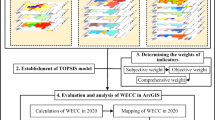
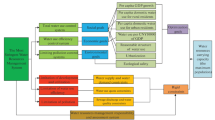
Abstract
Factors like intensive industrial and socio-economic development can lead to the deterioration of the water environment. At the same time, economic, social, and population sustainability rely on good water conditions in the river. Therefore, it is important to calculate the water environment capacity and allocate it accordingly. Our research selects the economic, social, and environmental factors to construct a water environment capacity allocation model using the analytic network process. Allocation results are as follows: there are Liaozhong County, Tiexi District, and Liaoyang County, where the water environment capacity allocation value exceeds 10 000 t/a at 18 336.25, 12 743.19, and 10 585.53 t/a, respectively. Dashiqiao City’s water environmental capacity allocation is the least, at only 78.30 t/a. In the paper, the goal to allocate water environment capacity from the three major rivers to the administrative area is achieved in Liaoning Province, thus making the allocation result more comprehensive and fairer. It provides a scientific basis for controlling the water environment in Liaoning Province.






Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Burn, D.H. and Lence, B.J., Comparison of optimization formulations for waste-load allocations, J. Environ. Eng., 1992, vol. 118, no. 4, pp. 597–612.
Cao, X.H., The Dynamic Water Environment Capacity and Total Pollution Control Strategy in Mudanjiang section, Harbin Institute of Technology, 2015.
Chadderton, R.A. and Kropp, I.S., An evaluation of eight wasteload allocation methods, JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc., 1985, vol. 21, no. 5, pp. 833–839.
Chadderton, R.A., Miller, A.C., and McDonnell, A.J., Analysis of waste load allocation procedures, JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc., 2010, vol. 17, no. 5, pp. 760–766.
Chen, D.J., Lv, J., and Shen, Y.N., Water environment Gini coefficient method for multi-objective equitable allocation of interregional water environmental capacity, Environ. Pollut. Prevent., 2010, vol. 32, no. 1, pp. 88–91.
Dong, Z.F., Research on the Total Amount Allocation Methods of the Water Pollutant among Different Provinces: Taking COD Allocation as a Case, Nanjing University, 2010.
Fu, Z.H., Xie, Y.L., Li, W., and Guo, H., An inexact multi-objective programming model for an economy-energy-environment system under uncertainty: A case study of Urumqi, China, Energy, 2017, vol. 126, pp. 165–178.
Fujiwara, O., Gnanendran, S.K., and Ohgaki, S., River quality management under stochastic streamflow, J. Environ. Eng., 2014, vol. 112, no. 2, pp. 185–198.
Hao, X.D., The Application of Information Entropy in Total Waste Load Allocation for Surface-Water and Control Policy, Tianjin Univ., 2010.
Jiao, F. and Gu, F.Y., Distribution of water environmental capacity of nitrogen ammonium in Suzhou Section of Jinghang Canal, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2011, vol. 34, no. 11, pp. 158–163.
Karamouz, M., Mahjouring, N., and Kerachian, R., River water quality zoning: A case study of Karoon and Dez river system, Iran. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng., 2004, vol. 1, no. 2, pp. 16–27.
Lin, W., Fu, G.W., and Liu, C.H., Study on allocating permissible pollutants discharge based on axioms system, Environ. Sci., 1996, vol. 17 no. 3, pp. 35–37.
Liu, B.C., Study on Water Environment Carrying Capacity in Mudanjiang River Basin, Harbin Inst. Technol., 2006.
Luo, P.P., Zhou, M.M., Deng, H.Z., Lyu, J.Q., and Cao, W.Q., Impact of forest maintenance on water shortages: Hydrologic modeling and effects of climate change, Sci. Total Environ., 2018, vol. 615, pp. 1355–1363.
Mahjouri, N. and Bizhani-Manzar, M., Waste load allocation in rivers using fallback bargaining, Water Resour. Manag., 2013, vol. 27, no. 7, pp. 2125–2136.
Qin, D.L., Wei, A.L., Lu, S.Y., Luo, Y.P., Liao, Y.H., Yi, M., and Song, B.B., Total water pollutant load allocation in Dongting Lake area based on the Environmental Gini Coefficient Method, Res. Environ. Sci., 2013, vol. 42, no. 42, pp. 209–219.
