Abstract
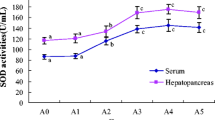
The innate immune system plays a vital role to resist the environmental stresses and infectious pathogens in marine mammal pups. To get a baseline level of innate immune capacity in spotted seals, the concentrations of several antioxidant and immune-related factors in the serum of wild and captive spotted seal (Phoca largha) pups from the Liaodong Bay colony were measured and compared. Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase and peroxidase were mainly responsible for the antioxidant system of spotted seal pups, and wild pups possessed stronger antioxidant capacity than captive ones. Against infectious pathogens, wild spotted seal pups also had an advantage over the captive counterparts. Specifically, the activities of acid phosphatase, phenoloxidase, and lysozyme in the serum of wild spotted seal pups were significantly higher than those in captive animals. The present study provides the normal activities of several serum immune enzymes for wild and captive spotted seal pups from the Liaodong Bay colony, which is benefit to the conservation of this species.

Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Comparative Immunology of Marine Mammals, Di Guardo, G., Criscitiello, M.F., Sierra, E., and Mazzariol, S., Eds., Lausanne: Frontiers Media, 2019.
Mancia, A., Chapter 21 – Marine mammal immunity toward environmental challenges, in Lessons in Immunity: From Single-Cell Organisms to Mammals, New York: Academic, 2016, pp. 287–294.
Sharma, V., Hecker, N., Walther, F., et al., Convergent losses of TLR5 suggest altered extracellular flagellin detection in four mammalian lineages, Mol. Biol. Evol., 2020, vol. 37, no. 7, pp. 1847–1854. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msaa058
Meyer, W., Seegers, U., Herrmann, J., and Schnapper, A., Further aspects of the general antimicrobial properties of pinniped skin secretions, Dis. Aquat. Org., 2003, vol. 53, pp. 177–179.
Kim, B.-M., Ahn, D.-H., Kang, S., et al., De novo assembly and annotation of the blood transcriptome of the southern elephant seal Mirounga leonina from the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica, Ocean Sci. J., 2019, vol. 54, pp. 307–315.
Rugh, D.J., Shelden, K.E., and Withrow, D.E., Spotted seals, Phoca largha, in Alaska, Mar. Fish. Rev., 1997, vol. 59, pp. 1–18.
Dong, J., Estimates of historical population size of harbor seal (Phoca largha) in Liaodong Bay, Mar. Sci., 1991, vol. 3, pp. 26–31.
Han, J.-B., Sun, F.-Y., Gao, X.-G., et al., Low microsatellite variation in spotted seal (Phoca largha) shows a decrease in population size in the Liaodong Gulf colony, Ann. Zool. Fenn., 2010, vol. 47, pp. 15–27.
Wang, P.L., Han, J.B., and Ma, Z.Q., Status survey of spotted seal (Phoca largha) in Bohai and Yellow Sea, Chin. J. Wildl., 2008, vol. 29, pp. 29–31.
Han, J.B., Lu, Z.C., Tian, J.S., et al., Release studies on spotted seals (Phoca largha) using satellite telemetry tracking technique, Acta Theriol. Sin., 2013, vol. 33, pp. 300–307.
Gao, X.G., Han, J.B., Lu, Z.C., et al., De novo assembly and characterization of spotted seal Phoca largha transcriptome using Illumina paired-end sequencing, Comp. Biochem. Physiol., Part D: Genomics Proteomics, 2013, vol. 8, pp. 103–110.
Gao, X.G., Han, J.B., Lu, Z.C., et al., Sequence variation and gene duplication at the MHC DRB loci of the spotted seal Phoca largha, GMR, Genet. Mol. Res., 2015, vol. 14, pp. 2055–2062.
Zhang, P., Yang, Y., Han, J., et al., Serum testosterone, progesterone, and estradiol concentrations and sexual maturation in spotted seals (Phoca largha), Theriogenology, 2014, vol. 82, pp. 475–480.
