Abstract
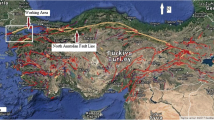
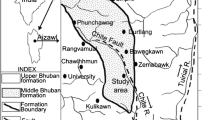
A study involving soil radon monitoring using RAD-7 instrument was carried out near Balakot-Bagh (B-B) Fault line hit by a 7.6 magnitude earthquake in October 2005. The study aimed to determine the spatial distribution of soil radon gas levels and the relationship between the soil radon gas and fracture density. Eleven soil samples were collected near the fault line, and 56 more samples (fourteen each from the adjoining district/area). Field measurements were made in the summer season of 2013, as a part of continuous measurement for regular monitoring the area for radon emanation and for observing the anomalies with previous values. The study area is located in Lesser Himalayas, North Pakistan, the Balakot–Bagh (B–B) fault in the Hazara–Kashmir Syntaxis. Soil gas radon concentrations were found higher near the Balakot-Bagh Fault line with an average value of 11.9\({\text{kBq}}\;{{\text{m}}^{ - 3}}\) compared to other sites of the study area with an average value of around 6.5 \({\text{kBq}}\;{{\text{m}}^{ - 3}}\). The radon value near the fault line is 70% higher as compared to the surrounding area.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali N, Khan EU, Akhter P, Khattak NU, Khan F, Rana MA (2011) The effect of air mass origin on the ambient concentrations of 7Be and 210Pb in Islamabad, Pakistan. J Environ Radioact 102(1):35–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvrad.2010.08.010
Al-Jarallah MI, Rehman F, Abdallah K (2008) Comparative study of short- and long-term indoor radon measurements. Radiat Meas 43:471–473
Bilham R (2005) The Kashmir earthquake. Web report: http://cires.calorado.edu/∼bilham/Kashmir%202005.html
Calkins JA, Offield TW, Abdullah SKM, Ali ST (1975) Geology of the southern Himalaya in Hazara, Pakistan, and adjacent areas. US Geol Surv Prof Paper 716:29
Cevik U, Kara A, Celik N, Karabidak M, Celik A (2011) Radon survey and exposure assessment in Karaca and Cal caves, Turkey. Water Air Soil Pollut 214:461–469
DiPietro JA (1991) Metamorphic pressure–temperature conditions of Indian plate rocks south of the main mantle thrust, Lower Swat, Pakistan. Tectonics 10:742–757
DiPietro JA, Pogue KR (2004) Tectonostratigraphic subdivisions of the Himalaya: a view from the west. Tectonics 23:TC5001. https://doi.org/10.1029/2003TAC001554
DiPietro JA, Pogue KR, Hussain A, Ahmad I (1999) Geologic map of the Indus syntaxis and surrounding area, northwest Himalaya, Pakistan, map, plate 1. Geol Soc Am Spec Pap 328:159–178
US EPA (2004) A citizen guide to radon: the guide to protecting yourselfand your family from radon. EPA, Washington
Hussain A, DiPietro JA, Pogue KR, Ahmad I (2004a) Geological map of the 43B degree sheet, NWFP, Pakistan. In: Geological Survey of Pakistan Degree Sheet Map Series Geological Map 11, 1:250,000
Hussain SH, Haq I, Hussain A (2004b) Geological map of the Khuiratta area, District Kotli, AJK: Geol. Survey of Pakistan Geological Map Series v, VI, no. 27, Sheet No. 43 K/3, 1:50,000
IARC (1988) Monographs on the evaluation of carcinogenic risk to humans, vol 43. IARC Press, Lyon, p 33
ICRP International Commission on Radiological Protection (2007) The 2007 recommendations of the international commission onradiological protection ICRP Publication 103. Ann ICRP 37:1–332
Kaneda H, Nakata T, Tsutsumi H, Kondo H, Sugito N, AwataY ASS, Majid A, Khattak W, Awan AA, Yeats RS, Hussain A, Ashraf M, Wesnousky SG, Kausar AB (2008) Surface rupture of the 2005 Kashmir, Pakistan, earthquake, and its active tectonic implications. Bull Seismol Soc Am. https://doi.org/10.1785/0120070073