Saheed, O.Y. and Uta, W., Institutional dynamics in national strategy development pp. a case study of the capacity development strategy of Ganda’s water and environment sector, Water Policy, 2016, vol. 18, no. 5, pp. 1174–1193.
Shan, B.Q., Wang, C., Li, X.Y., Li, W.Z., and Zhang, H., Method for river pollution control plan based on water quality target management and the case study, J. Environ. Sci., 2015, vol. 35, no. 8, pp. 2314–2323.
Thomann, R.V. and Sobel, M.J., Estuarine water quality management and forecasting, J. Sanit. Eng. Div., 1964, vol. 90, no. 5, pp. 9–38.
Wang, Y.L., Study on the multi-purposes combination planning model of regional water pollution control, Acta Sci. Circumstantiae, 2002, vol. 22, no. 1, pp. 107–110.
Yue, Q., Hou, L.M., Wang, T., Wang, L.S., Zhu, Y., and Cheng, X.L., Optimization of industrial structure based on water environmental carrying capacity in Tieling City, Water Sci. Technol., 2015, vol. 71, no. 8, pp. 1255–1262.
Zhang, T.Z., The economic principle of total water pollutant emission control management, Environ. Sci., 1990, vol. 11, no. 6, pp. 2–6.
Zeng, W.H., Wu, B., and Chai, Y., Dynamic simulation of urban water metabolism under water environmental carrying capacity restrictions, Front. Environ. Sci. Eng., 2016, vol. 10, no. 1, pp. 114–128.
Zhou, G., Lei, K., Fu, G., and Zhang, S., Multi-objective river waste load allocation model based on rationality evaluation index, J. Applied Foundation and Eng. Sci., 2015, no. 3, pp. 499–511.
FUNDING
This research was supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities of China (no. 182 502 045) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (71 373 003).
This manuscript has been edited by professional editors at Editage, a division of Cactus Communications.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All the authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest. The authors confirm that this is an original submission which has not been published previously or submitted to any other journal.
APPENDIX
APPENDIX
Basic data of districts and counties in Liaohe River | |||||||||||
District and county | Index | ||||||||||
GDP per capita, yuan/ person | urban residents’ income level, yuan | the proportion of the first industry output to GDP, % | the proportion of environmental protection investment to GDP, % | population density, 104/km2 | social education account for total financial expenditure | treatment rate of sewage treatment plant | the industrial wastewater discharge volume per ten thousand values, t/104 yuan | the industrial fresh water consumption per ten thousand values, m3/104 yuan | the effective irrigation area, ha | the COD discharge volume per ten thousand values, t/104 yuan | |
Kangping County | 62 632.71 | 22 924 | 18.62 | 9.92 | 0.0079 | 18.86% | 0.90 | 2.0717 | 246.35 | 9329 | 0.0047 |
Changtu County | 21 880.32 | 21 528 | 37.63 | 3.36 | 0.0122 | 66.35% | 0.90 | 0.9891 | 1.18 | 71 950 | 0.0143 |
Faku County | 77 689.65 | 21 352 | 14.99 | 6.32 | 0.0096 | 19.78% | 0.90 | 0.1113 | 5.07 | 29 913 | 0.0082 |
