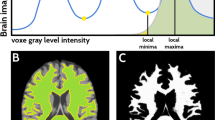
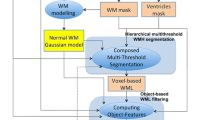
Abstract
In this study, we perform a comparative analysis of automated image segmentation of subcortical structures in the elderly brain. Manual segmentation is very time-consuming and automated methods are gaining importance as a clinical tool for diagnosis. The two most commonly used software libraries for brain segmentation -FreeSurfer and FSL- are put to work in a large dataset of 4,028 magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans collected for this study. We find a lack of linear correlation between the segmentation volume estimates obtained from FreeSurfer and FSL. On the other hand, FreeSurfer volume estimates tend to be larger thanFSL estimates of the areas putamen, thalamus, amygdala, caudate, pallidum, hippocampus, and accumbens. The characterization of the performance of brain segmentation algorithms in large datasets as the one presented here is a necessary step towards partially or fully automated end-to-end neuroimaging workflow both in clinical and research settings.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andravizou, A., Dardiotis, E., Artemiadis, A., Sokratous, M., Siokas, V., Tsouris, Z., Aloizou, A. -M., Nikolaidis, I., Bakirtzis, C., Tsivgoulis, G., & et al. (2019). Brain atrophy in multiple sclerosis: mechanisms, clinical relevance and treatment options. Autoimmunity Highlights, 10(1), 7.
Azevedo, C. J., Cen, S. Y., Jaberzadeh, A., Zheng, L., Hauser, S. L., & Pelletier, D. (2019). Contribution of normal aging to brain atrophy in ms. Neurology-Neuroimmunology Neuroinflammation, 6(6), e616.
Beyer, M. K., Larsen, J. P., & Aarsland, D. (2007). Gray matter atrophy in parkinson disease with dementia and dementia with lewy bodies. Neurology, 69(8), 747–754.
Bug, W. (2005). The impact of the nih public access policy on literature informatics. Neuroinformatics, 3(2), 81–91.
Carlson, N. E., Moore, M. M., Dame, A., Howieson, D., Silbert, L. C., Quinn, J. F., & Kaye, J. A. (2008). Trajectories of brain loss in aging and the development of cognitive impairment. Neurology, 70(11), 828–833.
Cohen, J. (1988). Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences, 2nd edn. á/l.
Collier, D. C., Burnett, S. S., Amin, M., Bilton, S., Brooks, C., Ryan, A., Roniger, D., Tran, D., & Starkschall, G. (2003). Assessment of consistency in contouring of normal-tissue anatomic structures. Journal of Applied Clinical Medical Physics, 4(1), 17–24.
Dale, A., Fischl, B., & Sereno, M. I. (1999). Cortical surface-based analysis: i. Segmentation and surface reconstruction. NeuroImage, 9(2), 179–194.
Dale, A. M., & Sereno, M. I. (1993). Improved localizadon of cortical activity by combining eeg and meg with mri cortical surface reconstruction: a linear approach. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 5(2), 162–176. PMID 23972151.
de Flores, R., Joie, R. L., & Chetelat, G. (2015). Structural imaging of hippocampal subfields in healthy aging and Alzheimer’s disease. Neuroscience, 309, 29–50. Hippocampal vulnerability: from molecules to disease.
Desikan, R. S., Ségonne, F., Fischl, B., Quinn, B. T., Dickerson, B. C., Blacker, D., Buckner, R.L., Dale, A. M., Maguire, R. P., Hyman, B. T., Albert, M. S., & Killiany, R. J. (2006). An automated labeling system for subdividing the human cerebral cortex on mri scans into gyral based regions of interest. NeuroImage, 31(3), 968–980.
Despotović, I., Goossens, B., & Philips, W. (2015). Mri segmentation of the human brain: challenges, methods, and applications. Computational and mathematical methods in medicine.
Destrieux, C., Fischl, B., Dale, A., & Halgren, E. (2010). Automatic parcellation of human cortical gyri and sulci using standard anatomical nomenclature. NeuroImage, 53(1), 1–15.