Khan F, Ali N, Khan EU, Khattak NU, Khan K (2010) Radon monitoring in water sources of Balakot and Mansehra cities lying on a geological fault line. Radit Protect Dosim 138(2):174–179
Kumahara Y, Nakata T (2006) Active faults in the epicentral area of the 2005 Pakistan earthquake, vol 41. Hiroshima University Research Center for Regional Geography, Hiroshima, p 54
Latif MA (1974) A Cambrian age for the Abbottabad Group of Hazara, Pakistan. Geol Bull Punjab Univ 10:1–20
Martinez T, Navarrete M, Cabrera L, Gonzalez P, Ramirez A (2001) Relationship between short and long term radon measurements. Radiat Phys Chem 61:687–688
Miles JCH (2001) Temporal variation of radon levels in houses and implications for radon measurement strategies. Radiat Protect Dosim 93:369–375
Molnar P, Tapponnier P (1975) Cenozoic tectonics of Asia: efforts of a continental collision. Science 189:419–426
Mona Lisa KAA, Khwaja AA, Jan Q (2007) Seismic hazard assessment of the NW Himalayan fold-and-thrust belt, Pakistan, using probabilistic approach. J Earthq Eng 11:257–301
Nakata T, Otsuki K, Khan S (1990) Active faults, stress field and plate motion along the Indo-Eurasian plate boundary. Tectonophysics 181:83–95
Nielson KK, Rogers VC, Rogers V, Holt RB (1994) The RAETRAD model of radon generation and transport from soils into slab-on-grade houses. Health Phys 67:363–377
Pogue KR, Wardlaw BR, Harris AG, Hussain A (1992) Paleozoic stratigraphy of the Peshawar basin, Pakistan: correlations and implications. Geol Soc Am Bull 104:915–927
Rafique M, Rahman SU, Nasir T, Matiullah M (2011) Radiation doses due to indoor radon exposure before and after 2005-earthquake in the dwellings of Muzaffarabad and Jhelum valley, Azad Kashmir, Pakistan. Indoor Built Environ 20:259–264
Rahman S, Matiullah GBM (2010) Comparison of seasonal and yearly average indoor radon levels using CR-39 detectors. Radiat Meas 45:247–252
Richard C, Rebers PA (1991) Radon, radium and uranium in drinking water. Lewis Publishers, Inc., Chelsea, pp 48–118 (ISBN 0-87371-207-2)
Sapkota SN, Bollinger L, Klinger L, Tapponnier P, Gaudemer Y, Tewari D (2013) Primary surface ruptures of the great Himalayan earthquakes in 1934 and 1255. Nat Geosci 6:71–76
Serra O (1984) Fundamentals of well-log interpretation former Chef du Service DhgraphiesDifferkes a la Direction Exploration de la SNEA (P), Pau, France and Geological Interpretation Development Manager. Schlumberger Technical Services Inc., Singapore
Sesana L, Begnini S (2004) Hourly indoor radon measurement in a research house. Radiat Protect Dosim 112:277–279
Thakur VC (2008) Active tectonics of the Himalaya. J Geol Soc India 66:227–258
Wadia DN (1931) The syntaxis of the north–west Himalaya—its rocks, tectonics, and orogeny. Rec Geol Surv India 65:189–220
Wheeler BR, Bufe CG, Johnson ML, Dart RL, Norton GA (2005) Seismotectonic map of Afghanistan, with annotated bibliography. USGS Open File report
Yeats RS, Hussain A (1987) Timing of structural events in the Himalayan foothills of northwestern Pakistan. Geol Soc Am Bull 99:161–176
Yeats RS, Kausar AB, Nakata T (2006) Conferees examine deadly 2005 Kashmir earthquake. Eos 87:115
UNSCEAR (2000) Effects of ionizing radiation. In: Report of the United Nations scientific committee on the effects of atomic radiation report to the general assembly, with scientific annexes, United Nations, New York
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khan, F., Khattak, S.A., Wazir, Z. et al. Spatial distribution of radon concentrations in Balakot-Bagh (B–B) Fault Line and adjoining areas, Lesser Himalayas, North Pakistan. Environ Earth Sci 80, 291 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-021-09569-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-021-09569-8