxidase of substances which antagonize 5-hydroxytryptamine more than tryptamine on the rat fundus strip. Br J Pharmacol Chemother 16(2):153–162
Bear HA, Edbrooke-Childs J, Norton S, Krause KR, Wolpert M (2019) Systematic review and meta-analysis: outcomes of routine specialist mental health care for young people with depression and/or anxiety. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry
Benneh CK, Biney RP, Mante PK, Tandoh A, Adongo DW, Woode E (2017) Maerua angolensis stem bark extract reverses anxiety and related behaviours in zebrafish—involvement of GABAergic and 5-HT systems. J Ethnopharmacol 207:129–145
Bergner CL, Smolinsky AN, Hart PC, Dufour BD, Egan RJ, LaPorte JL et al (2016) Mouse models for studying depression-like states and antidepressant drugs. In: Mouse Models for Drug Discovery. Springer, pp 255–269
Bian HT, Wang GH, Huang JJ, Liang L, Xiao L, Wang HL (2020) Scutellarin protects against lipopolysaccharide-induced behavioral deficits by inhibiting neuroinflammation and microglia activation in rats. Int Immunopharmacol 88:106943
Biney RP, Mante PK, Boakye-Gyasi E, Kukuia KE, Woode E (2014) Neuropharmacological effects of an ethanolic fruit extract of Xylopia aethiopica and xylopic acid, a kaurene diterpene isolate, in mice. West Afr J Pharm 25(1):106–117
Biney RP, Benneh CK, Ameyaw EO, Boakye-Gyasi E, Woode E (2016) Xylopia aethiopica fruit extract exhibits antidepressant-like effect via interaction with serotonergic neurotransmission in mice. J Ethnopharmacol 184:49–57
Biney RP, Benneh CK, Kyekyeku JO, Ameyaw EO, Boakye-Gyasi E, Woode E (2018) Attenuation of anxiety behaviours by xylopic acid in mice and zebrafish models of anxiety disorder. UKJPB 6(3):7–16
Bourin M (2019) Animal research in psychiatry. In: Frontiers in Psychiatry. Springer, pp 283–296
Bourin M, Chenu F, Ripoll N, David DJP (2005) A proposal of decision tree to screen putative antidepressants using forced swim and tail suspension tests. Behav Brain Res 164(2):266–269
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72(1–2):248–254
Cavalcanti B, Ferreira J, Moura D, Rosa R, Furtado G, Burbano R et al (2010) Structure–mutagenicity relationship of kaurenoic acid from Xylopia sericeae (Annonaceae). Mutat Res Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen 701(2):153–163
Chakravarty S, Reddy BR, Sudhakar SR, Saxena S, Das T, Meghah V et al (2013) Chronic unpredictable stress (CUS)-induced anxiety and related mood disorders in a zebrafish model: altered brain proteome profile implicates mitochondrial dysfunction. PLoS One 8(5):e63302
Cipriani A, Furukawa TA, Salanti G, Chaimani A, Atkinson LZ, Ogawa Y et al (2018) Comparative efficacy and acceptability of 21 antidepressant drugs for the acute treatment of adults with major depressive disorder: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Lancet 391(10128):1357–1366
Crestani F, Seguy F, Dantzer R (1991) Behavioural effects of peripherally injected interleukin-1: role of prostaglandins. Brain Res 542(2):330–335
Czarny P, Wigner P, Galecki P, Sliwinski T (2018) The interplay between inflammation, oxidative stress, DNA damage, DNA repair and mitochondrial dysfunction in depression. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 80:309–321
Dantzer R, O’Connor JC, Freund GG, Johnson RW, Kelley KW (2008) From inflammation to sickness and depression: when the immune system subjugates the brain. Nat Rev Neurosci 9(1):46–56
Draper H, Hadley M (1990) Malondialdehyde determination as index of lipid peroxidation. In: Methods in enzymology, vol 186. Elsevier, pp 421–431
Ekuadzi E, Biney RP, Benneh CK, Osei Amankwaa B, Jato J (2018) Antiinflammatory properties of betulinic acid and xylopic acid in the carrageenan-induced pleurisy model of lung inflammation in mice. Phytother Res 32(3):480–487
Ellman GL (1959) Tissue sulfhydryl groups. Arch Biochem Biophys 82(1):70–77
