Abstract
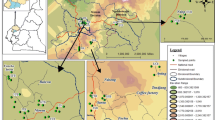
Today, population growth and demand for agricultural production have resulted in the significant damage to the natural ecosystem, including forests and rangelands, and have turned them into farmlands. Territorial land use changes can result in changes in chemical and physical features of soils, which in turn, may ultimately lead to land degradation. Understanding the effects of land use changes on soil features is very important as it helps with assessing the sustainability of natural ecosystems. Therefore, in the current study, we sought to compare changes in soil physico-chemical properties, soil deterioration index (SDI), soil erodibility factor (K factor) and the soil organic carbon (SOC) stock in three types of land use, namely: protected forest (PF), natural forest (NF) with common exploitation (overgrazing and fuel wood) and cultivated land (CL) in semi-arid regions in western Iran. Soil samples were randomly collected from 0–30 cm depths (16 + 18 + 18 at each land use, respectively; 52 samples in total). The soil texture, pH, exchangeable K, available P, total N, soil organic carbon and SOC stock were measured in soil samples. The findings indicated that in general, overgrazing with the exploitation of trees in the NF and changing the NF to CL caused a significant increase in sand (by 22.3–90.5%) and bulk density (6.1–9.16%) and a significant decrease in silt (4.34–13.56%), clay (2.36–13.5%) exchangeable K (37.68–50.63%), available P (15.58–27.42%), total N (22.2–55.5%), soil organic carbon (22.3–52.4%) and SOC stock (22.87–52.3%) (P < 0.01). The outcomes of multivariate analysis (RDA) indicated that CL correlated with sand, pH and bulk density, and EF correlated with most soil properties. The outcomes of SDI were indicative of a significant reduction in quality of soil (-5.5%) under CL, compared with NF (–21.5%) and EF (0.1%). The highest value of soil erodibility factor (K factor) was observed in the CL (0.260), and the lowest was at the PF (0.214). In general, the findings of this study showed that the exploitation of trees for fuel wood with overgrazing in the NF and after transformation of the NF to the CL caused a significant deterioration in the soil properties in the semi-arid region in western Iran.



Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Abril, A., Barttfelda, P., and Bucherb, E.H., The effect of fire and overgrazing disturbs on soil carbon balance in the Dry Chaco forest, For. Ecol. Manage., 2005, vol. 206, pp. 399–405.
Basaran, M., Erpul, G., Tercan, A.E., and Anga, C.M.R., The effects of land use changes on some soil properties in Indagı Mountain Pass Cankırı, Turkey, Environ., Monit. Assess., 2008, vol. 136, pp. 101–119.
Bewketa, W. and Stroosnijder, L., Effects of agro ecological land use succession on soil properties in Chemoga watershed, Blue Nile basin, Ethiopia, Geoderma, 2003, vol. 111, pp. 85–98.
Borumand, M.G., Hajarsepanlu, M., and Bahmanyar, A., The effect of land use change on some of the physical and chemical properties of soil (case study: Semeskande Area of Sari), J. Watershed Manage. Res., 2014, vol. 5, no. 9, pp. 78–94.
Celik, I., Land-use effects on organic matter and physical properties of soil in a southern Mediterranean highland of Turkey, Soil Tillage Res., 2005, vol. 83, pp. 270–277.
Chen, X. and Duan, Z., Changes in soil physical and chemical properties during reversal of desertification in Yanchi County of Ningxia Hui Autonomous region, China, Environ. Geol., 2009, vol. 57, pp. 975–985.
Chibsa, T. and Taa, A., Assessment of soil organic matter under four land use systems in Bale Highlands, Southeast Ethiopia. A. Soil organic matter contents in four land use systems: forestland, grassland, fallow land and cultivated land, World Appl. Sci. J., 2009, vol. 6, no. 9, pp. 1231–1246.
Costa, C., Papatheodorou, E.M., Monokrousos, N., and Stamou, G.P., Spatial variability of soil organic C, inorganic N and extractable P in a Mediterranean grazed area, Land Degrad. Dev., 2015, vol. 26, pp. 103–109.
Cotching, W.E. and Kidd, D.B., Soil quality evaluation and the interaction with land use and soil order in Tasmania, Australia, Agric., Ecosyst. Environ., 2010, vol. 137, pp. 358–366.
Dakhah, M. and Gifford, G.F., Influence of vegetation, rock cover and trampling on infiltration rates and sediment production, J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc., 1980, vol. 16, no. 6, pp. 979–986.
Doran, J.W., Soil health and global sustainability, translating science into practice, Agric. Ecosyst. Environ., 2002, vol. 88, pp. 119–127.
