Abstract
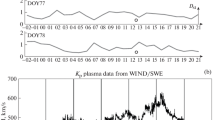
The results of are presented of determining the height profiles of electron concentration \(N(h)\) during the daytime solstice of June 19–30, 2015. Dependences of \(N(h)\) recorded in a calm state and the presence of sporadic structures of varying intensity are given. The histograms of the distribution of the variable plasma concentration for four values of the height of the lower ionosphere were determined. It is shown that, at an altitude of 100 km, an increase in the electron concentration by a factor of 4–5 occurs under the action of an X-ray flare from the Sun. Manifestations of different types of sporadic formations in changes in the amplitude of radio signals are considered and three types of amplitude variations characteristic of sporadic structures are identified.





Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Hajj, G.A. and Romans, L.I., Ionospheric electron density profiles obtained with the GPS: Results from the GPS/MET experiment, Radio Sci., 1998, vol. 33, no. 1, pp. 175–190.
Kucheryavenkov, A.I., Yakovlev, O.I., Kucheryavenkova, I.L., and Samoznaev, L.N., Regularities of ionospheric variations of the frequency and amplitude of radio waves in radio-shadow experiments on the satellite-to-satellite path, J. Commun. Technol. Electron., 1998, vol. 43, no. 8, pp. 880–885.
Schreiner, W., Sokolovsky, S., Rocken, C., and Hunt, D., Analysis and validation of GPS/MET radio occultation data in the ionosphere, Radio Sci., 1999, vol. 34, no. 4, pp. 949–966.
Hajj, G.A., Lee, L.C., Pi, X., et al., Cosmic GPS ionospheric sensing and space weather, Terr. Atmos. Oceanic Sci., 2000, vol. 11, no. 1, pp. 235–272.
Hocke, K., Igarashi, K., Nakamura, M., et al., Global sounding of sporadic E layers by the GPS–MET radio occultation experiment, J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys., 2001, vol. 63, no. 18, pp. 1973– 1980.
Yakovlev, O.I., Matyugov, S.S., and Anufriev, V.A., Scintillations centimeter waves and atmospheric irregularities from radio occultation data, Radio Sci., 2003, vol. 38, no. 2, pp. 2-1–2-11. https://doi.org/10.1029/2000RS002546
Yakowski, N., Leitinger, R., and Angling, M., Radio occultation techniques for probing the ionosphere, Ann. Geophys., 2004, vol. 47, nos. 2–3, pp. 1049–1066.
Pavelyev, A.G., Matyugov, S.S., and Yakovlev, O.I., Global satellite monitoring of the atmosphere and ionosphere, J. Commun. Technol. Electron., 2008, vol. 53, no. 9, pp. 1021–1033.
Yakovlev, O.I., Anufriev, V.A., Wickert, J., and Matyugov, S.S., Potentialities of radio-occultation monitoring of the lower ionosphere on satellite-to-satellite paths, J. Commun. Technol. Electron., 2008, vol. 53, no. 2, pp. 155–162.
Yakovlev, O.I., Wickert, J., Pavelyev, A.G., et al., Sporadic structures in equatorial ionosphere as revealed from GPS occultation data, Acta Astronaut., 2008, vol. 63, nos. 11–12, pp. 1350–1359.
Matyugov, S.S., Yakovlev, O.I., and Anufriev, V.A., Sporadic structures in the equatorial ionosphere inferred from radio occultation data on satellite-to-satellite paths, Radiophys. Quantum Electron., 2008, vol. 51, no. 3, pp. 161–169.
Matyugov, S.S., Yakovlev, O.I., Pavel’ev, A.G., et al., Sporadic structures in the equatorial ionosphere from the GPS–Formosat-3 radio-occultation experiments, Radiophys. Quantum Electron., 2015, vol. 58, no. 4, pp. 233–244.
Polar Upper Atmosphere, Deer, C.S. and Holtet, J.A., Eds., Dordrecht: Reidel, 1981.
Pavelyev, A., Igarashi, K., Reigber, C., et al., First application of the radioholographic method to wave observations in the upper atmosphere, Radio Sci., 2002, vol. 37, no. 3, pp. 15-1–15-11. https://doi.org/10.1029/2000RS002501
Wickert, J., Yakovlev O.I., Pavel’ev A.G., et al., Ionospheric fluctuations of decimeter radio waves along satellite-to-satellite paths, J. Commun. Technol. Electron., 2004, vol. 49, no. 10, pp. 1109–1116.