Fontana BD, Mezzomo NJ, Kalueff AV, Rosemberg DB (2018) The developing utility of zebrafish models of neurological and neuropsychiatric disorders: a critical review. Exp Neurol 299:157–171
Gross C, Seroogy KB (2020) Neuroprotective roles of neurotrophic factors in depression. In: Neuroprotection in Autism, Schizophrenia and Alzheimer’s Disease. Elsevier, pp 125–144
Harro J (2019) Animal models of depression: pros and cons. Cell Tissue Res 1–16
James SL, Abate D, Abate KH, Abay SM, Abbafati C, Abbasi N et al (2018) Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 354 diseases and injuries for 195 countries and territories, 1990–2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet 392(10159):1789–1858
Jangra A, Lukhi MM, Sulakhiya K, Baruah CC, Lahkar M (2014) Protective effect of mangiferin against lipopolysaccharide-induced depressive and anxiety-like behaviour in mice. Eur J Pharmacol 740:337–345
Jangra A, Kwatra M, Singh T, Pant R, Kushwah P, Sharma Y et al (2016) Piperine augments the protective effect of curcumin against lipopolysaccharide-induced neurobehavioral and neurochemical deficits in mice. Inflammation 39(3):1025–1038
Kalueff AV, Stewart AM, Gerlai R (2014) Zebrafish as an emerging model for studying complex brain disorders. Trends Pharmacol Sci 35(2):63–75
Kokel D, Peterson RT (2011) Using the zebrafish photomotor response for psychotropic drug screening. Methods Cell Biol 105:517–524
Kolbeck R, Bartke I, Eberle W, Barde YA (1999) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor levels in the nervous system of wild-type and neurotrophin gene mutant mice. J Neurochem 72(5):1930–1938
Li Y-F (2020) A hypothesis of monoamine (5-HT) – glutamate/GABA long neural circuit: aiming for fast-onset antidepressant discovery. Pharmacol Ther 208:107494
Maximino C, de Brito TM, da Silva Batista AW, Herculano AM, Morato S, Gouveia A Jr (2010) Measuring anxiety in zebrafish: a critical review. Behav Brain Res 214(2):157–171
Meshalkina DA, Kysil EV, Antonova KA, Demin KA, Kolesnikova TO, Khatsko SL et al (2018) The effects of chronic amitriptyline on zebrafish behavior and monoamine neurochemistry. Neurochem Res 43(6):1191–1199
Mizui T, Ishikawa Y, Kumanogoh H, Kojima M (2016) Neurobiological actions by three distinct subtypes of brain-derived neurotrophic factor: multi-ligand model of growth factor signaling. Pharmacol Res 105:93–98
Mnie-Filali O, Faure C, Lambás-Señas L, El Mansari M, Belblidia H, Gondard E et al (2011) Pharmacological blockade of 5-HT7 receptors as a putative fast acting antidepressant strategy. Neuropsychopharmacology 36(6):1275–1288
Mussulini BHM, Leite CE, Zenki KC, Moro L, Baggio S, Rico EP et al (2013) Seizures induced by pentylenetetrazole in the adult zebrafish: a detailed behavioral characterization. PLoS One 8(1):e54515
Nowakowska K, Giebułtowicz J, Kamaszewski M, Adamski A, Szudrowicz H, Ostaszewska T et al (2020) Acute exposure of zebrafish (Danio rerio) larvae to environmental concentrations of selected antidepressants: bioaccumulation, physiological and histological changes. Comp Biochem Physiol, Part C: Toxicol Pharmacol 229:108670
O’Leary OF, Bechtholt AJ, Crowley JJ, Hill TE, Page ME, Lucki I (2007) Depletion of serotonin and catecholamines block the acute behavioral response to different classes of antidepressant drugs in the mouse tail suspension test. Psychopharmacology 192(3):357–371
Opal MD, Klenotich SC, Morais M, Bessa J, Winkle J, Doukas D et al (2014) Serotonin 2C receptor antagonists induce fast-onset antidepressant effects. Mol Psychiatry 19(10):1106–1114
Osafo N, Biney RP, Obiri DD (2016) Aqueous ethanol fruit extract of Xylopia aethiopica and xylopic acid exhibit anti-inflammatory activity through inhibition of the arachidonic acid pathway. UK J Pharm Biosci 4:35–41
