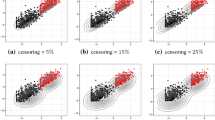
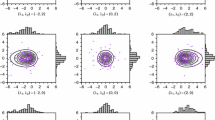
Abstract
Mixtures of t factor analyzers (MtFA) have been well recognized as a prominent tool in modeling and clustering multivariate data contaminated with heterogeneity and outliers. In certain practical situations, however, data are likely to be censored such that the standard methodology becomes computationally complicated or even infeasible. This paper presents an extended framework of MtFA that can accommodate censored data, referred to as MtFAC in short. For maximum likelihood estimation, we construct an alternating expectation conditional maximization algorithm in which the E-step relies on the first-two moments of truncated multivariate-t distributions and CM-steps offer tractable solutions of updated estimators. Asymptotic standard errors of mixing proportions and component mean vectors are derived by means of missing information principle, or the so-called Louis’ method. Several numerical experiments are conducted to examine the finite-sample properties of estimators and the ability of the proposed model to downweight the impact of censoring and outlying effects. Further, the efficacy and usefulness of the proposed method are also demonstrated by analyzing a real dataset with genuine censored observations.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aitken AC (1926) On Bernoulli’s numerical solution of algebraic equations. Proc R Soc Edinb 46:289–305
Andrews JL, McNicholas PD (2011) Extending mixtures of multivariate \(t\)-factor analyzers. Stat Comput 21:361–373
Arellano-Valle RB, Genton MG (2005) On fundamental skew distributions. J Multivar Anal 96:93–116
Arellano-Valle RB, Castro LM, Gonzalez-Farías G, Munos Gajardo K (2012) Student-\(t\) censored regression model: properties and inference. Stat Methods Appl 21:453–473
Azzalini A, Capitanio A (2003) Distributions generated by perturbation of symmetry with emphasis on a multivariate skew \(t\)-distribution. J R Stat Soc Ser B 65:367–389
Baek J, McLachlan GJ (2011) Mixtures of common \(t\)-factor analyzers for clustering high-dimensional microarray data. Bioinformatics 27:1269–1276
Banfield JD, Raftery AE (1993) Model-based Gaussian and non-Gaussian clustering. Biometrics 49:803–821
Baudry JP, Raftery AE, Celeux G, Lo K, Gottardo R (2010) Combining mixture components for clustering. J Comput Graph Stat 9:332–353
Biernacki C, Celeux G, Govaert G (2000) Assessing a mixture model for clustering with the integrated completed likelihood. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 22:719–725
Biernacki C, Celeux G, Govaert G (2003) Choosing starting values for the EM algorithm for getting the highest likelihood in multivariate Gaussian mixture models. Comput Stat Data Anal 41:561–575
Böhning D, Dietz E, Schaub R, Schlattmann P, Lindsay B (1994) The distribution of the likelihood ratio for mixtures of densities from the one-parameter exponential family. Ann Inst Stat Math 46:373–388
Branco M, Dey D (2001) A general class of multivariate skew-elliptical distribution. J Multivar Anal 79:93–113
Cabral CR, Lachos VH, Prates MO (2012) Multivariate mixture modeling using skew-normal independent distributions. Comput Stat Data Anal 56:126–142
Carin L, Baraniuk RG, Cevher V, Dunson D, Jordan MI, Sapiro G, Wakin MB (2011) Learning low-dimensional signal models. IEEE Signal Process Mag 28:381–396
Castro LM, Costa DR, Prates MO, Lachos VH (2015) Likelihood-based inference for Tobit confirmatory factor analysis using the multivariate Student-\(t\) distribution. Stat Comput 25:1163–1183
Celeux G, Govaert G (1995) Gaussian parsimonious clustering models. Pattern Recognit 28:781–793
Cohen AC (1957) On the solution of estimating equations for truncated and censored samples from normal populations. Biometrika 44:225–236
Cohen AC (1959) Simplified estimators for the normal distribution when samples are singly censored or truncated. Technometrics 1:217–237
Costa DR, Lachos VH, Bazan JL, Azevedo CLN (2014) Estimation methods for multivariate Tobit confirmatory factor analysis. Comput Stat Data Anal 79:248–260
Cramér H (1946) Mathematical methods of Statistics. Princeton University Press, Princeton
