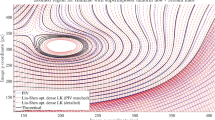
Abstract
In this study, we propose a novel optical flow formulation for estimating high-accuracy velocity fields from tracer particle image sequences. According to the Helmholtz velocity decomposition theorem, the proposed optical flow method decomposes the two-dimensional velocity field into four components: translation motion, linear distortion motion, shear distortion motion and rotation motion. In this context, regularization terms for different motion components are designed, which have a reasonable physical interpretation for the flow characteristics of the fluid. Subsequently, we design specific regularization parameters for the corresponding regularization terms according to the flow characteristics of the motion components. These regularization parameters can be adaptively adjusted with changes in the image space and velocity field. In addition, the data term of the optical flow formulation is based on the projected-motion equation derived from the continuity equation, which maintains the compressibility of the fluid in the two-dimensional plane. Velocity fields are estimated from synthetic tracer particle images and hypersonic experimental image sequences, and the velocity results are compared to those of an advanced cross-correlation-based PIV method and previous advanced optical flow methods. The results and comparisons indicate that the proposed method shows good performance and high measurement accuracy when acquiring compressible flow structures from fluid measurements.
Graphic abstract











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adrian RJ, Westerweel J (2011) Particle image velocimetry. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Astarita T (2008) Analysis of velocity interpolation schemes for image deformation methods in PIV. Exp Fluids 45(2):257–266
Astarita T (2009) Adaptive space resolution for PIV. Exp Fluids 46(6):1115
Becker F, Wieneke B, Petra S, Schröder A, Schnörr C (2012) Variational adaptive correlation method for flow estimation. IEEE Trans Image Process 21(6):3053–3065
Bhatia H, Norgard G, Pascucci V, Bremer PT (2013) The Helmholtz-Hodge decompositiona survey. IEEE Trans Vis Comput Graph 19(8):1386–1404
Cai S, Mémin E, Dérian P, Xu C (2018) Motion estimation under location uncertainty for turbulent fluid flows. Exp Fluids 59(1):8
Carlier J (2005) Second set of fluid mechanics image sequences. European Project “Fluid Image Analysis and Description” (FLUID). http://www.fluid.irisa.fr
Carlier J, Wieneke B (2005) Report 1 on production and diffusion of fluid mechanics images and data. Fluid project deliverable 1.2. European Project “Fluid Image Analysis and Description” (FLUID). http://www.fluid.irisa.fr
Cassisa C, Simoens S, Prinet V, Shao L (2011) Subgrid scale formulation of optical flow for the study of turbulent flow. Exp Fluids 51(6):1739–1754
Chen X, Zillé P, Shao L, Corpetti T (2015) Optical flow for incompressible turbulence motion estimation. Exp Fluids 56(1):8
Corpetti T, Mémin E, Pérez P (2002) Dense estimation of fluid flows. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 24(3):365–380
Corpetti T, Heitz D, Arroyo G, Mémin E, Santa-Cruz A (2006) Fluid experimental flow estimation based on an optical-flow scheme. Exp Fluids 40(1):80–97
Corpetti T, Mémin E, Pérez P (2000) Estimating fluid optical flow. In: Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Pattern Recognition, IEEE, vol 3, pp 1033–1036
Dérian P, Héas P, Herzet C, Mémin E (2013) Wavelets and optical flow motion estimation. Numer Math Theory Methods Appl 6(1):116–137
Dérian P, Héas P, Herzet C, Mémin E (2011) Wavelet-based fluid motion estimation. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Scale Space and Variational Methods in Computer Vision, Springer, pp 737–748
Drulea M, Nedevschi S (2011) Total variation regularization of local-global optical flow. In: Proceedings of the 14th International IEEE Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems, IEEE, pp 318–323
Heitz D, Héas P, Mémin E, Carlier J (2008) Dynamic consistent correlation-variational approach for robust optical flow estimation. Exp Fluids 45(4):595–608
Heitz D, Mémin E, Schnörr C (2010) Variational fluid flow measurements from image sequences: synopsis and perspectives. Exp Fluids 48(3):369–393
Horn BK, Schunck BG (1981) Determining optical flow. Artif Intell 17(1–3):185–203
Kadri-Harouna S, Dérian P, Héas P, Mémin E (2013) Divergence-free wavelets and high order regularization. Int J Comput Vision 103(1):80–99
