Abstract
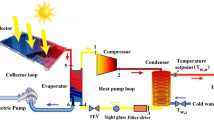
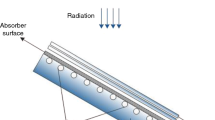
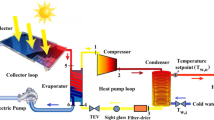
This study aims to develop a multi-objective version of the search group algorithm (SGA) called the multi-objective search group algorithm (MOSGA) to help determine thermo-economic optimization of flat-plate solar collector (FPSC) systems. Search mechanisms of the SGA were modified to determine non-dominated solutions through mutation, generation, and selection stages. Authors also mined the Pareto archive with a selection mechanism to maintain and intensify convergence and distribution of solutions. The study tested the proposed MOSGA with well-known multi-objective benchmark problems. Results were compared with outcomes from conventional algorithms using the same performance metrics to validate the capability and performance of the MOSGA. Afterward, MOSGA was applied to find the best design parameters to simultaneously optimize thermal efficiency and the total annual cost of FPSC systems. Four case studies were conducted with four different working fluids (pure water, SiO2, Al2O3, and CuO nanofluids). Optimization results obtained by the MOSGA were analyzed and compared with solutions provided by other algorithms. The findings revealed relative improvement in thermal efficiency and reduced annual cost for all nanofluids compared to pure water. Thermal efficiency was improved by 2.2748%, 2.4298%, and 2.7948% for SiO2, Al2O3, and CuO case studies, respectively, compared to pure water. Meanwhile, TAC rates were increased by 2.4111%, 2.3403%, and 2.9133% for these case studies, respectively. Comparative results also demonstrated that MOGSA was robustly effective and superior in the selection of appropriate design parameters of FPSC systems.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agency IE (2018) Renewables 2018
Raj P, Subudhi S (2018) A review of studies using nanofluids in flat-plate and direct absorption solar collectors. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 84:54–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2017.10.012
Evangelisti L, De Lieto VR, Asdrubali F (2019) Latest advances on solar thermal collectors: a comprehensive review. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 114:109318. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2019.109318
(2018) Renewables 2018 global status report. In: Green growth knowledge platform. https://www.greengrowthknowledge.org/resource/renewables-2018-global-status-report. Accessed 31 Oct 2019
Kalogirou S (2003) The potential of solar industrial process heat applications. Appl Energy 76:337–361. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0306-2619(02)00176-9
Karki S, Haapala KR, Fronk BM (2019) Technical and economic feasibility of solar flat-plate collector thermal energy systems for small and medium manufacturers. Appl Energy 254:113649. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2019.113649
Jing OL, Bashir MJK, Kao J-J (2015) Solar radiation based benefit and cost evaluation for solar water heater expansion in Malaysia. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 48:328–335. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2015.04.031
Huy TH, Nallagownden P, Kannan R (2019) Energetic optimization of solar water heating system with flat plate collector using search group algorithm. J Adv Res Fluid Mech Therm Sci 61:17
Farahat S, Sarhaddi F, Ajam H (2009) Exergetic optimization of flat plate solar collectors. Renew Energy 34:1169–1174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2008.06.014
Jafarkazemi F, Ahmadifard E (2013) Energetic and exergetic evaluation of flat plate solar collectors. Renew Energy 56:55–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2012.10.031
Badr O, Mohammed A, Brahim D (2018) Optimization of the thermal performance of the solar water heater (SWH) using stochastic technique 10
Wenceslas KY, Ghislain T (2019) Experimental validation of exergy optimization of a flat-plate solar collector in a thermosyphon solar water heater. Arab J Sci Eng 44:2535–2549. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-018-3227-x
Khademi M, Jafarkazemi F, Ahmadifard E, Younesnejad S (2012) Optimizing exergy efficiency of flat plate solar collectors using SQP and genetic algorithm. AMM 253–255:760–765. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.253-255.760