Zhang, P.J., Lu, J.J., Li, S.H., et al., In-air vocal repertoires of spotted seals, Phoca largha, J. Acoust. Soc. Am., 2016, vol. 140, art. ID 1101. https://doi.org/10.1121/1.4961048
Choi, C.Y., Shin, H.S., Choi, Y.J., et al., Effect of LED light spectra on starvation-induced oxidative stress in the cinnamon clownfish Amphiprion melanopus, Comp. Biochem. Physiol., Part A: Mol. Integr. Physiol., 2012, vol. 163, pp. 357–363.
Homayouni-Tabrizi, M., Asoodeh, A., and Soltani, M., Cytotoxic and antioxidant capacity of camel milk peptides: Effects of isolated peptide on superoxide dismutase and catalase gene expression, J. Food Drug Anal., 2017, vol. 25, pp. 567–575.
Michiels, C., Raes, M., Toussaint, O., and Remacle, J., Importance of SE-glutathione peroxidase, catalase, and CU/ZN-SOD for cell survival against oxidative stress, Free Radicals Biol. Med., 1994, vol. 17, pp. 235–248.
Van Bressem, M.-F., Raga, J.A., Di Guardo, G., et al., Emerging infectious diseases in cetaceans worldwide and the possible role of environmental stressors, Dis. Aquat. Org., 2009, vol. 86, pp. 143–157.
Duignan, P.J., Van Bressem, M.-F., Baker, J.D., et al., Phocine distemper virus: current knowledge and future directions, Viruses, 2014, vol. 6, pp. 5093–5134.
Van Bressem, M.-F., Duignan, P.J., Banyard, A., et al., Cetacean morbillivirus: current knowledge and future directions, Viruses, 2014, vol. 6, pp. 5145–5181.
Jiang, J., Zhou, Z., Dong, Y., et al., Comparative analysis of immunocompetence between females and males in the sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus, Fish Shellfish Immunol., 2017, vol. 63, pp. 438–443.
Dell’Angelica, E.C., Mullins, C., Caplan, S., and Bonifacino, J.S., Lysosome-related organelles, FASEB J., 2000, vol. 14, pp. 1265–1278.
Pillay, C.S., Elliott, E., and Dennison, C., Endolysosomal proteolysis and its regulation, Biochem. J., 2002, vol. 363, pp. 417–429.
Wu, C., Charoensapsri, W., Nakamura, S., et al., An BBL-like protein may interfere with the activation of the proPO-system, an important innate immune reaction in invertebrates, Immunobiology, 2013, vol. 218, pp. 159–168.
Cerenius, L., Babu, R., Söderhäll, K., and Jiravanichpaisal, P., In vitro effects on bacterial growth of phenoloxidase reaction products, J. Invertebr. Pathol., 2010, vol. 103, pp. 21–23.
Amparyup, P., Charoensapsri, W., and Tassanakajon, A., Prophenoloxidase system and its role in shrimp immune responses against major pathogens, Fish Shellfish Immunol., 2013, vol. 34, pp. 990–1001.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work was supported by the Foundation of Liaoning Province Department of Ocean and Fisheries (201812/201822) and the China Environment and Zoology Protection for Offshore Oil and Ocean Foundation (CF-MEEC/ER/2019-10). We also thank the staff of the Dalian Sun Asia Aquarium for their assistance in collecting the blood samples of spotted seals.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests. The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Statement on the welfare of animals. All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed.
Samples of spotted seals collected in Liaodong Bay, China, were authorized under the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of the People’s Republic of China, permit no. 1376.
Additional information
The text was submitted by the authors in English.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiashen Tian, Du, J., Han, J. et al. Differences in the Activities of Serum Antioxidant and Immune Factors between Wild and Captive Spotted Seal (Phoca largha) Pups from the Liaodong Bay Colony. Russ J Mar Biol 47, 68–71 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063074021010107
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063074021010107