Osafo N, Obiri DD, Antwi AO, Yeboah OK (2018) The acute anti-inflammatory action of xylopic acid isolated from Xylopia aethiopica. J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol 29(6):659–669
Osafo N, Obiri DD, Danquah KO, Essel LB, Antwi AO (2019) Potential effects of xylopic acid on acetic acid-induced ulcerative colitis in rats. Turk J Gastroenterol 30(8):732–744
Ostadhadi S, Khan MI, Norouzi-Javidan A, Chamanara M, Jazaeri F, Zolfaghari S et al (2016) Involvement of NMDA receptors and L-arginine/nitric oxide/cyclic guanosine monophosphate pathway in the antidepressant-like effects of topiramate in mice forced swimming test. Brain Res Bull 122:62–70
Otte C, Gold SM, Penninx BW, Pariante CM, Etkin A, Fava M et al (2016) Major depressive disorder. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2(1):1–20
Pehrson AL, Sanchez C (2014) Serotonergic modulation of glutamate neurotransmission as a strategy for treating depression and cognitive dysfunction. CNS Spectrums 19(2):121–133
Piato ÂL, Capiotti KM, Tamborski AR, Oses JP, Barcellos LJ, Bogo MR et al (2011) Unpredictable chronic stress model in zebrafish (Danio rerio): behavioral and physiological responses. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 35(2):561–567
Poleszak E, Wlaź P, Szewczyk B, Wlaź A, Kasperek R, Wróbel A et al (2011) A complex interaction between glycine/NMDA receptors and serotonergic/noradrenergic antidepressants in the forced swim test in mice. J Neural Transm 118(11):1535–1546
Poleszak E, Stasiuk W, Szopa A, Wyska E, Serefko A, Oniszczuk A et al (2016) Traxoprodil, a selective antagonist of the NR2B subunit of the NMDA receptor, potentiates the antidepressant-like effects of certain antidepressant drugs in the forced swim test in mice. Metab Brain Dis 31(4):803–814
Porsolt RD, Le Pichon M, Jalfre M (1977) Depression: a new animal model sensitive to antidepressant treatments. Nature 266(5604):730–732
Ramaker M, Dulawa S (2017) Identifying fast-onset antidepressants using rodent models. Mol Psychiatry 22(5):656–665
Réus GZ, Abelaira HM, Tuon T, Titus SE, Ignácio ZM, Rodrigues ALS et al (2016) Glutamatergic NMDA receptor as therapeutic target for depression. In: Advances in protein chemistry and structural biology, vol 103. Elsevier, pp 169–202
Ripoll N, David DJP, Dailly E, Hascoët M, Bourin M (2003) Antidepressant-like effects in various mice strains in the tail suspension test. Behav Brain Res 143(2):193–200
Rossi S, Studer V, Motta C, Polidoro S, Perugini J, Macchiarulo G et al (2017) Neuroinflammation drives anxiety and depression in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. Neurology 89(13):1338–1347
Ruhé HG, Mason NS, Schene AH (2007) Mood is indirectly related to serotonin, norepinephrine and dopamine levels in humans: a meta-analysis of monoamine depletion studies. Mol Psychiatry 12(4):331–359
Schröter K, Brum M, Brunkhorst-Kanaan N, Tole F, Ziegler C, Domschke K et al (2020) Longitudinal multi-level biomarker analysis of BDNF in major depression and bipolar disorder. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 270(2):169–181
Sinha AK (1972) Colorimetric assay of catalase. Anal Biochem 47(2):389–394
Smolinsky AN, Bergner CL, LaPorte JL, Kalueff AV (2009) Analysis of grooming behavior and its utility in studying animal stress, anxiety, and depression. In: Mood and anxiety related phenotypes in mice. Springer, pp 21–36
Steru L, Chermat R, Thierry B, Simon P (1985) The tail suspension test: a new method for screening antidepressants in mice. Psychopharmacology 85(3):367–370
Stewart AM, Braubach O, Spitsbergen J, Gerlai R, Kalueff AV (2014) Zebrafish models for translational neuroscience research: from tank to bedside. Trends Neurosci 37(5):264–278
Stone EA, Lin Y (2011) Open-space forced swim model of depression for mice. Curr Protoc Neurosci 54(1):9.36. 31–39.36. 38
Strawn JR, Mills JA, Sauley BA, Welge JA (2018) The impact of antidepressant dose and class on treatment response in pediatric anxiety disorders: a meta-analysis. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 57(4):235–244 e232