Siddhartha SN, Varun, (2012) A particle swarm optimization algorithm for optimization of thermal performance of a smooth flat plate solar air heater. Energy 38:406–413. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2011.11.026
Siddhartha, Chauhan SR, Varun, Sharma N (2011) Thermal performance optimization of smooth flat plate solar air heater (SFPSAH) using simulated annealing: evaluation and comparisons. In: 2011 international conference utility exhibition on power and energy systems: issues and prospects for Asia (ICUE), pp 1–5
Varun S (2010) Thermal performance optimization of a flat plate solar air heater using genetic algorithm. Appl Energy 87:1793–1799. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2009.10.015
Varun SN, Bhat IK, Grover D (2011) Optimization of a smooth flat plate solar air heater using stochastic iterative perturbation technique. Sol Energy 85:2331–2337. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2011.06.022
Rao RV, Waghmare G (2015) Optimization of thermal performance of a smooth flat-plate solar air heater using teaching–learning-based optimization algorithm. Cog Eng 2:997421. https://doi.org/10.1080/23311916.2014.997421
Şencan Şahin A (2012) Optimization of solar air collector using genetic algorithm and artificial bee colony algorithm. Heat Mass Transf 48:1921–1928. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00231-012-1038-2
Yıldırım C, Aydoğdu İ (2017) Artificial bee colony algorithm for thermohydraulic optimization of flat plate solar air heaters. J Mech Sci Technol 31:3593–3602. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-017-0647-6
Jiandong Z, Hanzhong T, Susu C (2015) Numerical simulation for structural parameters of flat-plate solar collector. Sol Energy 117:192–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2015.04.027
Bornatico R, Pfeiffer M, Witzig A, Guzzella L (2012) Optimal sizing of a solar thermal building installation using particle swarm optimization. Energy 41:31–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2011.05.026
Araya R, Bustos F, Contreras J, Fuentes A (2017) Life-cycle savings for a flat-plate solar water collector plant in Chile. Renew Energy 112:365–377. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2017.05.036
Ko MJ (2015) Analysis and optimization design of a solar water heating system based on life cycle cost using a genetic algorithm. Energies 8:11380–11403. https://doi.org/10.3390/en81011380
Cheng Hin JN, Zmeureanu R (2014) Optimization of a residential solar combisystem for minimum life cycle cost, energy use and exergy destroyed. Sol Energy 100:102–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2013.12.001
Yaman K, Arslan G (2018) Modeling, simulation, and optimization of a solar water heating system in different climate regions. J Renew Sustain Energy 10:023703. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5004069
Kusyy O, Kuethe S, Vajen K (2010) Simulation-based optimization of a solar water heating system by a hybrid genetic-binary search algorithm. In: 2010 XVth international seminar/workshop on direct and inverse problems of electromagnetic and acoustic wave theory (DIPED), pp 201–206
Hajabdollahi Z, Hajabdollahi H (2017) Thermo-economic modeling and multi-objective optimization of solar water heater using flat plate collectors. Sol Energy 155:191–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2017.06.023
Hajabdollahi F, Premnath K (2017) Numerical study of the effect of nanoparticles on thermoeconomic improvement of a solar flat plate collector. Appl Therm Eng 127:390–401. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2017.08.058
Hajabdollahi H (2018) Investigating the effect of nanofluid on optimal design of solar flat plate collector. In: 2018 5th international conference on renewable energy: generation and applications (ICREGA), pp 188–191
Hajabdollahi Z, Hajabdollahi H, Kim KC (2019) Multi-objective optimization of solar collector using water-based nanofluids with different types of nanoparticles. J Therm Anal Calorim. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-08444-w
Gonçalves MS, Lopez RH, Miguel LFF (2015) Search group algorithm: a new metaheuristic method for the optimization of truss structures. Comput Struct 153:165–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruc.2015.03.003