Enzinger, C., Fazekas, F., Matthews, P. M., Ropele, S., Schmidt, H., Smith, S., & Schmidt, R. (2005). Risk factors for progression of brain atrophy in aging. Neurology, 64(10), 1704–1711.
Esteva, A., Chou, K., Yeung, S., Naik, N., Madani, A., Mottaghi, A., Liu, Y., Topol, E., Dean, J., & Socher, R. (2021). Deep learning-enabled medical computer vision. npj Digital Medicine, 4(1), 1–9.
Fernández-Blázquez, M. A., Noriega-Ruiz, B., Ávila Villanueva, M., Valentí-Soler, M., Frades-Payo, B., Ser, T. D., & Gómez-Ramírez, J. (2020). Impact of individual and neighborhood dimensions of socioeconomic status on the prevalence of mild cognitive impairment over seven-year follow-up. Aging & Mental Health, 0(0), 1–10. PMID 32067489.
Firbank, M. J., Barber, R., Burton, E. J., & O’Brien, J. T. (2008). Validation of a fully automated hippocampal segmentation method on patients with dementia. Human Brain Mapping, 29(12), 1442–1449.
Fischl, B., Salat, D. H., Busa, E., Albert, M., Dieterich, M., Haselgrove, C., van der Kouwe, A., Killiany, R., Kennedy, D., Klaveness, S., Montillo, A., Makris, N., Rosen, B., & Dale, A. M. (2002). Whole brain segmentation: automated labeling of neuroanatomical structures in the human brain. Neuron, 33, 341–355.
Fischl, B., Sereno, M. I., & Dale, A. (1999). Cortical surface-based analysis: Ii: inflation, flattening, and a surface-based coordinate system. NeuroImage, 9(2), 195–207.
Fischl, B., van der Kouwe, A., Destrieux, C., Halgren, E., Ségonne, F., Salat, D.H., Busa, E., Seidman, L.J., Goldstein, J., Kennedy, D., Caviness, V., Makris, N., Rosen, B., & Dale, A.M. (2004). Automatically parcellating the human cerebral cortex. Cerebral Cortex, 14(1), 11–22.
Fjell, A. M., McEvoy, L., Holland, D., Dale, A. M., & Walhovd, K. B. (2013). Brain changes in older adults at very low risk for Alzheimer’s disease. Journal of Neuroscience, 33(19), 8237–8242.
Fjell, A. M., Walhovd, K. B., Fennema-Notestine, C., McEvoy, L. K., Hagler, D. J., Holland, D., Brewer, J. B., & Dale, A. M. (2009). One-year brain atrophy evident in healthy aging. Journal of Neuroscience, 29(48), 15223–15231.
Fox, N., Jenkins, R., Leary, S., Stevenson, V., Losseff, N., Crum, W., Harvey, R. J., Rossor, M., Miller, D., & Thompson, A. (2000). Progressive cerebral atrophy in ms: a serial study using registered, volumetric mri. Neurology, 54(4), 807–812.
Fox, N. C., & Freeborough, P. A. (1997). Brain atrophy progression measured from registered serial mri: Validation and application to Alzheimer’s disease. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 7(6), 1069–1075.
FreeSurfer cortical reconstruction and parcellation process. (2017). Anatomical processing script: recon-all. https://surfer.nmr.mgh.harvard.edu/fswiki/recon-all, Last accessed on 2020-15-30.
FSL. (2017). Anatomical processing script: fsl_anat. https://fsl.fmrib.ox.ac.uk/fsl/fslwiki/fsl_anat, Last accessed on 2020-15-30.
Gado, M., Hughes, C. P., Danziger, W., & Chi, D. (1983). Aging, dementia, and brain atrophy: a longitudinal computed tomographic study. American Journal of Neuroradiology, 4(3), 699–702.
Gómez-Ramírez, J., Ávila-Villanueva, M., & Fernández-Blázquez, M.Á. (2020). Selecting the most important self-assessed features for predicting conversion to mild cognitive impairment with random forest and permutation-based methods. Scientific Reports, 10(1), 1–15.
Gronenschild, E. H. B. M., Habets, P., Jacobs, H. I. L., Mengelers, R., Rozendaal, N., van Os, J., & Marcelis, M. (2012). The effects of freesurfer version, workstation type, and macintosh operating system version on anatomical volume and cortical thickness measurements. PLOS ONE, 7(6), 1–13.