Edmondson, J.L., Davies, Z.G., McCormack, S.A., Gaston, K.J., and Leake, J.R., Land cover effects on soil organic carbon stocks in an European city, Sci. Total Environ., 2014, vol. 472, pp. 444–453.
Fleischner, T.L., Ecological costs of livestock grazing in western North America, Conserv. Biol., 1994, vol. 8, no. 3, pp. 629–644.
Gillson, L. and Hoffman, M.T., Rangeland ecology in a changing world, Science, 2007, vol. 315, pp. 53–54.
Ghazanfari, H., Namiranian, M., Sobhan, H., and Mohajer, R.M., Traditional forest management and its application to encourage public participation for sustainable forest management in the northern Zagros mountain of Kurdistan province, Iran, Scand. J. For. Sci., 2004, vol. 19, no. 4, pp. 65–71.
Graham, R.C. and O’Geen, A.T., Soil mineralogy trends in California landscapes, Geoderma, 2010, vol. 154, pp. 418–437.
Hajabbasi, M.A., Jalalian, A., and Karimzadeh, H.R., Deforestation effects on soil physical and chemical properties, Lordegan, Iran, Plant Soil, 1997, vol. 190, pp. 301–308.
Hill, M.J., Braaten, R., and Mckeon, G.M., A scenario calculator for effect of grazing land management on carbon stocks in Australian rangelands, J. Environ. Model. Software, 2003, vol. 7, no. 18, pp. 627–644.
Islam, K.R. and Weil, R.R., Land use effects on soil quality in a tropical forest ecosystem of Bangladesh, Agric., Ecosyst. Environ., 2000, vol. 79, pp. 9–16.
Izquierdo, A.E. and Grau, R.H., Agriculture adjustment, land-use transition and protected areas in Northwestern Argentina, J. Environ. Manage., 2009, vol. 90, pp. 858–865.
Jazirehi, M.H. and Rostaghi, E.M., Silviculture in Zagros, Tehran: Univ. of Tehran Press, 2003.
Jeddi, K. and Chaieb, M., Changes in soil properties and vegetation following livestock grazing exclusion in degraded arid environments of South Tunisia, J. Flora, 2010, vol. 205, pp. 184–189.
Kavian, A., Azmoodeh, A., and Solaimani, K., Deforestation effects on soil properties, runoff and erosion in northern Iran, Arab. J. Geosci., 2014, vol. 7, pp. 1941–1950.
Khresat, S., Al-Bakri, J., and Al-Tahhan, R., Impact of land use/cover change on soil properties in the Mediterranean region of Northwestern Jordan, Land Degrad. Dev., 2008, vol. 19, pp. 397–407.
Lal, R., Soil carbon sequestration impact on global climate change and food security, Science, 2004, vol. 304, pp. 1623–1627.
Lemenih, M., Olsson, M., and Karltun, E., Comparison of soil attributes under Cupressus lusitanica and Eucalyptus saligna established on abandoned farmlands with continuously cropped farmlands and natural forest in Ethiopia, For. Ecol. Manage., 2004, vol. 195, pp. 57–67.
Leps, J. and Smilauer, P., Multivariate Analysis of Ecological Data using CANOCO, Cambridge: Cambridge Univ. Press, 2005.
Le Quere, C., Raupach, M.R., Canadell, J.G., Marland, G., Bopp, L., and Ciais, P., Trends in the sources and sinks of carbon dioxide, Nat. Geosci., 2009, vol. 2, pp. 831–836.
Li, Q., Zhou, D., Jin, Y., Wang, M., Song, Y., and Li, G., Effects of fencing on vegetation and soil restoration in a degraded alkaline grassland in northeast China, J. Arid Land, 2014, vol. 6, no. 4, pp. 478–487.
Liu, M.Y., Chang, Q.R., Qi, Y.B., Liu, J., and Chen, T., Aggregation and soil organic carbon fractions under different land uses on the tableland of the Loess Plateau of China, Catena, 2014, vol. 115, pp. 19–28.
MacDicken, K.G., A Guide to Monitoring Carbon Storage in Forestry and Agroforestry Projects, Little Rock, AR: Winrock Int. Inst. Agric. Dev., 1997.
Manzano, M.G. and Navar, J., Processes of desertification by goats overgrazing in the Tamaulipan thornscrub (matorral) in north-eastern Mexico, J. Arid Environ., 2000, vol. 44, no. 1, pp. 1–17.
Martinez-Mena, M., Lopez, J., Almagro, M., Boix-Fayos, V., and Albaladejo, J., Effect of water erosion and cultivation on the soil carbon stock in a semiarid area of south-east Spain, Soil Tillage Res., 2008, vol. 99, pp. 119–129.