Tieling County | 38 672.30 | 23 430 | 24.48 | 4.84 | 0.0095 | 15.60% | 0.85 | 0.7867 | 611.13 | 32 077 | 0.0182 |
Kaiyuan City | 31 255.19 | 24 244 | 27.62 | 4.19 | 0.0107 | 12.47% | 0.93 | 0.1460 | 0.18 | 50 400 | 0.0252 |
Shenbei Area | 101 484.22 | 28 200 | 7.06 | 4.54 | 0.0275 | 10.81% | 0.96 | 0.0352 | 0.06 | 14 510 | 0.0044 |
Xinmin City | 67 554.60 | 24 970 | 18.10 | 4.45 | 0.0109 | 24.90% | 1.00 | 0.0572 | 0.07 | 57 166 | 0.0138 |
Diaobingshan City | 44 174.52 | 23 870 | 5.36 | 6.64 | 0.0514 | 14.55% | 0.90 | 1.4803 | 23.95 | 3666 | 0.0098 |
Zhangwu County | 28 456.57 | 19 466 | 44.68 | 5.32 | 0.0062 | 14.44% | 0.99 | 1.0444 | 1.49 | 34 349 | 0.0193 |
Liaozhong County | 93 248.92 | 27 650 | 18.93 | 16.71 | 0.0144 | 25.54% | 1.00 | 0.8146 | 1.05 | 43 386 | 0.0064 |
Taian County | 63 914.11 | 24 054 | 20.04 | 1.19 | 0.0151 | 9.88% | 0.95 | 2.1907 | 5.05 | 26 170 | 0.0064 |
Panshan County | 52 749.06 | 26 090 | 30.38 | 1.83 | 0.0089 | 7.69% | 0.78 | 4.1364 | 0.56 | 45 151 | 0.0554 |
Dawa County | 62 491.92 | 29 150 | 20.94 | 1.78 | 0.0185 | 5.25% | 0.99 | 0.0856 | 0.13 | 54 753 | 0.0098 |
Basic data of districts and counties in Hunhe River | |||||||||||
District and county | Index | ||||||||||
GDP per capita, yuan/person | urban residents' income level, yuan | the proportion of the first industry output to GDP, % | the proportion of environmental protection investment to GDP, % | population density, 104/km2 | social education account for total financial expenditure | treatment rate of sewage treatment plant | the industrial wastewater discharge volume per ten thousand values, t/104 yuan | the industrial fresh water consumption per ten thousand values, m3/104 yuan | the effective irrigation area, ha | the COD discharge volume per ten thousand values, t/104 yuan | |
Xinbin County | 40 648.6 | 10 255 | 20.86 | 5.45 | 0.0039 | 11.07% | 0.95 | 0.0825 | 2.52 | 7572 | 0.0052 |
Fushun County | 75 733.7 | 11 542 | 19.23 | 7.61 | 0.0028 | 10.50% | 0.82 | 0.0315 | 15.47 | 3490 | 0.0045 |
Dongzhou District | 64 514.4 | 25 452 | 4.39 | 28.64 | 0.0105 | 12.00% | 0.92 | 58.3829 | 4735.99 | 0 | 0.0306 |
Shunchen City | 40 042.4 | 27 925 | 2.06 | 3.88 | 0.0863 | – | 0.92 | 0.2192 | 190.18 | 6271 | 0.0059 |
Xinfu District | 55 926.3 | 23 170 | 0.30 | 25.77 | 0.0910 | 11.76% | 0.95 | 1.3913 | 37.10 | 0 | 0.0213 |
Wanghua District | 7524.3 | 26 321 | 3.66 | 32.56 | 0.0720 | 13.40% | 0.92 | 22.4403 | 3300.65 | 0 | 0.0394 |
Dongling District | 100 698.2 | 32 100 | 1.48 | 1.56 | 0.0262 | 7.78% | 0.99 | 0.7647 | 1.20 | 1569 | 0.0042 |
Dadongqu District | 65 851.8 | 31 030 | 0.00 | 7.81 | 0.5075 | – | 0.99 | 3.7483 | 0.00 | 0 | 0.0044 |
Shenhe District | 98 522.7 | 40 987 | 0.00 | 6.66 | 0.9174 | – | 0.99 | 0.3557 | 0.00 | 0 | 0.0037 |
Heping District | 100 544.7 | 40 205 | 0.04 | 6.53 | 0.7837 | 18.20% | 0.99 | 0.1345 | 0.21 | 0 | 0.0039 |
Tiexi District | 92 130.0 | 38 124 | 0.09 | 7.69 | 0.1161 | – | 0.98 | 7.7056 | 117.75 | 0 | 0.0060 |
Huanggu District | 44 487.3 | 30 013 | 11.59 | 13.83 | 0.4832 | – | 0.99 | 1.2717 | 9.92 | 0 | 0.0091 |