Hosny, A., Parmar, C., Quackenbush, J., Schwartz, L. H., & Aerts, H. J. W. L. (2018). Artificial intelligence in radiology. Nature Reviews Cancer, 18(8), 500–510.
Jack Jr, C.R., Bernstein, M. A., Fox, N. C., Thompson, P., Alexander, G., Harvey, D., Borowski, B., Britson, P. J., Whitwell, J.L., Ward, C., & et al. (2008). The Alzheimer’s disease neuroimaging initiative (adni): Mri methods. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging: An Official Journal of the International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 27(4), 685–691.
Jenkinson, M., Beckmann, C. F., Behrens, T. E., Woolrich, M. W., & Smith, S.M. (2012). Fsl. NeuroImage, 62(2), 782–790. 20 YEARS OF fMRI.
Kecskemeti, S. R., & Alexander, A. L. (2020). Test-retest of automated segmentation with different motion correction strategies: a comparison of prospective versus retrospective methods. NeuroImage, 209, 116494.
Klein, A., & Tourville, J. (2012). 101 labeled brain images and a consistent human cortical labeling protocol. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 6, 171.
Losseff, N., Wang, L., Lai, H., Yoo, D., Gawne-Cain, M., McDonald, W., Miller, D., & Thompson, A. (1996). Progressive cerebral atrophy in multiple sclerosis a serial mri study. Brain: A Journal of Neurology, 119(6), 2009–2019.
Makowski, C., Béland, S., Kostopoulos, P., Bhagwat, N., Devenyi, G.A., Malla, A.K., Joober, R., Lepage, M., & Chakravarty, M.M. (2018). Evaluating accuracy of striatal, pallidal, and thalamic segmentation methods: Comparing automated approaches to manual delineation. NeuroImage, 170, 182–198. Segmenting the Brain.
Mazurowski, M. A., Buda, M., Saha, A., & Bashir, M. R. (2019). Deep learning in radiology: an overview of the concepts and a survey of the state of the art with focus on mri. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 49(4), 939–954.
Miller, K. L., Alfaro-Almagro, F., Bangerter, N. K., Thomas, D. L., Yacoub, E., Xu, J., Bartsch, A. J., Jbabdi, S., Sotiropoulos, S. N., Andersson, J. L., & et al. (2016). Multimodal population brain imaging in the uk biobank prospective epidemiological study. Nature Neuroscience, 19(11), 1523–1536.
Morey, R. A., Petty, C. M., Xu, Y., Hayes, J. P., Wagner, H. R., Lewis, D. V., LaBar, K. S., Styner, M., & McCarthy, G. (2009). A comparison of automated segmentation and manual tracing for quantifying hippocampal and amygdala volumes. NeuroImage, 45(3), 855–866.
Morey, R. A., Selgrade, E. S., Wagner II, H.R., Huettel, S.A., Wang, L., & McCarthy, G. (2010). Scan-rescan reliability of subcortical brain volumes derived from automated segmentation. Human Brain Mapping, 31(11), 1751–1762.
O’Brien, J. T., Paling, S., Barber, R., Williams, E. D., Ballard, C., McKeith, I., Gholkar, A., Crum, W. R., Rossor, M. N., & Fox, N. C. (2001). Progressive brain atrophy on serial mri in dementia with lewy bodies, ad, and vascular dementia. Neurology, 56(10), 1386–1388.
Patenaude, B., Smith, S. M., Kennedy, D. N., & Jenkinson, M. (2011). A bayesian model of shape and appearance for subcortical brain segmentation. NeuroImage, 56(3), 907–922.
Peter, J., Scheef, L., Abdulkadir, A., Boecker, H., Heneka, M., Wagner, M., Koppara, A., Kloppel, S., & Jessen, F. (2014). Gray matter atrophy pattern in elderly with subjective memory impairment. Alzheimer’s and Dementia, 10(1), 99– 108.
Pini, L., Pievani, M., Bocchetta, M., Altomare, D., Bosco, P., Cavedo, E., Galluzzi, S., Marizzoni, M., & Frisoni, G. B. (2016). Brain atrophy in Alzheimer’s disease and aging. Ageing Research Reviews, 30, 25–48.