Yakovlev, O.I., Wickert, J., Matyugov S.S., and Anufriev, V.A., Radiowave fluctuations in the polar ionosphere on the satellite-to-satellite paths under high solar activity, Radiophys. Quantum Electron., 2006, vol. 49, no. 3, pp. 167–173.
Yakovlev, O.I., Matyugov, S.S., and Anufriev, V.A., Lower polar ionosphere during a solar flare as revealed from radiooccultation data in satellite-to-satellite links, Radiophys. Quantum Electron., 2009, vol. 52, no. 3, pp. 165–174.
Yakovlev, O.I., Matyugov, S.S., and Anufriev V.A., Sporadic structures and small-scale irregularity in the nighttime polar ionosphere in the period of high solar activity according to the data of radio occultation measurements on satellite-to-satellite paths, Cosmic Res., 2009, vol. 47, no. 4, pp. 259–267.
Yakovlev, O.I., Wickert, J., Pavelyev, A.G., et al., Results of radio occultation measurement of polar ionosphere at satellite paths during strong flare solar activity, Acta Astronaut., 2010, vol. 67, nos. 3–4, pp. 315–323.
Atmosphere and Climate Studies by Occultation Methods, Foelsche, U., Kirchengast, G., and Steiner, A., Eds., Berlin: Springer, 2006.
New Horizons in Occultation Research, Steiner, A., Pirscher, B., Foelsche, U., and Kirchengast, G., Eds., Berlin: Springer, 2009.
Liou, Y.A., Pavelyev, A.G., Matyugov, S.S., et al., Radio Occultation Method for Remote Sensing of the Atmosphere and Ionosphere, IntechOpen, 2010. https://doi.org/10.5772/46148
Yakovlev, O.I., Pavel’ev, A.G., and Matyugov, S.S., Sputnikovyi monitoring Zemli. Radiozatmennyi monitoring atmosfery i ionosfery (Satellite Monitoring of the Earth. Radio Occultation Monitoring of the Atmosphere and Ionosphere), Moscow: Librokom, 2010.
Whitehead, J.D., The formation of the sporadic E layer in the temperature zones, J. Atmos. Terr. Phys., 1961, vol. 20, pp. 49–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/0021-9169(61)90097-6
Carrasco, A.J., Batista, I.S., and Abdu, M.A., Simulation of the sporadic E layer response to prereversal associated evening vertical electric field, J. Geophys. Res., 2007, vol. 112, id. A06324. https://doi.org/10.1029/2006JA012143
Zeng, Z. and Sokolovskiy, S., Effect of sporadic E cloud on GPS radio occultation signal, Geophys. Rev. Lett., 2010, vol. 37, id. L18817. https://doi.org/10.1029/2010GL044561
Arras, C. and Wickert, J., Estimation of ionospheric sporadic E intensities from GPS radio occultation measurements, J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys., 2018, vol. 171, pp. 60–63.
Wen-Hao Yeh, Cheng-Yung Huang, Tung-Yuan Hsiao, et al., Amplitude morphology of GPS radio occultation data for sporadic E layers, J. Geophys. Res., 2012, vol. 117, id. A11304. https://doi.org/10.1029/2012JA017875
Kolosov, M.A., Yakovlev, O.I., Efimov, A.I., et al., Radio occultation of the Venusian atmosphere and bistatic radiolocation of the surface of Venus using the Venera-9 and Venera-10 satellites, Radio Sci., 1979, vol. 14, no. 1, pp. 163–173.
Kolosov, M.A., Yakovlev, O.I., Trusov, B.P., et al., On radio sounding of the atmosphere of Venus using Venera-9 and Venera-10 satellites, Radiotekh. Elektron., 1976, vol. 21, no. 8, pp. 1585.
Yakovlev, O.I., Grishmanovskii, V.A., Eliseev, S.D., et al., Two-satellite radio probing of the Earth’s atmosphere, Dokl. Akad. Nauk SSSR, 1990, vol. 315, no. 1, pp. 101–103.
Eliseev, S.D. and Yakovlev, O.I., Using millimeter radio waves to probe the earth’s atmosphere, Radiophys. Quantum Electron., 1989, vol. 32, no. 1, pp. 1–7.
Funding
This study was performed in the framework of state assignment no. 0030-2019-0008.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Matyugov, S.S., Yakovlev, O.I. & Pavel’ev, A.A. Lower Ionosphere of the Arctic in June 2015 during a Strong Magnetic Storm and Solar X-Ray Flares According to Eclipsing Radiosonde Data on GPS–Formosat Intersatellite Paths. Cosmic Res 59, 96–103 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0010952521020052
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0010952521020052