Kähler CJ, Scharnowski S, Cierpka C (2012) On the resolution limit of digital particle image velocimetry. Exp Fluids 52(6):1629–1639
Kohlberger T, Mémin E, Schnörr C (2003) Variational dense motion estimation using the Helmholtz decomposition. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Scale-Space Theories in Computer Vision, Springer, pp 432–448
Lin WYD, Cheng MM, Lu J, Yang H, Do MN, Torr P (2014) Bilateral functions for global motion modeling. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Springer, pp 341–356
Liu T (2017) Openopticalfow: an open source program for extraction of velocity felds from fow visualization images. J Open Res Softw 5(1):29
Liu T, Shen L (2008) Fluid flow and optical flow. J Fluid Mech 614:253–291
Liu T, Merat A, Makhmalbaf M, Fajardo C, Merati P (2015) Comparison between optical flow and cross-correlation methods for extraction of velocity fields from particle images. Exp Fluids 56(8):166
Liu W, Ribeiro E (2011) A higher-order model for fluid motion estimation. In: Proceedings of the International Conference Image Analysis and Recognition, Springer, pp 325–334
Lu J, Yang H, Zhang Q, Yin Z (2019) A field-segmentation-based variational optical flow method for PIV measurements of nonuniform flows. Exp Fluids 60(9):142
Lu J, Yang H, Zhang Q, Yin Z (2019) PIV measurements of hypersonic laminar flow over a compression ramp. In: Proceedings of the 13th International Symposium on Particle Image Velocimetry, pp 797–806
McWilliams JC (2006) Fundamentals of geophysical fluid dynamics. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Quénot GM, Pakleza J, Kowalewski TA (1998) Particle image velocimetry with optical flow. Exp Fluids 25(3):177–189
Raffel M, Willert CE, Scarano F, Kähler CJ, Wereley ST, Kompenhans J (2018) Particle image velocimetry: a practical guide. Springer, Berlin
Ruhnau P, Schnörr C (2007) Optical stokes flow estimation: an imaging-based control approach. Exp Fluids 42(1):61–78
Ruhnau P, Kohlberger T, Schnörr C, Nobach H (2005) Variational optical flow estimation for particle image velocimetry. Exp Fluids 38(1):21–32
Sánchez J, Monzón López N, Salgado de la Nuez AJ (2013) Robust optical flow estimation. IPOL J Image Process Online 3:252–270
Schmidt B, Sutton J (2019) High-resolution velocimetry from tracer particle fields using a wavelet-based optical flow method. Exp Fluids 60(3):37
Schmidt B, Sutton J (2020) Improvements in the accuracy of wavelet-based optical flow velocimetry (wOFV) using an efficient and physically based implementation of velocity regularization. Exp Fluids 61(2):32
Seong JH, Song MS, Nunez D, Manera A, Kim ES (2019) Velocity refinement of PIV using global optical flow. Exp Fluids 60(11):174
Simonini A, Theunissen R, Masullo A, Vetrano MR (2019) PIV adaptive interrogation and sampling with image projection applied to water sloshing. Exp Therm Fluid Sci 102:559–574
Sun D, Roth S, Black MJ (2014) A quantitative analysis of current practices in optical flow estimation and the principles behind them. Int J Comput Vis 106(2):115–137
Theunissen R, Scarano F, Riethmuller M (2007) An adaptive sampling and windowing interrogation method in PIV. Meas Sci Technol 18(1):275–287
Theunissen R, Scarano F, Riethmuller ML (2010) Spatially adaptive PIV interrogation based on data ensemble. Exp Fluids 48(5):875–887
Westerweel J, Elsinga GE, Adrian RJ (2013) Particle image velocimetry for complex and turbulent flows. Annu Rev Fluid Mech 45:409–436
Yu K, Xu J (2016) Adaptive PIV algorithm based on seeding density and velocity information. Flow Meas Instrum 51:21–29
Yuan J, Schnörr C, Mémin E (2007) Discrete orthogonal decomposition and variational fluid flow estimation. J Math Imaging Vis 28(1):67–80
Zhong Q, Yang H, Yin Z (2017) An optical flow algorithm based on gradient constancy assumption for PIV image processing. Meas Sci Technol 28(5):055208
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51875228), the National Key R&D Program of China (Grant No. 2020YFA0405700), and the National Defense Science and Technology Innovation Special Zone Project (Grant No. 193-A14-202-01-23).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, J., Yang, H., Zhang, Q. et al. An accurate optical flow estimation of PIV using fluid velocity decomposition. Exp Fluids 62, 78 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00348-021-03176-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00348-021-03176-w