Marvie-Mohadjer, M.M.R., Silviculture, Tehran: Univ. of Tehran Press, 2005.
Materechera, S.A., Influence of agricultural land use and management practices on selected soil properties of a semi-arid savanna environment in South Africa, J. Arid Environ., 2014, vol. 102, pp. 98–103.
Meng, Q., Fu, B., Tang, X., and Ren, H., Effect of land use on phosphorus loss in the hilly area of the Loess Plateau, China, Environ. Monit. Assess., 2008, vol. 139, pp. 195–204.
Murty, D., Kirschbaum, M.F., Mcmurtrie, R.E., and Mcgilvray, H., Does conversion of forest to agricultural land change soil carbon and nitrogen? A review of the literature, Global Change Biol., 2002, vol. 8, pp. 105–123.
Navidi, M.N., Sarmadian, F., and Mahmoodi, Sh., Studying the effects of land use change on soil physical and chemical quality indicators of surface horizons in rangelands of eastern Qazvin province, J. Range Watershed Manage., 2009, vol. 62, no. 2, pp. 299–310.
Gharmakher, N.H. and Maramaei, M., Effects of land use changes on soil properties (case study: the Kechik catchment), J. Soil Manage. Sustainable, 2011, vol. 1, no. 2, pp. 81–96.
Olsen, S.R. and Sommers, L.E., Phosphorus, in Methods of Soil Analysis, Part 2: Chemical and Microbiological Properties, Page, A.L., Ed., Madison, WI: Am. Soc. Agron., Soil Sci. Soc. Am., 1982, pp. 403–430.
Otto, R., Krusi, B.O., and Kienast, F., Degradation of an arid coastal landscape in relation to land use change in Southern Tenerife (Canary Island), J. Arid Environ., 2007, vol. 70, pp. 527–539.
Page, A.L., Methods of Soil Analysis, Madison, WI: Am. Soc. Agron., Soil Sci. Soc. Am., 1992.
Pei, S.F., Fu, H., and Wan, C.G., Changes in soil properties and vegetation following exclosure and grazing in degraded Alxa desert steppe of Inner Mongolia, China, Agric., Ecosyst. Environ., 2008, vol. 124, no. 1, pp. 33–39.
Piñeiro, G., Paruelo, J.M., and Oesterheld, M., Potential long-term impacts of livestock introduction on carbon and nitrogen cycling in grasslands of Southern South America, Global Change Biol., 2006, vol. 12, pp. 1267–1284.
Rezapour, S., Response of some soil attributes to different land use types in calcareous soils with Mediterranean type climate in north-west of Iran, Environ. Earth Sci., 2014, vol. 71, pp. 2199–2210.
Rubio, R.W. and Bochet, E., Desertification indicators as diagnosis criteria for desertification risk assessment in Europe, J. Arid Environ., 1998, vol. 39, no. 2, pp. 113–120.
Sadegh, H.R., Vangah, G.B., and Safaian, N., Comparison between effects of open grazing and manual harvesting of cultivated summer rangelands of Northern Iran on infiltration, runoff and sediment yield, Land Degrad. Dev., 2007, vol. 18, pp. 608–620.
Sagheb-Talebi, K.H., Sajedi, T., and Yazdian, F., Forests of Iran: Technical Publication No. 339, Tehran: Res. Inst. For. Rangelands, 2004.
Salardini, A.A., Soil Fertility, Tehran: Univ. of Tehran Press, 1995.
Salehi, A., Livelihood dependency and management on semiarid oak forests (the case of southern Zagros, Iran), PhD Thesis, Uppsala: Swed. Univ. Agric. Sci., 2009, p. 21.
Schneider, L.C. and Pontius, R.G., Modeling land-use change in the Ipswich watershed, Massachusetts, USA, Agric. Ecosyst. Environ., 2001, vol. 85, pp. 83–94.
Shrestha, G. and Stahla, P.D., Carbon accumulation and storage in semi-arid sagebrush steppe: effects of long-term grazing exclusion, Agric. Ecosyst. Environ., 2008, vol. 125, pp. 173–181.
Singh, R.S., Tripathi, N., and Singh, S.K., Impact of degradation on nitrogen transformation in a forest ecosystem of India, Environ. Monit. Assess., 2007, vol. 125, pp. 165–173.
Stolt, M.H., Baker, J.C., and Simpson, T.W., Soil-landscape relationships in Virginia: II. Reconstruction analysis and soil genesis, Soil Sci. Am. J., 1993, vol. 57, pp. 422–428.