Dempster AP, Laird NM, Rubin DB (1977) Maximum likelihood from incomplete data via the EM algorithm (with discussion). J R Stat Soc Ser B 9:1–38
Fokoué E, Titterington DM (2003) Mixtures of factor analyzers. Bayesian estimation and inference by stochastic simulation. Mach Learn 50:73–94
Fraley C (1998) Algorithms for model-based Gaussian hierarchical clustering. SIAM J Sci Comput 20:270–281
Fraley C, Raftery AE (1998) How many clusters? Which clustering method? Answers via model-based cluster analysis. Comput J 41:578–588
Fraley C, Raftery AE (2002) Model-based clustering, discriminant analysis, and density estimation. J Am Stat Assoc 97:611–612
Galarza CE, Lachos VH (2019) MomTrunc: moments of folded and doubly truncated multivariate distributions. R Package Version 4.51. http://CRAN.R-project.org/package=MomTrunc. Accessed 1 Mar 2021
Galarza CE, Lin TI, Wang WL, Lachos VH (2021) On moments of folded and truncated multivariate Student-t distributions based on recurrence relations. Metrika. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00184-020-00802-1
Ghahramani Z, Hinton GE (1997) The EM algorithm for factor analyzers. Technical report no. CRG-TR-96-1. The University of Toronto, Toronto
Hartigan JA, Wong MA (1979) Algorithm AS 136: a \(K\)-means clustering algorithm. J R Stat Soc Ser C 28:100–108
He J (2013) Mixture model based multivariate statistical analysis of multiply censored environmental data. Adv Water Resour 59:15–24
Hinton GE, Dayan P, Revow M (1997) Modeling the manifolds of images of handwritten digits. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 8:65–74
Ho HJ, Lin TI, Chen HY, Wang WL (2012) Some results on the truncated multivariate \(t\) distribution. J Stat Plan Inference 142:25–40
Hubert LJ, Arabie P (1985) Comparing partitions. J Classif 2:193–218
Hughes JP (1999) Mixed-effects models with censored data with application to HIV RNA levels. Biometrics 55:625–629
Kamakura WA, Wedel M (2001) Exploratory Tobit factor analysis for multivariate censored data. Multivar Behav Res 36:53–82
Karlis D, Xekalaki E (2003) Choosing initial values for the EM algorithm for finite mixtures. Comput Stat Data Anal 41:577–590
Lachos VH, López Moreno EJ, Chen K, Cabral CRB (2017) Finite mixture modeling of censored data using the multivariate Student-\(t\) distribution. J Multivar Anal 159:151–167
Lawley DN, Maxwell AE (1971) Factor analysis as a statistical method, 2nd edn. Butterworths, London
Lee S, McLachlan GJ (2013) On mixtures of skew normal and skew \(t\)-distributions. Adv Data Anal Classif 7:241–266
Lee S, McLachlan GJ (2016) Finite mixtures of canonical fundamental skew \(t\)-distributions: the unication of the restricted and unrestricted skew \(t\)-mixture models. Stat Comput 26:573–589
Lehmann EL, Casella G (1998) Theory of point estimation, 2nd edn. Springer, New York
Lin TI, Wang WL (2020) Multivariate-\(t\) linear mixed models with censored responses, intermittent missing values and heavy tails. Stat Methods Med Res 29:1299–1304
Lin TI, Ho HJ, Lee CR (2014) Flexible mixture modelling using the multivariate skew-t-normal distribution. Stat Comput 24:531–546
Lin TI, McLachlan GJ, Lee SX (2016) Extending mixtures of factor models using the restricted multivariate skew-normal distribution. J Multivar Anal 143:398–413
Lin TI, Lachos VH, Wang WL (2018a) Multivariate longitudinal data analysis with censored and intermittent missing responses. Stat Med 37:2822–2835
Lin TI, Wang WL, McLachlan GJ, Lee SX (2018b) Robust mixtures of factor analysis models using the restricted multivariate skew-\(t\) distribution. Stat Mod 28:50–72
Liu CH, Rubin DB (1994) The ECME algorithm: a simple extension of EM and ECM with faster monotone convergence. Biometrika 81:633–648
Louis TA (1982) Finding the observed information matrix when using the EM algorithm. J R Stat Soc Ser B 44:226–233
Matos LA, Prates MO, Chen MH, Lachos VH (2013) Likelihood-based inference for mixed-effects models with censored response using the multivariate-\(t\) distribution. Stat Sin 23:1323–1345
McLachlan GJ, Krishnan T (2008) The EM algorithm and extensions, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York
McLachlan GJ, Peel D (2000) Finite mixture models. Wiley, New York
McLachlan GJ, Bean RW, Peel D (2002) A mixture model-based approach to the clustering of microarray expression data. Bioinformatics 18:413–422