Pedro RL, Demarche J, Miguel LFF, Lopez RH (2017) An efficient approach for the optimization of simply supported steel-concrete composite I-girder bridges. Adv Eng Softw 112:31–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advengsoft.2017.06.009
Carraro F, Lopez RH, Miguel LFF (2017) Optimum design of planar steel frames using the search group algorithm. J Braz Soc Mech Sci Eng 39:1405–1418. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-016-0628-1
Noorbin SFH, Alfi A (2018) Adaptive parameter control of search group algorithm using fuzzy logic applied to networked control systems. Soft Comput 22:7939–7960. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-017-2742-0
Khamari D, Sahu RK, Panda S (2019) Application of search group algorithm for automatic generation control of interconnected power system. In: Behera HS, Nayak J, Naik B, Abraham A (eds) Computational intelligence in data mining. Springer, Singapore, pp 557–568
Khamari D, Sahu RK, Panda S (2019) Application of search group algorithm for automatic generation control of multi-area multi-source power systems. E3S Web Conf 87:01005. https://doi.org/10.1051/e3sconf/20198701005
Acampora G, Caruso D, Vaccaro A, Vitiello A (2016) A search group algorithm for optimal voltage regulation in power systems. In: 2016 IEEE congress on evolutionary computation (CEC), pp 3662–3669
Sadollah A, Eskandar H, Bahreininejad A, Kim JH (2015) Water cycle algorithm for solving multi-objective optimization problems. Soft Comput 19:2587–2603. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-014-1424-4
Sadollah A, Eskandar H, Kim JH (2015) Water cycle algorithm for solving constrained multi-objective optimization problems. Appl Soft Comput 27:279–298. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2014.10.042
Mirjalili S, Saremi S, Mirjalili SM, dos Coelho LS (2016) Multi-objective grey wolf optimizer: a novel algorithm for multi-criterion optimization. Expert Syst Appl 47:106–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2015.10.039
Tran D-H, Cheng M-Y, Prayogo D (2016) A novel multiple objective symbiotic organisms search (MOSOS) for time–cost–labor utilization tradeoff problem. Knowl Based Syst 94:132–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2015.11.016
Mirjalili S, Jangir P, Mirjalili SZ et al (2017) Optimization of problems with multiple objectives using the multi-verse optimization algorithm. Knowl Based Syst 134:50–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2017.07.018
Foroughi Nematollahi A, Rahiminejad A, Vahidi B (2019) A novel multi-objective optimization algorithm based on lightning attachment procedure optimization algorithm. Appl Soft Comput 75:404–427. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2018.11.032
Wolpert DH, Macready WG (1997) No free lunch theorems for optimization. IEEE Trans Evol Comput 1:67–82. https://doi.org/10.1109/4235.585893
Kalogirou SA (2004) Solar thermal collectors and applications. Prog Energy Combust Sci 30:231–295. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pecs.2004.02.001
Agarwal VK, Larson DC (1981) Calculation of the top loss coefficient of a flat-plate collector. Sol Energy 27:69–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/0038-092X(81)90022-0
Mahian O, Kianifar A, Sahin AZ, Wongwises S (2015) Heat transfer, pressure drop, and entropy generation in a solar collector using SiO2/water nanofluids: effects of nanoparticle size and pH. J Heat Transf. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4029870
Pak BC, Cho YI (1998) Hydrodynamic and heat transfer study of dispersed fluids with submicron metallic oxide particles. Exp Heat Transf 11:151–170. https://doi.org/10.1080/08916159808946559
Xuan Y, Roetzel W (2000) Conceptions for heat transfer correlation of nanofluids. Int J Heat Mass Transf 43:3701–3707. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0017-9310(99)00369-5
Xuan Y, Li Q, Hu W (2003) Aggregation structure and thermal conductivity of nanofluids. AIChE J 49:1038–1043. https://doi.org/10.1002/aic.690490420
Maïga SEB, Nguyen CT, Galanis N, Roy G (2004) Heat transfer behaviours of nanofluids in a uniformly heated tube. Superlattices Microstruct 35:543–557. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spmi.2003.09.012