Sulakhiya K, Keshavlal GP, Bezbaruah BB, Dwivedi S, Gurjar SS, Munde N et al (2016) Lipopolysaccharide induced anxiety-and depressive-like behaviour in mice are prevented by chronic pre-treatment of esculetin. Neurosci Lett 611:106–111
Sun Y, Oberley LW, Li Y (1988) A simple method for clinical assay of superoxide dismutase. Clin Chem 34(3):497–500
Takahashi JA, Boaventura MAD, de Carvalho BJ (1995) Frutoic acid, a dimeric kaurane diterpene from Xylopia frutescens. Phytochemistry 40(2):607–609
Tomaz V, Cordeiro R, Costa A, De Lucena D, Júnior HN, De Sousa F et al (2014) Antidepressant-like effect of nitric oxide synthase inhibitors and sildenafil against lipopolysaccharide-induced depressive-like behavior in mice. Neuroscience 268:236–246
Vane J (1959) The relative activities of some tryptamine analogues on the isolated rat stomach strip preparation. Br J Pharmacol Chemother 14(1):87–98
Vidal R, Castro E, Pilar-Cuellar F, Pascual-Brazo J, Diaz A, Luisa Rojo M et al (2014) Serotonin 5-HT4 receptors: a new strategy for developing fast acting antidepressants? Curr Pharm Des 20(23):3751–3762
Wang J, Jing L, Toledo-Salas J-C, Xu L (2015) Rapid-onset antidepressant efficacy of glutamatergic system modulators: the neural plasticity hypothesis of depression. Neurosci Bull 31(1):75–86
Wang X, Zhu L, Hu J, Guo R, Ye S, Liu F et al (2020) FGF21 attenuated LPS-induced depressive-like behavior via inhibiting the inflammatory pathway. Front Pharmacol 11:154
Whooley MA, Wong JM (2013) Depression and cardiovascular disorders. Annu Rev Clin Psychol 9:327–354
Woelfer M, Kasties V, Kahlfuss S, Walter M (2019) The role of depressive subtypes within the neuroinflammation hypothesis of major depressive disorder. Neuroscience 403:93–110
Xu J, Guo P, Liu C, Sun Z, Gui L, Guo Y et al (2011) Neuroprotective kaurane diterpenes from Fritillaria ebeiensis. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 75(7):1386–1388
Yalcin I, Aksu F, Bodard S, Chalon S, Belzung C (2007) Antidepressant-like effect of tramadol in the unpredictable chronic mild stress procedure: possible involvement of the noradrenergic system. Behav Pharmacol 18(7):623–631
Zanos P, Thompson SM, Duman RS, Zarate CA, Gould TD (2018) Convergent mechanisms underlying rapid antidepressant action. CNS Drugs 32(3):197–227
Zhang J, Yi S, Li Y, Xiao C, Liu C, Jiang W et al (2020) The antidepressant effects of asperosaponin VI are mediated by the suppression of microglial activation and reduction of TLR4/NF-κB-induced IDO expression. Psychopharmacology 237:2531–2545
Zhou Q-G, Zhu X-H, Nemes AD, Zhu D-Y (2018) Neuronal nitric oxide synthase and affective disorders. IBRO Rep 5:116–132
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to technicians of the Departments of Pharmacology in Kwame Nkrumah University of Science and Technology and in University of Cape Coast for their technical support at various stages of the project.
Funding
This work was funded using personal funds of all contributing authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RPB conducted all experiments, analysed the data and wrote the first draft of manuscript. CKB participated in the carrying experiments on mechanism of action and zebrafish assays. DWA participated in chronic depression experiments and analyses of the data. EW and EOA conceptualised the work, provided supervision of the experiments and reviewed the analyses. All authors reviewed the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Biney, R.P., Benneh, C.K., Adongo, D.W. et al. Evidence of an antidepressant-like effect of xylopic acid mediated by serotonergic mechanisms. Psychopharmacology 238, 2105–2120 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-021-05835-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-021-05835-6