Abstract
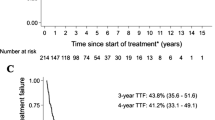
Lymphoma that on morphology appear blastoid or intermediate between DLBCL and BL but who lack myc and bcl-2 and/or bcl-6 rearrangements are grouped under high grade B-cell lymphoma, not otherwise specified (HGBL, NOS). Only a few studies have yet compared the outcome of HGBL, NOS treated with different chemo-immunotherapy regimens. HGBL, NOS patients were analyzed retrospectively, who were treated with CHOP or DAEPOCH regimens every 21 days for six cycles with or without rituximab. The primary clinical objective was progression free survival. One and two year PFS rates were 29.4% and 20.6% for the CHOP arm and, 65.2% and 47.8% for the DAEPOCH arm respectively. There was statistically significant difference in mean PFS between the arms (DAEPOCH vs CHOP: 19.7 months vs 12.8 months; HR = 0.44, p = 0.02, 95% CI: 0.22–0.88). One and two year OS rates were 91.1% and 20.5% for the CHOP arm and 95.6% and 60.8% for the DAEPOCH arm respectively. Mean OS was significantly better for DAEPOCH arm (28.1 months vs 20.7 months: HR = 0.43, p = 0.03, 95% CI: 0.20–0.92). Grade 3 and 4 hematological and non-hematological toxicities were more common in DAEPOCH arm. There were 2 treatment related deaths, 1 in each arm (4.3% for DAEPOCH vs 2.9% for CHOP). HGBL, NOS is a heterogeneous group of aggressive lymphoma associated with early relapse in nearly half of the cases. Intensive regimens like DAEPOCH is associated with improved outcome in terms of PFS and OS. Though toxicities are more with DAEPOCH, they are manageable and treatment related mortality is low.




Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of Data and Material
The datasets used and analyzed during the current study are available from the first or corresponding author on request.
References
Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Pileri SA et al (2016) The 2016 revision of the World Health Organization classification of lymphoid neoplasms. Blood 127(20):2375–2390. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2016-01-643569
Bartlett NL, Wilson WH, Jung SH et al (2019) Dose-adjusted EPOCH-R compared with R-CHOP as frontline therapy for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: clinical outcomes of the phase III intergroup Trial Alliance/CALGB 50303. J Clin Oncol 37(21):1790–1799. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.18.01994
Wästerlid T, Brown PN, Hagberg O et al (2013) Impact of chemotherapy regimen and rituximab in adult burkitt lymphoma: a retrospective population-based study from the nordic lymphoma group. Ann Oncol 24(7):1879–1886. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdt058
Oosten LEM, Chamuleau MED, Thielen FW et al (2018) Treatment of sporadic burkitt lymphoma in adults, a retrospective comparison of four treatment regimens. Ann Hematol 97(2):255–266. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-017-3167-7
Petrich AM, Gandhi M, Jovanovic B et al (2014) Impact of induction regimen and stem cell transplantation on outcomes in double-hit lymphoma: a multicenter retrospective analysis. Blood 124(15):2354–2361. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2014-05-578963
Howlett C, Snedecor SJ, Landsburg DJ et al (2015) Front-line, dose-escalated immunochemotherapy is associated with a significant progression-free survival advantage in patients with double-hit lymphomas: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Haematol 170(4):504–514. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjh.13463
Rush J, Sehgal AR, Roth CG (2016) Michael Boyiadzis; The effect of therapy on high grade B cell lymphoma, not otherwise specified and outcomes in comparison with double hit lymphoma. Blood 128(22):4224. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood.V128.22.4224.4224
Li J, Liu X, Yao Z, Zhang M (2020) High-Grade B-cell lymphomas, not otherwise specified: a study of 41 cases. Cancer Manag Res. 13(12):1903–1912. https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S243753.PMID:32214848;PMCID:PMC7082796
Cerhan JR, Link BK, Habermann TM et al (2017) Cohort profile: the lymphoma specialized program of research excellence (SPORE) Molecular epidemiology resource (MER) cohort study. Int J Epidemiol 46(6):1753–1754i. https://doi.org/10.1093/ije/dyx119
Funding
No external funding was taken for the study and authors have no relationships with any industry.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
LAJ conceived the idea and supervised the study and the findings. LM and KS retrieved the data from the individual patient files. LM analyzed the data, and wrote the manuscript. All the authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Ethical Approval
Ethical approval for the study has been taken from the institute ethical committee.
Consent to Participate
Consent for participation in clinical study was taken from all the patients.
Consent for Publication
Consent for publication of clinical data had been taken from all the patients.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moharana, L., Dasappa, L., Babu, S. et al. Comparison Between CHOP and DAEPOCH with or Without Rituximab in Adult High Grade B Cell Lymphoma, Not Otherwise Specified; A Retrospective Study From a Tertiary Cancer Hospital in South India. Indian J Hematol Blood Transfus 38, 15–23 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12288-021-01427-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12288-021-01427-8