Abstract
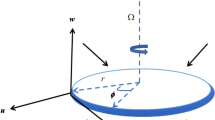
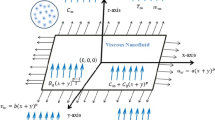
The existing study observed 3-D Darcy-Forchheimer MHD Casson fluid, steady flow between the gap of a disk and a cone in a spinning scheme. Energy ascription is considered in the existence of thermophoresis effect and Brownian motion. Mass transfer and gyrotactic microorganism are also considered, and the impact of the various embedded constraints has been observed on these profiles. The similarity alterations are used to transform the partial differential equations into the set of ordinary differential equations (ODEs). To solve the ODEs, we have chosen the homotopy analysis method of BVPh 2.0 package. The important physical parameters of interest like, heat transfer rate, mass transfer, and motile have been calculated numerically and discussed. The obtained results show that the velocity profiles decreased for inertial parameter \(F_{1}\), magnetic field \(M\), and permeability constraint \(Kr\). The effects of other constraints such as Brownian motion constraint \(N_{b}\), Schmidt number \(Sc\), Prandtl number \(\Pr\), and thermo physical constraint on the concentration and temperature fields have been analyzed and debated. The accumulative standards of the Casson constraint are declining the fluid motion. But the temperature field is rising with growing Casson parameter. It is detected that the motile density of microorganisms displays a falling behavior for rising values of Lewis and Peclet numbers.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. Himasekhar, P.K. Sarma, K. Janardhan, Laminar mixed convection from a vertical rotating cone. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Trans. 16, 99–106 (1989)
C.Y. Wang, Boundary layers on rotating cones, discs and axisymmetric surfaces with a concentrated heat source. Acta Mech. 81, 245–251 (1990)
S. Roy, D. Anilkumar, Unsteady mixed convection from a rotating cone in a rotating fluid due to the combined effects of thermal and mass diffusion. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 47, 1673–1684 (2004)
N. Gregory, J.T. Stuart, W.S. Walker, On the stability of three-dimensional boundary layers with application to the flow due to a rotating disk. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. A. 248, 155–199 (1955)
M. Turkyilmazoglu, N. Uygun, Basic compressible flow over a rotating disk. Hace. J. Math. Stat. 33, 1–10 (2004)
M. Turkyilmazoglu, Lower branch modes of the compressible boundary layer flow due to a rotating disk. Stud. Appl. Math. 114, 17–43 (2005)
M. Turkyilmazoglu, Influence of finite amplitude disturbances on the non-stationary modes of a compressible boundary layer flow. Stud. Appl. Math. 118, 199–220 (2007)
H.S. Takhar, A.J. Chamkha, G. Nath, Effect of thermophysical quantities on the natural convection flow of gases over a vertical cone. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 42, 243–256 (2004)
T. Hayat, A. Sohail Khan, M. Ijaz Khan, A. Alsaedi, Irreversibility characterization and investigation of mixed convective reactive flow over a rotating cone. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmpb.2019.105168
T. Hayat, T. Muhammad, S.A. Shehzad, A. Alsaedi, On magnetohydrodynamic flow of nanofluid due to a rotating 12 Mathematical Problems in Engineering disk with slip effect: a numerical study. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 315, 467–477 (2017)
M. Imtiaz, T. Hayat, A. Alsaedi, B. Ahmad, Convective flow of carbon nanotubes between rotating stretchable disks with thermal radiation effects. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 101, 948–957 (2016)
B. Mahanthesh, B. J. Gireesha, I. L. Animasaun, T. Muhammad and N. S. Shashikumar, MHD flow of SWCNTand MWCNT nanofluids past a rotating stretchable disk with thermal and exponential space dependent heat source. Physica. Scripta. 94(8), Article ID 085214 (2019)
K. U. Rehman, M. Y. Malik, W. A. Khan, I. Khan and S. O. Alharbi, Numerical solution of non-Newtonian fluid flow due to rotatory rigid disk. Symmetry 11, 699 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3390/sym11050699
M. Asma, W. A. M. Othman, T. Muhammad, F. Mallawi, B. R. Wong, Numerical study for magnetohydrodynamic flow of nanofluid due to a rotating disk with binary chemical reaction and Arrhenius activation energy. Symmetry 11, 1282 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3390/sym11101282
