Abstract
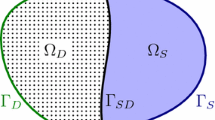
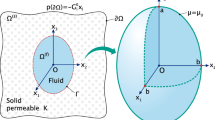
Multidomain mixed pairs of coupled stationary constrained boundary value problems, are formulated variationally in frameworks of reflexive Banach spaces as macro-hybrid systems, and analyzed. Interior synchronizing and interface coupling transmission constraints are modeled in terms of Lagrange multipliers as solutions of dual variational subpotential maximal monotone inclusions. Existence and uniqueness results are established via resolvent fixed-point characterizations of the corresponding primal and dual macro-hybridized problems. Multimedia mixed mechanical subsurface-surface Darcy/Stokes incompressible flow coupled pairs with intrinsic distributed control constraints exemplify the general macro-hybrid mixed systems. Coupling dual-primal and primal-dual interface macro-hybrid mixed variational conditions are lastly developed and applied to the Darcy/Stokes multimedia pair model.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams A, Fournier JF (2003) Sobolev spaces. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Alduncin G (1989) Subdifferential and variational formulations of boundary value problems. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 72:173–186
Alduncin G (1997) On Gabay’s Algorithms for Mixed Variational Inequalities. Appl Math Optim 35:21–24
Alduncin G (2005) Composition duality methods for mixed variational inclusions. Appl Math Optim 52:311–348
Alduncin G (2007) Macro-hybrid variational formulations of constrained boundary value problems. Numer Funct Anal Optim 28:751–774
Alduncin G (2010) Variational formulations of nonlinear constrained boundary value problems. Nonlinear Anal 72:2639–2644
Alduncin G (2011) Primal and dual evolution macro-hybrid mixed variational inclusions. Int J Math Anal (Ruse) 5:1631–1664
Alduncin G (2012) Mixed variational modeling of multiphase flow and transport in the subsurface. Far East J Appl Math 71:1–42
Alduncin G (2014) Fixed-point variational existence analysis of evolution mixed inclusions. Int J Math Anal (Ruse) 8:1833–1846
Alduncin G (2017) Proximation penalty-duality algorithms for mixed optimality conditions. Fixed Point Theory Appl 19:1775–1791
Badia S, Quaini A, Quarteroni A (2009) Coupling Biot and Navier-Stokes equations for modelling fluid-poroelastic media interaction. J Comput Phys 228:7986–8014
Barbu V (2010) Nonlinear differential equations of monotone types in banach spaces. Springer, New York
Beavres GS, Joseph DD (1967) Boundary conditions at a naturally permeable wall. J Fluid Mech 30:197–207
Cesmelioglu A, Giraul V, Rivière B (2013) Time-dependent coupling of Navier-Stokes and Darcy flows. Math Modelling Numer Anal 47:539–554
Chidyagwai P, Riviére B (2009) On the solution of the coupled NavierStokes and Darcy equations. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 198:3806–3820
Cimolin F, Discacciati M (2013) Navier-Stokes/Forchheimer models for filtration through porous media. Appl Numer Math 72:205–224
Dawson C, Wheeler S, Sun MF (2004) Compatible algorithms for coupled flow and transport. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 5:1922565–1932580
Dean RH, Stone CM (2006) Minkoff SE A comparison of techniques for coupling porous flow and geomechanics. SPE J 11:132–140
Discacciati M, Miglio E, Quarteroni A (2002) Mathematical and numerical models for coupling surface and groundwater flows. Appl Numer Math 43:57–74
Discacciativ M, Quarteroni A (2003) Analysis of a domain decomposition method for the coupling of Stokes and Darcy equations. In: Brezzi F et al (eds) Numerical analysis and advanced applications-ENUMATH 2001. Springer, Milan, pp 3–20
Du G, Zuo L (2017) Local and parallel finite element method for the mixed Navier-Stokes/Darcy model with Beavers-Joseph interface conditions. Acta Mathematica Scientia 37B:1331–1347
Duvaut G, Lions JL (1972) Les Inéquations en Méchanique et en Physique. Dunod, Paris
Ervin VJ, Jenkins EW, Hyesuk L (2014) Approximation of the StokesDarcy System by Optimization. J Sci Comput 59:775794
Feng W, He X, Wang Z, Zhang X (2012) Non-iterative domain decomposition methods for a non-stationary Stokes-Darcy model with Beavers-Joseph interface condition. Appl Math Comput 219:453463
Gabay D (1982) Application de la méthode des multiplicateurs aux inéquations variationnelles. In: Fortin M, Glowinski R (eds) Méthodes de Lagrangien Augmenté. Dunod-Bordas, Paris, pp 279–307
Girault V (1992) The gradient, divergence, curl and Stokes operators in weighted Sobolev spaces of \(R^3\). J Fac Sci Univ Tokyo Sect IA Math 39:279–307
Girault V, Raviart PA (1986) Finite element methods for Navier-Stokes equations. Springer, Berlin
Girault V, Riviére B (2009) DG approximation of coupled Navier-Stokes and Darcy equations by Beaver-Joseph-Shaffman interface condition. SIAM Numer Anal 47:2052–2089
Gurtin M, Fried E, Anand L (2010) The mechanics and thermodynamics of continuum. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Hyesuk L, Kelsey R (2014) Least squares approach for the time-dependent nonlinear StokesDarcy flow. Comput Math Appl 67:1806–1815
Kim J, Tchelepi H, Juanes R (2011a) Stability and convergence of sequentiel methods for coupled flow and geomechanics: fixed-stress and fixed-strain splits. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 200:1591–1606
Kim J, Tchelepi HA, Juanes R (2011b) Accuracy and efficiency of sequential methods for coupled flow and geomechanics. SPE J 16:249–262
Layton W, Schieweck F, Yotov I (2003) Coupling fluid flow with porous media flow. SIAM J Numer Anal 40:2195–2218
Mikelić A, Wheeler MF (2013) Convergence of iterative coupling for coupled flow and geomechanics. Comput Geosci 17:455–461
Panagiotopoulos PD (1985) Inequality problems in mechanics and applications. Convex and nonconvex energy functions. Birkhäuser, Boston
Rivière B (2005) Analysis of a discontinuous finite element method for the coupled Stokes and Darcy problems. J Sci Comput 22:479–500
Rockafellar RT (1970) On the maximal monotonicity of subdifferential mappings. Pacific J Math 33:209–216
Saffman P (1971) On the boundary condition at the surface of a porous media. Stud Appl Math 50:292–315
Temam R (1970) Analyse Numérique. Presses Universitaires de France, Paris
Yosida K (1974) Functional analysis. Springer, New York
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alduncin, G. Variational interior and interface transmission conditions: multidomain mixed Darcy/Stokes control problems. Optim Eng 23, 797–826 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11081-021-09606-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11081-021-09606-2
Keywords
- Mixed variational mechanics
- Multidomain macro-hybrid mixed system pair
- Interior synchronizing transmission condition
- Coupling interface transmission condition
- Constrained boundary value controlled problem
- Subsurface-surface Darcy/Stokes flow