Abstract
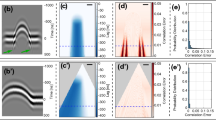
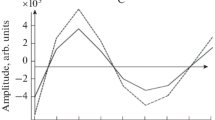
The diagnosis of cyst structures that can be seen in almost every part of the body can be made using various medical imaging methods recently. Although the used methods and devices provide convenience in diagnosis and treatment, sometimes they can not detect early-stage cyst structures without showing any symptoms. In this study, the cystic structures with different size and formation in phantoms which are soft tissue-mimicking structures created without the need for any living tissue obtained with biopsy process are visualized by the proposed Phase Shifted-Lateral Shearing Digital Holographic Microscopy in three dimensional. The proposed method is verified with experimental results obtained by using various phantom models created at different times and structures. Experimental results illustrate the applicability of the proposed method for imaging of the cyst structures in the created soft tissue-mimicking phantoms even if they are in different structures, formations and stages (especially in early stage). In other respects, it enables to image the biological specimens in small size using simple and low-cost setup.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Kasban, M.A.M. El-Bendary, D.H. Salama, A comparative study of medical imaging techniques. Int. J. Inf. Sci. Intell. Syst. (IJSR) 4(2), 37–58 (2015)
J.Z. Cheng et al., Computer-aided diagnosis with deep learning architecture: applications to breast lesions in US images and pulmonary nodules in CT scans. Sci. Rep. 6(1), 1–13 (2016)
Y. Lee, Improved total-variation noise-reduction technique with gradient method using iteration counter and its application in medical diagnostic chest and abdominal X-ray imaging. Optik 170(1), 475–483 (2018)
E.K. Wang et al., A deep learning based medical image segmentation technique in Internet-of-Medical-Things domain. Futur. Gener. Comp. Syst. 108, 135–144 (2020)
J.P. Angelo et al., Review of structured light in diffuse optical imaging. J. Biomed. Opt. 24(7), 071602 (2019)
X. Dang et al., Deep-tissue optical imaging of near cellular-sized features. Sci. Rep. 9(1), 1–12 (2019)
P. Farzam et al., Shedding light on the neonatal brain: probing cerebral hemodynamics by diffuse optical spectroscopic methods. Sci. Rep. 7(1), 1–10 (2017)
N. Honda et al., Determination of optical properties of human brain tumor tissues from 350 to 1000 nm to investigate the cause of false negatives in fluorescence-guided resection with 5-aminolevulinic acid. J. Biomed. Opt. 23(7), 075006 (2018)
F. Vasefi, N. MacKinnon, D.L. Farkas, B. Kateb, Review of the potential of optical technologies for cancer diagnosis in neurosurgery: a step toward intraoperative neurophotonics. Neurophotonics 4(1), 011010 (2017)
B.M. Haas et al., Comparison of tomosynthesis plus digital mammography and digital mammography alone for breast cancer screening. Radiology 269(3), 694–700 (2013)
I.M. Berke et al., Seeing through musculoskeletal tissues: improving in situ imaging of bone and the lacunar canalicular system through optical clearing. PLoS One 11(3), 1–29 (2016)
J. Garrett, E. Fear, A new breast phantom with a durable skin layer for microwave breast imaging. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 63(4), 1693–1700 (2015)
T.D. Vreugdenburg, C.D. Willis, L. Mundy, J.E. Hiller, A systematic review of elastography, electrical impedance scanning, and digital infrared thermography for breast cancer screening and diagnosis. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 137(3), 665–676 (2013)
Y. Xiao, Q. Zhou, Z. Chen, Automated breast volume scanning versus conventional ultrasound in breast cancer screening. Acad. Radiol. 22(3), 387–399 (2015)
A. Anand, I. Moon, B. Javidi, Automated disease identification with 3-D optical imaging: a medical diagnostic tool. Proc. IEEE 105(5), 924–946 (2017)
A. Anand et al., Compact, common path quantitative phase microscopic techniques for imaging cell dynamics. Pramana 82(1), 71–78 (2014)
Y. Park, C. Depeursinge, G. Popescu, Quantitative phase imaging in biomedicine. Nat. Photon. 12(10), 578–589 (2018)
V. Kumar, G.S. Khan., C. Shakher, Phase contrast imaging of red blood cells using digital holographic interferometric microscope, Proc. SPIE 10453 Third International Conference on Applications of Optics and Photonics, (2017) pp. 104532T