McLachlan GJ, Bean RW, Jones LBT (2007) Extension of the mixture of factor analyzers model to incorporate the multivariate \(t\)-distribution. Comput Stat Data Anal 51:5327–5338
Meng XL, van Dyk D (1997) The EM algorithm-an old folk song sung to a fast new tune. J R Stat Soc Ser B 59:511–567
Meng XL, Rubin DB (1993) Maximum likelihood estimation via the ECM algorithm: a general framework. Biometrika 80:267–278
Murray PM, Browne RP, McNicholas PD (2014) Mixtures of skew-\(t\) factor analyzers. Comput Stat Data Anal 77:326–335
Murray PM, Browne RP, McNicholas PD (2017) A mixture of SDB skew-\(t\) factor analyzers. Econ Stat 3:160–168
Murray PM, Browne RP, McNicholas PD (2020) Mixtures of hidden truncation hyperbolic factor analyzers. J Classif 37:366–379
Muthén BO (1989) Tobit factor analysis. Br J Math Stat Psychol 42:241–250
Orchard T, Woodbury MA (1972) A missing information principle: theory and applications. In: Proceedings of the 6th Berkeley symposium on mathematical statistics and probability, vol 1, pp 697–715
Peel D, McLachlan GJ (2000) Robust mixture modeling using the \(t\) distribution. Stat Comput 10:339–348
Pyne S, Hu X, Wang K, Rossin E, Lin TI, Maier LM, Baecher-Allan C, McLachlan GJ, Tamayo P, Hafler DA, De Jager PL, Mesirov JP (2009) Automated high-dimensional flow cytometric data analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:8519–8524
R Core Team (2019) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria
Redner RA, Walker HF (1984) Mixture densities, maximum likelihood and the EM algorithm. SIAM Rev 26:195–239
Sahu SK, Dey DK, Branco MD (2003) A new class of multivariate skew distributions with application to Bayesian regression models. Can J Stat 31:129–150
Schwarz G (1978) Estimating the dimension of a model. Ann Stat 6:461–464
Scrucca L, Fop M, Murphy TB, Raftery AE (2016) mclust 5: clustering, classification and density estimation using Gaussian finite mixture models. R J 8:205–233
Shumway RH, Azari RS, Johnson P (1989) Estimating mean concentrations under transformation for environmental data with detection limits. Technometrics 31:347–56
Spearman C (1904) General intelligence, objectively determined and measured. Am J Psychol 15:201–293
Tobin J (1958) Estimation of relationships for limited dependent variables. Econometrica 26:24–36
Ueda N, Nakano R, Ghahramani Z, Hinton GE (2000) SMEM algorithm for mixture models. Neural Comput 12:2109–2128
VDEQ (2003) The quality of Virginia non-tidal streams: first year report. VDEQ technical bulletin WQA/2002–2001, Office of Water Quality and Assessments, Virginia Department of Environmental Quality
VDEQ (2008) Virginia Water Quality Assessment. Integrated report 305(b)/303(d), Virginia Department of Environmental Quality
VDEQ (2009) Virginia Water Quality Standards. Technical report regulation 9 VAC 25–260, State Water Control Board, Virginia Department of Environmental Quality
Wang WL, Castro LM, Lachos VH, Lin TI (2019) Model-based clustering of censored data via mixtures of factor analyzers. Comput Stat Data Anal 140:104–121
Zeller CB, Cabral CRB, Lachos VH, Benites L (2019) Finite mixture of regression models for censored data based on scale mixtures of normal distributions. Adv Data Anal Classif 13:89–116
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the editors and two anonymous referees for their insightful comments and constructive suggestions that greatly improved the quality of this paper. We are also grateful to Ms. Ting-Yu Lin for her skillful assistance in initial simulations and help sketching some graphs. This research was supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology of Taiwan under Grant Nos. 107-2628-M-035-001-MY3 and 109-2118-M-005-005-MY3.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, WL., Lin, TI. Robust clustering of multiply censored data via mixtures of t factor analyzers. TEST 31, 22–53 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11749-021-00766-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11749-021-00766-y
Keywords
- AECM algorithm
- Censored data
- Factor analysis
- Maximum likelihood estimation
- Missing information principle
- Truncated multivariate t distribution