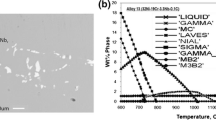
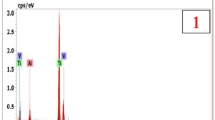
Abstract
The oxidation behavior of alumina-forming alloys was studied after oxidation treatments conducted at 900 °C for 24 h in air or in steam. Alloys with sulfur contents ranging from 1 to 82 ppm in wt% were used. The influence of trace sulfur as well as the presence of steam in the oxidizing atmosphere were investigated. Under oxidation conditions, higher sulfur contents led to higher mass gains and the trend was more pronounced in steam than in air. Oxides were identified by Raman spectroscopy: a thin and continuous α-Al2O3 layer was formed at the metal-oxide interface in all cases. The mass gain differences were caused by other oxides formed at the surface of the samples—mainly spinel and Cr2O3—and in the internal oxidation zone too— mainly α-Al2O3 and θ-Al2O3—indicating that the protectiveness of the alumina layer greatly depends on the sulfur content in the base material and the oxidizing atmosphere. In order to explain this phenomenon, oxide structures were analyzed at various scales using scanning electron microscopy, transmission electron microscopy and nanoscale secondary ion mass spectrometry. Sulfur was detected at metal-oxide interfaces and also in the alumina layer in regions enriched with chromium. In addition, we demonstrate that steam oxidation leads to finer alumina grains as compared to air oxidation. Finally, the relationship between oxidation conditions, nanoscaled structural features and oxidation kinetics is discussed.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability and Material
Data and material can be provided on request.
References
T.L. Silveira Da , I.L. May. Reformer furnaces: Materials, damage mechanisms and assessment. Arabian Journal for Science and Engineering. 2006;99–119.
F. Abe, T.U. Kern, R. Viswanathan, Creep-Resistant Steels. Elsevier; 2008.
L. H. De Almeida, A. F. Ribeiro, and I. Le May, Microstructural characterization of modified 25Cr–35Ni centrifugally cast steel furnace tubes. Mater. Charact. 49, 2002 (219–229).
L. Bonaccorsi, E. Guglielmino, R. Pino, C. Servetto, and A. Sili, Damage analysis in Fe–Cr–Ni centrifugally cast alloy tubes for reforming furnaces. Eng. Fail. Anal. 36, 2014 (65–74).
D. J. Young, High temperature oxidation and corrosion of metals, (Elsevier Corrosion Series, Cambridge, 2008).
B. Cottis, M. Graham, . Lindsay et al. SHREIR’S CORROSION Volume I : Basic Concepts, High Temperature Corrosion. The Netherlands : ELSEVIER-ACADEMIC PRESS; 1963.
W. Gao and Z. Li, Developments in high-temperature corrosion and protection of materials, (Woodhead Publishing In Materials, Cambridge, 2008).
F. Pons, J. Thuillier. Nickel- and chromium-base alloys possessing very-high resistance to carburization at very-high temperature. US4248629A. 1981.
S. H. Symoens, N. Olahova, A. Munoz Gandarilla, et al., State-of-the-art of Coke Formation during Steam Cracking: Anti-Coking Surface Technologies. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 57, 2018 (16117–16136).
A. Facco, M. Couvrat, D. Magné, M. Roussel, A. Guillet, C. Pareige. Microstructure influence on creep properties of heat-resistant austenitic alloys with high aluminum content. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 2020;139276.
M. A. Smith, W. E. Frazier, and B. A. Pregger, Effect of sulfur on the cyclic oxidation behavior of a single crystalline, nickel-base superalloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 203, 1995 (388–398).
J. Stringer, The reactive element effect in high-temperature corrosion. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 120–121, 1989 (129–137).
J. G. Smeggil, A. W. Funkenbusch, and N. S. Bornstein, A relationship between indigenous impurity elements and protective oxide scale adherence characteristics. Metall. Trans. A. 17, 1986 (923–932).