V. Rastogi et al., Design and development of volume phase holographic grating based digital holographic interferometer for label free quantitative cell imaging. Appl. Opt. 59(12), 3773–3783 (2020)
V.K. Lam et al., Quantitative assessment of cancer cell morphology and motility using telecentric digital holographic microscopy and machine learning. Cytom. Part A 93(3), 334–345 (2018)
Z. El-Schich, A.L. Mölder, A.G. Wingren, Quantitative phase imaging for label-free analysis of cancer cells-focus on digital holographic microscopy. Appl. Sci. 8(7), 1027 (2018)
P. Vora et al., Wide field of view common-path lateral-shearing digital holographic interference microscope. J. Biomed. Opt. 22(12), 126001(1–11) (2017)
A.S. Singh, A. Anand, R.A. Leitgeb, B. Javidi, Lateral shearing digital holographic imaging of small biological specimens. Opt. Express 20(21), 23617–23622 (2012)
S. Devinder, A. Lal, T.R. Dastidar, S.K. Dubey, Quantitative analysis of numerically focused red blood cells using subdivided two-beam interference (STBI) based lateral-shearing digital holographic microscope, [Online]. Available: arXiv preprint arXiv:1909.03454, (2019)
J. Di et al., Dual-wavelength common-path digital holographic microscopy for quantitative phase imaging based on lateral shearing interferometry. Appl. Opt. 55(26), 7287–7293 (2016)
P. Marquet, C. Depeursinge, P.J. Magistretti, Review of quantitative phase-digital holographic microscopy: promising novel imaging technique to resolve neuronal network activity and identify cellular biomarkers of psychiatric disorders. Neurophotonics 1(2), 020901 (2014)
Y. Cao, G.Y. Li, X. Zhang, Y.L. Liu, Tissue-mimicking materials for elastography phantoms: a review. Extreme Mech. Lett. 17(1), 62–70 (2017)
V. Kumari, G. Sheoran, T. Kanumuri, SAR analysis of directive antenna on anatomically real breast phantoms for microwave holography. Microw. Opt. Techn. Lett. 62(1), 466–473 (2020)
B. Karaböce, E. Çetin, M. Özdingiş, H.O. Durmuş, Image measurement verification studies of different objects in tissue-mimicking fantom, in Proc. TIPTEKNO, (2017) pp. 1-4
M. Ziemczonok, A. Kuś, P. Wasylczyk, M. Kujawińska, 3D-printed biological cell phantom for testing 3D quantitative phase imaging systems. Sci. Rep. 9(1), 1–9 (2019)
W.K. Lee et al., Biosynthesis of agar in red seaweeds: a review. Carbohydr. Polym. 164 (2017)
M. Earle, G. De Portu, E. DeVos, Agar ultrasound phantoms for low-cost training without refrigeration. Afr. J. Emerg. Med. 6(1), 18–23 (2016)
T. Tahara et al., High-speed three-dimensional microscope for based dynamically moving biological objects based on parallel phase-shift digital holographic microscopy. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 18(4), 1387–1393 (2012)
T. Kreis, Handbook of Holographic Interferometry: Optical and Digital Methods, 2nd edn. (Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2005).
T. Fukuda et al., Three-dimensional motion-picture imaging of dynamic object by parallel-phase-shifting digital holographic microscopy using an inverted magnification optical system. Opt. Rev. 24(2), 206–211 (2017)
T. Fukuda et al., Three-dimensional imaging of distribution of refractive index by parallel phase-shifting digital holography using Abel inversion. Opt. Express 25(15), 18066–18071 (2017)
K. Ishikawa et al., High-speed imaging of sound using parallel phase-shifting interferometry. Opt. Express 24(12), 12922–12932 (2016)
CR600x2 Product information, http://optronis.com/en/products/cr600x2-mc/
CR600x2 Camera Users’ Manual, http://optronis.com/nwp-content/uploads/2017/02/Camera-manual-english-1830-SU-02-N.pdf
E. Sánchez-Ortiga et al., Off-axis digital holographic microscopy: practical design parameters for operating at diffraction limit. Appl. Opt. 53(10), 2058–2066 (2014)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Onur, T.O., Ustabas Kaya, G. & Kaya, C. Phase shifted-lateral shearing digital holographic microscopy imaging for early diagnosis of cysts in soft tissue-mimicking phantom. Appl. Phys. B 127, 61 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00340-021-07607-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00340-021-07607-8