Su, Y.Z., Li, Y.L., and Cui, J.Y., Influences of continuous grazing and livestock exclusion on soil properties in a degraded sandy grassland, Inner Mongolia, Northern China, Catena, 2005, vol. 59, no. 3, pp. 267–278.
Tate, K.R., Ross, D.J., Saggar, S., Hedley, C.B., Dando, J., Singh, B.K., and Lambie, S.M., Methane uptake in soils from Pinus radiata plantations, a reverting shrub land and adjacent pastures: effects of land use change, and soil texture, water and mineral nitrogen, Soil Biol. Biochem., 2007, vol. 39, pp. 1437–1449.
Thomas, G.W., Exchangeable cations, in Methods of Soil Analysis, Part 2: Chemical and Microbiological Properties, Page, A.L., Miller, R.H., and Keeney, D.R., Eds., Madison, WI: Am. Soc. Agron., Soil Sci. Soc. Am., 1982, pp. 159–166.
Tilman, D., Fargione, J., Wolff, B., d’Antonio, C., Dobson, A., Howarth, R., Schindler, D., Schlesinger, W., Simberloff, D., and Swackhamer, D., Forecasting agriculturally driven environmental change, Science, 2001, vol. 292, pp. 281–284.
UNEP 1993-94: Environmental data report, in TERI Report No. 97/ED/52, New Delhi, 1997.
van Veen, J.A. and Kuikman, P.J., Soil structure aspects of decomposition of organic matter by microorganisms, Biochemistry, 1990, vol. 11, pp. 213–233.
Wang, S., Wilkes, A., Zhang, Z., Chang, X., Lang, R., Wang, Y., and Niu, H., Management and land use change effects on soil carbon in northern China’s grasslands: a synthesis, Agric., Ecosyst. Environ., 2011, vol. 142, pp. 329–340.
Wang, H., Guan, D., Zhang, R., Chen, Y., Hu, Y., and Xiao, L., Soil aggregates and organic carbon affected by the land use change from rice paddy to vegetable field, Ecol. Eng., 2014, vol. 70, pp. 206–211.
Wischmeier, W.H. and Smith, B.D., Prediction Rainfall Erosion Losses: A Guide for Conservation Planning Agriculture, Agriculture Handbook no. 537, Washington, DC: US Dep. Agric., 1978.
Wu, G.L., Du, G.Z., Liu, Z.H., and Thirgood, S., Effect of fencing and grazing on a Kobresia-dominated meadow in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau, Plant Soil, 2009, vol. 319, nos. 1–2, pp. 115–126.
Yang, J., Liu, J., Hu, X., Li, X., Wang, Y., and Li, H., Changes of soil organic carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus concentrations under different land uses in marshes of Sanjiang Plain, Acta Ecol. Sin., 2013, vol. 33, pp. 332–337.
Yousefifard, M., Khademi, H., and Jalalian, A., Decline in soil quality as a result of land use change in Cheshmeh Ali region, Chaharmahal Bakhtiari Province, J. Agric. Sci. Nat. Resour., 2007, vol. 14, no. 1, pp. 28–38.
Yuksek, T., Kurdoglu, O., and Yuksek, F., The effects of land use changes and management types on surface soil properties in Kafkasor protected area in Artvin, Turkey, Land Degrad. Dev., 2010, vol. 21, pp. 582–590.
Zahedi, G.H., Relation between Vegetation and Characteristics in a Mixed Hard Wood Stand, Ghent: Ghent Univ., 1998.
Zhao, W.Z., Xiao, H.L., Liu, Z.M., and Li, J., Soil degradation and restoration as affected by land use change in the semiarid Bashang area, northern China, Catena, 2005, vol. 59, pp. 173–186.
Zhao, Y., Xu, X., Darilek, J.L., Huang, B., Sun, W., and Shi, X., Spatial variability assessment of soil nutrients in an intense agricultural area, a case study of Rugao County in Yangtze River Delta Region China, Environ. Geol., 2009, vol. 57, pp. 1089–1102.
Zucca, C., Canu, A., and Previtali, F., Soil degradation by land use change in an agro pastoral area in Sardinia (Italy), Catena, 2010, vol. 83, pp. 46–54.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors would like to extend their deepest gratitude to the Iranian University of Yasouj for the financial support and assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests. The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Statement on the welfare of humans or animals. This article does not contain any studies involving animals performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jarideh, S., Alvaninezhad, S., Gholami, P. et al. Soil Properties and Soil Organic Carbon Stock Changes Resulted from Deforestation in a Semi-arid Region of Zagros Forests, Iran. Arid Ecosyst 11, 18–26 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1134/S2079096121010078
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S2079096121010078