J. L. Smialek and G. N. Morscher, Delayed alumina scale spallation on Rene’N5+Y: moisture effects and acoustic emission. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 332, 2002 (11–24).
M. C. Stasik, F. S. Pettit, G. H. Meier, A. Ashary, and J. L. Smialek, Effects of reactive element additions and sulfur removal on the oxidation behavior of fecral alloys. Scr. Metall. Mater. 31, 1994 (1645–1650).
D. Delaunay, A. M. Huntz, and P. Lacombe, Impurities influence on oxidation kinetics of Fe-Ni-Cr-Al alloys. Corros. Sci. 24, 1984 (13–25).
G. B. Abderrazik, G. Moulin, A. M. Huntz, and R. Berneron, Influence of impurities, such as carbon and sulphur, on the high temperature oxidation behaviour of Fe72Cr23Al5 alloys. J. Mater. Sci. 19, 1984 (3173–3184).
D. Wiemer, H. J. Grabke, and H. Viefhaus, Investigation on the influence of sulfur segregation on the adherence of protective oxide layers on high temperature materials. Fresenius J. Anal. Chem. 341, 1991 (402–405).
D. G. Lees, On the reasons for the effects of dispersions of stable oxides and additions of reactive elements on the adhesion and growth-mechanisms of chromia and alumina scales-the “sulfur effect”’. Oxid. Met. 27, 1987 (75–81).
D. A. Bonnell and J. Kiely, Plasticity at Multiple Length Scales in Metal-Ceramic Interface Fracture. Phys. Status Solidi A. 166, 1998 (7–17).
P. Fox, D. G. Lees, and G. W. Lorimer, Sulfur segregation during the high-temperature oxidation of chromium. Oxid. Met. 36, 1991 (491–491).
G. H. Meier, F. S. Pettit, and J. L. Smialek, The effects of reactive element additions and sulfur removal on the adherence of alumina to Ni- and Fe-base alloys. Mater. Corros. 46, 1995 (232–240).
R. Prescott and M. J. Graham, The formation of aluminum oxide scales on high-temperature alloys. Oxid. Met. 38, 1992 (233–254).
D. M. Lipkin, D. R. Clarke, and A. G. Evans, Effect of interfacial carbon on adhesion and toughness of gold–sapphire interfaces. Acta Mater. 46, 1998 (4835–4850).
J. D. Kiely and D. A. Bonnell, Metal ceramic interface toughness I: Plasticity on multiple length scales. J. Mater. Res. 13, 1998 (2871–2880).
B. A. Pint, On the formation of interfacial and internal voids in α-Al2O3 scales. Oxid. Met. 48, 1997 (303–328).
Hance KO. Effects of water vapor on the oxidation behavior of alumina and chromia forming superalloys at temperatures between 700C AND 1000C. 2005. Available at: http://d-scholarship.pitt.edu/6808. Accessed February 19, 2018.
S. R. J. Saunders, M. Monteiro, and F. Rizzo, The oxidation behaviour of metals and alloys at high temperatures in atmospheres containing water vapour: A review. Prog. Mater. Sci. 53, 2008 (775–837).
R. Janakiraman, G. H. Meier, and F. S. Pettit, The effect of water vapor on the oxidation of alloys that develop alumina scales for protection. Metall. Mater. Trans. A. 30, 1999 (2905–2913).
M. C. Maris-Sida, G. H. Meier, and F. S. Pettit, Some water vapor effects during the oxidation of alloys that are α-Al2O3- formers. Metall. Mater. Trans. A. 34, 2003 (2609–2619).
Maris-Sida MC. Effects of water vapor on the high temperature oxidation of alumina-forming coatings and ni base superalloys . 2005. Available at: http://d-scholarship.pitt.edu/9454. Accessed February 19, 2018.
