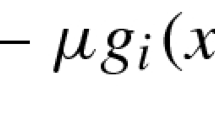Abstract
The purpose of this paper is to focus on continuous minimax problems with semi infinite constraints. We begin by proposing an algorithm for solving this kind of problems. The proposed algorithm combines the parametric approach and the Huard method of centers. That’s we extend the Method of Centers of Roubi for solving minimax fractional programs to continuous minimax problems. On the other hand, calculating the exact optimal solution of the proposed parametric problems, requires an extraordinary computational work per iteration. To overcome this problem we use an iterative entropic regularization method which allows us to solve each auxiliary problem inexactly generating an approximate sequence of optimal values and then the continuous minimax problem is reduced into a sequence of finite minimax problems. Examples for illustration are given to test our algorithm.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lin, J.Y., Sheu, R.L.: Modified Dinkelbach-type algorithm for generalized fractional programs with infinitely many ratios. J Optim Theory Appl. 126, 323–343 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10957-005-4717-z
Sheu, R.L., Lin, J.Y.: Solving continuous min-max problems by an iterative entropic regularization method. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 121, 597–612 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:JOTA.0000037605.19435.63
Roubi, A.: Global convergence and rate of convergence of a methods of centers. Comput. Optim. Appl. 3, 259–280 (1994)
Roubi, A.: Method of centers for generalized fractional programming. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 107(1), 123–143 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004660917684
Roubi, A.: Some properties of methods of centers. Comput. Optim. Appl. 19, 319–335 (2001)
Roubi, A.: Convergence of prox-regularization methods for generalized fractional programming. RAIRO Oper. Res. 36(1), 73–94 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1051/ro:2002006
Hettich, R., Kortanek, K.O.: Semi-infnite programming: theory, methods, and applications. SIAM Rev. (1993). https://doi.org/10.1137/1035089
Reemtsen, R., Görner, S.: (1998) Numerical Methods for Semi-Infinite Programming: A Survey. In: Reemtsen R., Rückmann J.J. (eds) Semi-Infinite Programming. Nonconvex Optimization and Its Applications, vol 25. Springer, pp. 380–429 (1993) https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4757-2868-2_7
Lopez, M., Still, G.: Semi-infinite programming. Eur. J. Operat. Res. 180(2), 491–518 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejor.2006.08.045
Qi, L., Ling, C., Tong, X., et al.: A smoothing projected Newton-type algorithm for semi-infinite programming. Comput Optim Appl. 42(4), 1–30 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10589-007-9117-x
Žaković, S., Rustem, B.: Semi-infinite programming and applications to minimax problems. Ann. Oper. Res. 124, 81–110 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:ANOR.0000004764.76984.30
Addoune, S., Boufi, K., Roubi, A.: Proximal bundle algorithms for nonlinearly constrained convex minimax fractional programs. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 179, 212–239 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10957-018-1342-1
Addoune, S., El Haffari, M., Roubi, A.: A proximal point algorithm for generalized fractional programs. Optimization 66(9), 1495–1517 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1080/02331934.2017.1338698
Barros, A.I.J., Frenk, B.G., Schaible, S., Zhang, S.: A new algorithm for generalized fractional programs. Math. Program. 72, 147–175 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02592087
Barros, A.I.J., Frenk, B.G., Schaible, S., Zhang, S.: Using duality to solve generalized fractional programming problems. J. Glob. Optim. 8, 139–170 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00138690
Bector, C.R., Chandra, S., Bector, M.K.: Generalized fractional programming duality: a parametric approach. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 60(2), 243–260 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00940006
Boualam, H., Roubi, A.: Dual algorithms based on the proximal bundle method for solving convex minimax fractional programs. J. Ind. Manag. Optim. 15(4), 1897–1920 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3934/jimo.2018128
Boualam, H., Roubi, A.: Proximal bundle methods based on approximate Subgradients for solving Lagrangian duals of minimax fractional programs. J. Global Optim. 74(2), 255–284 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10898-019-00757-2
Boufi, K., Roubi, A.: Dual method of centers for solving generalized fractional programs. J. Glob. Optim. 69(2), 387–426 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10898-017-0523-z
Boufi, K., Roubi, A.: Duality results and dual bundle methods based on the dual method of centers for minimax fractional programs. SIAM J. Optim. 29(2), 1578–1602 (2019)
Boufi, K., Roubi, A.: Prox-regularization of the dual method of centers for generalized fractional programs. Optim. Methods Softw. 34(3), 515–545 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1080/10556788.2017.1392520
Méthode, La., des Centres dans un Espace Topologique. : Buì-Trong-Liêũ, Huard, P. Numerische Mathematik 8, 56–67 (1966)
Crouzeix, J.P., Ferland, J.A.: Algorithms for generalized fractional programming. Math. Program. 52, 191–207 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01582887
Crouzeix, J.P., Ferland, J.A., Nguyen, H.V.: Revisiting Dinkelbach-type algorithms for generalized fractional programs. Opsearch 45, 97–110 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03398807
Crouzeix, J.P., Ferland, J.A., Schaible, S.: Duality in generalized linear fractional programming. Math. Program. 27, 342–354 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02591908
Crouzeix, J.P., Ferland, J.A., Schaible, S.: An algorithm for generalized fractional programs. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 47, 35–49 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00941314
Crouzeix, J.P., Ferland, J.A., Schaible, S.: A note on an algorithm for generalized fractional programs. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 50, 183–187 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00938484
El Haffari, M., Roubi, A.: Convergence of a proximal algorithm for solving the dual of a generalized fractional program. RAIRO-Oper. Res. 51(4), 985–1004 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1051/ro/2017004
El Haffari, M., Roubi, A.: Prox-dual regularization algorithm for generalized fractional programs. J. Ind. Manag. Optim. 13(4), 1991–2013 (2017). https://doi.org/10.3934/jimo.2017028
Huard, P.: Programmation Mathématique Convexe. R.I.R.O 7, 43–59 (1968)
Jagannathan, R., Schaible, S.: Duality in generalized fractional programming via Farkas’ Lemma. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 41(3), 417–424 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00935361
Polak, E., He, L.: Unified Steerabale Phase I-Phase II metohd of feasible directions for semi-infinite optimization. Math. Program. 59(1), 83–107 (1991)
Polak, E., Higgins, J.E., Mayne, D.Q.: A barrier function method for minimax problems. Math. Program. 54, 155–176 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01586049
Stancu-Minasian, I.M.: A ninth bibliography of fractional programming. Optimization 68(11), 2125–2169 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1080/02331934.2019.1632250
Dem’yanov, V.F., Malozemov, V.N.: Introduction to Minimax. Wiley, New York (1974)
Bertsekas, D.P.: Constrained Optimization and Lagrange Multiplier Methods. Academic Press, New York (1982)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
El Haffari, M. An entropic regularized method of centers for continuous minimax problem with semi infinite constraints. J. Appl. Math. Comput. 68, 637–653 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12190-021-01524-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12190-021-01524-x