Sujiatun District | 68 333.4 | 33 251 | 9.22 | 5.97 | 0.0343 | 17.42% | 0.70 | 1.6423 | 23.62 | 9473 | 0.0060 |
Yuhong District | 70 686.1 | 32 330 | 2.43 | 4.22 | 0.0542 | 4.77% | 0.82 | 0.4837 | 3.00 | 14 479 | 0.0036 |
Basic data of districts and counties in Taizihe River | |||||||||||
District and county | Index | ||||||||||
GDP per capita, yuan/person | urban residents' income level, yuan | the proportion of the first industry output to GDP, % | the proportion of environmental protection investment to GDP | population density, 104/km2 | social education account for total financial expenditure, % | treatment rate of sewage treatment plant | the industrial wastewater discharge volume per ten thousand values, t/104 yuan | the industrial fresh water consumption per ten thousand values, m3/104 yuan | the effective irrigation area, ha | the COD discharge volume per ten thousand values, t/104 yuan | |
Benxi County | 61 361.28 | 23 464 | 12.20 | 0.0283 | 0.0049 | 17.20 | 0.99 | 0.43 | 11.17 | 1970 | 0.0054 |
Mingshan District | 38 870.39 | 28 849 | 4.41 | 0.0315 | 0.0570 | 14.86 | 0.90 | 1.44 | 36.35 | 1101 | 0.0091 |
Fengcheng City | 48 145.08 | 27 210 | 10.82 | 0.0419 | 0.0059 | 22.73 | 0.90 | 1.36 | 12.10 | 9156 | 0.0038 |
Xihu District | 85 863.30 | 24 943 | 2.20 | 0.0280 | 0.0368 | 0.44 | 0.95 | 1.28 | 32.28 | 1149 | 0.0054 |
Pingshan District | 64 222.72 | 28 759 | 0.60 | 0.0224 | 0.1107 | 10.85 | 0.90 | 4.86 | 952.34 | 1128 | 0.0061 |
Nanfen District | 76 882.59 | 24 046 | 6.22 | 0.0784 | 0.0077 | 15.69 | 0.85 | 1.53 | 335.01 | 641 | 0.0133 |
Gongchangling District | 72 872.53 | 24 067 | 3.32 | 0.0328 | 0.0175 | 12.27 | 0.96 | 37.09 | 166.38 | 99 | 0.0088 |
Wensheng District | 42 269.76 | 20 000 | 7.39 | 0.0354 | 0.1975 | 5.98 | 0.16 | 7.79 | 23.12 | 1850 | 0.0081 |
Hongwei District | 36 500.76 | 23 480 | 1.25 | 0.0118 | 0.1158 | – | 0.99 | 786.21 | 20 629.25 | 229 | 0.0992 |
Taizihe District | 64 627.71 | 19 500 | 12.25 | 0.0376 | 0.0620 | 10.35 | 0.99 | 0.65 | 26.69 | 7174 | 0.0102 |
Qianshan District | 64 627.71 | 44 902 | 7.56 | 0.0371 | 0.0124 | 10.87 | 0.95 | 8.78 | 630.69 | 5860 | 0.0172 |
Tiedong District | 67 958.02 | 36 074 | 1.32 | 0.0079 | 1.3813 | – | 0.95 | 0.37 | 0.62 | 0 | 0.0036 |
Dashiqiao City | 60 064.39 | 28 872 | 10.86 | 0.0072 | 0.0250 | 12.41 | 0.87 | 1.53 | 4.08 | 34 167 | 0.0200 |
Dengta City | 58 519.76 | 26 299 | 9.79 | 0.0081 | 0.0194 | 9.34 | 0.99 | 1.05 | 80.49 | 25 546 | 0.0093 |
Haicheng City | 70 002.32 | 26 390 | 5.41 | 0.0034 | 0.0246 | 13.44 | 0.95 | 2.34 | 5.42 | 31 280 | 0.0068 |
Liaoyang County | 52 099.52 | 11 765 | 9.80 | 0.0084 | 0.0101 | 14.66 | 0.90 | 0.43 | 5.10 | 22 872 | 0.0055 |
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qiang Yue, Zhang, Y., Li, C. et al. Research of Water Environment Capacity Allocation in Liaoning Province Based on the Analytic Network Process. Water Resour 48, 310–323 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0097807821020111
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0097807821020111