K. Onal, M. C. Maris-Sida, G. H. Meier, and F. S. Pettit, Water vapor effects on the cyclic oxidation resistance of alumina forming alloys. Mater. High Temp. 20, 2003 (327–337).
W. J. Quadakkers, C. Wasserfuhr, A. S. Khanna, and H. Nickel, Influence of sulphur impurity on oxidation behaviour of Ni–10Cr–9Al in air at 1000°C. Mater. Sci. Technol. 4, 1988 (1119–1125).
T. T. Huang, R. Richter, Y. L. Chang, and E. Pfender, Formation of aluminum oxide scales in sulfur-containing high temperature environments. Metall. Trans. A. 16, 1985 (2051–2059).
L. Aranda, T. Schweitzer, L. Mouton, et al., Kinetic and metallographic study of oxidation at high temperature of cast Ni 25Cr alloy in water vapour rich air. Mater. High Temp. 32, 2015 (530–538).
H. Götlind, F. Liu, J. E. Svensson, M. Halvarsson, and L. G. Johansson, The Effect of Water Vapor on the Initial Stages of Oxidation of the FeCrAl Alloy Kanthal AF at 900 °C. Oxid. Met. 67, 2007 (251–266).
H. Buscail, S. Heinze, P. Dufour, JP. Larpin. Water-vapor-effect on the oxidation of Fe-21.5 wt.%Cr-5.6 wt.%Al at 1000°C. Oxid. Met. 1997;47:445–464.
M. P. Brady, Y. Yamamoto, M. L. Santella, and L. R. Walker, Composition, Microstructure, and Water Vapor Effects on Internal/External Oxidation of Alumina-Forming Austenitic Stainless Steels. Oxid. Met. 72, 2009 (311–333).
F. Tancret, J. Laigo, F. Christien, R. L. Gall, and J. Furtado, Phase transformations in Fe–Ni–Cr heat-resistant alloys for reformer tube applications. Mater. Sci. Technol. 34, 2018 (1333–1343).
G.D. Almeida Soares De , L.H. Almeida De, T.L. Silveira Da, I. May Le. Niobium additions in HP heat-resistant cast stainless steels. Materials Characterization. 1992:387–396.
S. H. Shim, T. S. Duffy, R. Jeanloz, C. S. Yoo, and V. Iota, Raman spectroscopy and x-ray diffraction of phase transitions in Cr 2 O 3 to 61 GPa. Phys. Rev. B. 69, 2004 (144107).
B. Hosterman. Raman Spectroscopic Study of Solid Solution Spinel Oxides. UNLV Theses Diss. Prof. Pap. Capstones, 2011. Available at: https://digitalscholarship.unlv.edu/thesesdissertations/1087.
V. D’Ippolito, G.B. Andreozzi, D. Bersani, P.P. Lottici. Raman fingerprint of chromate, aluminate and ferrite spinels. Journal of Raman Spectroscopy. 2015.
D. M. Lipkin and D. R. Clarke, Measurement of the stress in oxide scales formed by oxidation of alumina-forming alloys. Oxid. Met. 45, 1996 (267–280).
S. Boullosa-Eiras, E. Vanhaecke, T. Zhao, D. Chen, and A. Holmen, Raman spectroscopy and X-ray diffraction study of the phase transformation of ZrO2–Al2O3 and CeO2–Al2O3 nanocomposites. Catal. Today. 166, 2011 (10–17).
S. Hakkar, S. Achache, F. Sanchette, Z. Mekhalif, N. Kamoun, and A. Boumaza, Characterization by Photoluminescence and Raman Spectroscopy of the Oxide Scales Grown on the PM2000 at High Temperatures. J. Mol. Eng. Mater. 7, 2019 (1950003).
L. McNeil, M. Grimsditch, and R. H. French, Vibrational Spectroscopy of Aluminum Nitride. J Am Ceram Soc. 76, 1993 (1132–1136).