A.V. Kuznetsov, Nanofluid bioconvection in water-based suspensions containing nanoparticles and oxytactic microorganisms: oscillatory instability. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 6, 100 (2011)
M. F. M. Basir, M. J. Uddin, O. A. Bég, Influence of Stefan blowing on nanofluid flow submerged in microorganisms with leading edge accretion or ablation. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 39, 4519 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-017-0877-7
N.S. Khan, Bioconvection in second grade nanofluid flow containing nanoparticles and gyrotactic microorganisms. Braz. J. Phys. 43, 227–241 (2018)
S. Zuhra, N.S. Khan, S. Islam, Magnetohydrodynamic second grade nanofluid flow containing nanoparticles and gyrotactic microorganisms. Comput. Appl. Math. 37, 6332–6358 (2018)
K. Bhattacharyya, T. Hayat, A. Alsaedi, Analytic solution for magnetohydrodynamic boundary layer flow of Casson fluid over a stretching/shrinking sheet with wall mass transfer. Chin. Phys. B 22, 024702 (2013)
S. Nadeem, R. Ul Haq and C. Lee, MHD flow of a Casson fluid over an exponentially shrinking sheet. Sci. Iran. 19, 1550–1553 (2012)
N. In. Casson and C.C. Mill, Rheology of dispersed system. Oxford: Pergamon Press. vol. 84 (1959)
W.P. Walwander, T.Y. Chen, D.F. Cala, Biorheology 12, 111 (1975)
M.E. Fewell, J.D. Hellums, The secondary flow of Newtonian fluids in cone and plate viscometers with small gap angles. Trans. Soc. Rheol. 21, 535–5654 (1977)
M. Mooney, R.H. Ewart, The conicylindrical viscometer. Physics 5, 350–354 (1934)
H.P. Sdougos, S.R. Bussolari, C.F. Dewey, Secondary flow and turbulence in acone-and-plate device. J. Fluid. Mech. 138, 379–404 (1984)
M.H. Buschmann, A solution for the flow between a cone and a plate at low Reynolds number. J. Thermal. Sci. 11, 289–295 (2002)
M.H. Buschmann, P. Dieterich, N.A. Adams, H.J. Schnittler, Analysis of flow in acone-and-plate apparatus with respect to spatial and temporal effects on endothelial cells. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 89, 493–502 (2005)
P. Sucosky, M. Padala, A. Elhammali, K. Balachandran, H. Jo and A. P. Yoganathan, Design of an ex vivo culture system to investigate the effects of shear stress on cardiovascular tissue. Trans. ASME J. Biomech. Eng. 130, Paper 035001 (2008)
I.V. Shevchuk, A.A. Khalatov, H. Karabay, J.M. Owen, Heat transfer in turbulent centrifugal flow between rotating discs with flow swirling at the inlet. Heat Transfer Res. 29, 383–390 (1998)
C. Spruell, A.B. Baker, Analysis of a high-through put cone-and-plate apparatus for the application of defined spatiotemporal flow to cultured cells. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 110, 1782–1793 (2013)
N. Phan-Thien, Cone-and-plate flow of the Oldroyd-B fluid is unstable. J. Non-Newton. Fluid Mech. 17, 37–44 (1985)
M. Turkyilmazoglu, On the fluid flow and heat transfer between a cone and a disk both stationary or rotating. Math Comput. Simul. 177, 329–340 (2020)
T. Gul, R.S. Gul, W. Noman, A. Saeed, S. Mukhtar, W. Alghamdi and H. Alrabaiah, CNTs-Nanofluid flow in a rotating system between the gap of a disk and cone. Physica. Scripta. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1088/1402-4896/abbf1e
S.J. Liao, The proposed homotopy analysis technique for the solution of nonlinear problems. (Doctoral dissertation, Ph. D. Thesis, Shanghai Jiao Tong University)
S. Liao, Y. Tan, A general approach to obtain series solutions of nonlinear differential equations. Stud. Appl. Math. 119, 297–354 (2007)
S. Liao, Beyond perturbation: introduction to the homotopy analysis method. CRC press. (2003)
M. Turkyilmazoglu, Convergence accelerating in the homotopy analysis method: a new approach. Adv. Appl. Math. Mech. 10, 925–947 (2018)
T. Gul, W. Noman, M. Sohail, M.A. Khan, Impact of the Marangoni and thermal radiation convection on the graphene-oxide-water-based and ethylene-glycol-based nanofluids. Adv. Mech. Eng. 116, 567–573 (2019)
R. Ellahi, A. Riaz, Analytical solutions for MHD flow in a third-grade fluid with variable viscosity. Math. Comput. Model. 52, 1783–1793 (2010)
N. Shehzad, A. Zeeshan, R. Ellahi, K. Vafai, Convective heat transfer of nanofluid in a wavy channel: Buongiorno’s mathematical model. J. Mol. Liq. 222, 446–455 (2016)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gul, T., Ahmed, Z., Jawad, M. et al. Bio-convectional Nanofluid Flow Due to the Thermophoresis and Gyrotactic Microorganism Between the Gap of a Disk and Cone. Braz J Phys 51, 687–697 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13538-021-00888-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13538-021-00888-6