Taal M, Bulatov I, Klemeš J, Stehlík P (2003) Cost estimation and energy price forecasts for economic evaluation of retrofit projects. Appl Therm Eng 23:1819–1835. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1359-4311(03)00136-4
Deb K, Pratap A, Agarwal S, Meyarivan T (2002) A fast and elitist multiobjective genetic algorithm: NSGA-II. IEEE Trans Evol Comput 6:182–197. https://doi.org/10.1109/4235.996017
Goldberg DE (1989) Genetic algorithms in search, optimization and machine learning, 1st edn. Addison-Wesley Longman Publishing Co., Inc., Boston
Coello CAC, Lamont GB, Veldhuizen DAV (2006) Evolutionary algorithms for solving multi-objective problems (genetic and evolutionary computation). Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Veldhuizen DAV, Lamont GB (1998) Evolutionary computation and convergence to a Pareto front. Late breaking papers at the genetic programming 1998 conference. Stanford University Bookstore, Stanford, pp 221–228
Schott JR (1995) Fault tolerant design using single and multicriteria genetic algorithm optimization. Thesis, Massachusetts Institute of Technology
Zitzler E (1999) Evolutionary algorithms for multiobjective optimization: methods and applications. Swiss Federal Institute of Technology, Zurich
Deb K, Kalyanmoy D (2001) Multi-objective optimization using evolutionary algorithms. Wiley, New York
Zitzler E, Thiele L (1998) Multiobjective optimization using evolutionary algorithms—a comparative case study. In: Eiben AE, Bäck T, Schoenauer M, Schwefel H-P (eds) Parallel problem solving from nature—PPSN V. Springer, Berlin, pp 292–301
Tran D-H, Luong-Duc L, Duong M-T et al (2018) Opposition multiple objective symbiotic organisms search (OMOSOS) for time, cost, quality and work continuity tradeoff in repetitive projects. J Comput Des Eng 5:160–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcde.2017.11.008
Sheng W, Liu K-Y, Liu Y et al (2015) Optimal placement and sizing of distributed generation via an improved nondominated sorting genetic algorithm II. IEEE Trans Power Deliv 30:569–578. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPWRD.2014.2325938
Zitzler E, Deb K, Thiele L (2000) Comparison of multiobjective evolutionary algorithms: empirical results. Evol Comput 8:173–195. https://doi.org/10.1162/106365600568202
Schaffer JD (1984) Some experiments in machine learning using vector evaluated genetic algorithms (artificial intelligence, optimization, adaptation, pattern recognition). Phd, Vanderbilt University
Fonseca CM, Fleming PJ (1995) An overview of evolutionary algorithms in multiobjective optimization. Evol Comput 3:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1162/evco.1995.3.1.1
Poloni C, Giurgevich A, Onesti L, Pediroda V (2000) Hybridization of a multi-objective genetic algorithm, a neural network and a classical optimizer for a complex design problem in fluid dynamics. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 186:403–420. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0045-7825(99)00394-1
Kursawe F (1991) A variant of evolution strategies for vector optimization. In: Schwefel H-P, Männer R (eds) Parallel problem solving from nature. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp 193–197
Coello CAC, Pulido GT, Lechuga MS (2004) Handling multiple objectives with particle swarm optimization. IEEE Trans Evol Comput 8:256–279. https://doi.org/10.1109/TEVC.2004.826067
Flat plate panels. In: Kingspan|USA. https://www.kingspan.com/us/en-us/product-groups/renewable-technologies/solar-thermal/solar-flat-plate-panels/flat-plate-panels. Accessed 6 Nov 2019
Acknowledgements
This research is sponsored by YUTP–FRG and Graduate Research Assistantship (GRA) Scheme of Universiti Teknologi PETRONAS.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Our paper has no conflicts of interest with any other individuals or parties.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Truong, BH., Nallagownden, P., Truong, K.H. et al. Multi-objective search group algorithm for thermo-economic optimization of flat-plate solar collector. Neural Comput & Applic 33, 12661–12687 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-021-05915-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-021-05915-w