F. Mercier-Bion, S. Grousset, M. Bouttemy, A. Etcheberry, P. Dillmann, D. Neff. Multi-technique investigation of sulfur phases in the corrosion product of iron corroded in long term anoxic conditions: from micrometric to nanometric scale. ECASIA 17, 2017. Available at: https://hal-cea.archives-ouvertes.fr/cea-02331824. Accessed March 24, 2020.
T. Gheno, D. Monceau, D. Oquab, Y. Cadoret. Characterization of sulfur distribution in Ni-based superalloy and thermal barrier coatings after high temperature oxidation : A SIMS analysis. Oxid. Met. 2010:95–113.
EA Gulbransen and TP Copan, Crystal Growths and the Corrosion of Iron. Nature. 186, 1960 (959–960).
S. Chevalier. Diffusion of Oxygen in Thermally Grown Oxide Scales. Defect and Diffusion Forum, 2009. Available at: https://www.scientific.net/DDF.289-292.405. Accessed Apr. 25, 2019.
D. Clemens, K. Bongartz, W.J. Quadakkers, H. Nickel, H. Holzbrecher, J.S. Becker. Determination of lattice and grain boundary diffusion coefficients in protective alumina scales on high temperature alloys using SEM, TEM and SIMS. Fresenius J. Anal. Chem. 1995;353.
J. Balmain, A. M. Huntz, and J. Philibert, Defect Diffus. Forum. 143–147, 1997 (1189).
J.L.G. Smialek. Diffusion processes in Al2O3 scales - Void growth, grain growth, and scale growth. High temperature corrosion, San Diego, 1981. Available at: https://ntrs.nasa.gov/search.jsp?R=19830061020. Accessed April 02, 2020.
S. Floreen and J. H. Westbrook, Grain boundary segregation and the grain size dependence of strength of nickel-sulfur alloys. Acta Metall. 17, 1969 (1175–1181).
G Tauber and HJ Grabke, Grain Boundary Segregation of Sulfur, Nitrogen, and Carbon in α-Iron. Berichte Bunsenges. Für Phys. Chem. 82, 1978 (298–302).
NG Ainslie, RE Hoffman, and AU Seybolt, Sulfur segregation at α-iron grain boundaries—I. Acta Metall. 8, 1960 (523–527).
PY Hou, Compositions at Al2O3/FeCrAl interfaces after high temperature oxidation. Mater. Corros. 51, 2000 (329–337).
PY Hou, Impurity Effects on Alumina Scale Growth. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 86, 2003 (660–668).
PY Hou and GD Ackerman, Chemical state of segregants at Al2O3/alloy interfaces studied using Μxps. Appl. Surf. Sci. 178, 2001 (156–164).
JW Snoeck, GF Froment, and M Fowles, Filamentous Carbon Formation and Gasification: Thermodynamics, Driving Force, Nucleation, and Steady-State Growth. J. Catal. 169, 1997 (240–249).
RTK Baker, DJC Yates, and JA Dumesic, Filamentous Carbon Formation over Iron Surfaces. Coke Formation on Metal Surfaces. 202, 1983 (1–21).
Y. Nishiyama, T. Anraku, Y. Sawaragi, K. Ogawa, H. Okada. Heat resistant nickel base alloy. US6458318B1, 2002.
G. Zimmermann, W. Zychlinski, H. M. Woerde, and P. van den Oosterkamp, Absolute Rates of Coke Formation: A Relative Measure for the Assessment of the Chemical Behavior of High-Temperature Steels of Different Sources. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 37, 1998 (4302–4305).
Funding
This work was supported by the Agence National de la Recherche (ANR), project IPERS [Grant Number LAB COM – 15 LCV4 0003].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known conflict of interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Allo, J., Jouen, S., Roussel, M. et al. Influence of Sulfur and Water Vapor on High-Temperature Oxidation Resistance of an Alumina-Forming Austenitic Alloy. Oxid Met 95, 359–376 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11085-021-10028-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11085-021-10028-9