Rane, S., Plassard, A., Landman, B. A., Claassen, D. O., & Donahue, M. J. (2017). Comparison of cortical and subcortical measurements in normal older adults across databases and software packages. Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease Reports, 1, 59–70.
Reuter, M., & Fischl, B. (2011). Avoiding asymmetry-induced bias in longitudinal image processing. NeuroImage, 57(1), 19–21.
Reuter, M., Rosas, H. D., & Fischl, B. (2010). Highly accurate inverse consistent registration: a robust approach. NeuroImage, 53(4), 1181–1196.
Seixas, F. L., Débora, S., Saade, C., Conci, A., Souza, A., Tovar, F., & Bramati, I. (2010). Anatomical Brain mri segmentation methods: Volumetric assessment of the hippocampus. IWSSIP 2010–17 Th International conference on systems, signals and image processing; 2010 Jan 17–19.
Simpson, M. I. G., Woods, W. P., Prendergast, G., Johnson, S. R., & Green, G. G. R. (2012). Stimulus variability affects the amplitude of the auditory steady-state response. PLOS ONE, 7(4), 1–10.
Smith, S. M. (2002). Fast robust automated brain extraction. Human Brain Mapping, 17(3), 143–155.
Smith, S. M., Jenkinson, M., Woolrich, M. W., Beckmann, C. F., Behrens, T. E., Johansen-Berg, H., Bannister, P. R., Luca, M. D., Drobnjak, I., Flitney, D. E., Niazy, R. K., Saunders, J., Vickers, J., Zhang, Y., Stefano, N. D., Brady, J. M., & Matthews, P. M. (2004). Advances in functional and structural mr image analysis and implementation as fsl. NeuroImage, 23, S208 – S219. Mathematics in Brain Imaging.
Smith, S. M., Zhang, Y., Jenkinson, M., Chen, J., Matthews, P., Federico, A., & Stefano], N. D. (2002). Accurate, robust, and automated longitudinal and cross-sectional brain change analysis. NeuroImage, 17(1), 479–489.
Snowdon, D. A. (2003). Healthy aging and dementia: Findings from the nun study. Annals of Internal Medicine, 139(5 Part 2), 450–454.
Starmans, M. P., van der Voort, S. R., Tovar, J. M. C., Veenland, J. F., Klein, S., & Niessen, W. J. (2020). Chapter 18 - radiomics: Data mining using quantitative medical image features. In Zhou, S. K., Rueckert, D., & Fichtinger, G. (Eds.) Handbook of medical image computing and computer assisted intervention (pp. 429–456): Academic Press.
Thrall, J. H., Li, X., Li, Q., Cruz, C., Do, S., Dreyer, K., & Brink, J. (2018). Artificial intelligence and machine learning in radiology: Opportunities, challenges, pitfalls, and criteria for success. Journal of the American College of Radiology, 15(3 Part B), 504–508. Data Science: Big Data Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence.
Topol, E. (2019). Deep medicine: how artificial intelligence can make healthcare human again. Hachette UK.
Vollmer, T., Signorovitch, J., Huynh, L., Galebach, P., Kelley, C., DiBernardo, A., & Sasane, R. (2015). The natural history of brain volume loss among patients with multiple sclerosis: a systematic literature review and meta-analysis. Journal of the Neurological Sciences, 357(1-2), 8–18.
Wang, L., Swank, J. S., Glick, I. E., Gado, M. H., Miller, M. I., Morris, J. C., & Csernansky, J. G. (2003). Changes in hippocampal volume and shape across time distinguish dementia of the Alzheimer type from healthy aging. NeuroImage, 20(2), 667–682.
Woolrich, M.W., Jbabdi, S., Patenaude, B., Chappell, M., Makni, S., Behrens, T., Beckmann, C., Jenkinson, M., & Smith, S. M. (2009). Bayesian analysis of neuroimaging data in fsl. NeuroImage, 45(1, Supplement 1), S173 – S186. Mathematics in brain imaging.
Yan, C., Gong, B., Wei, Y., & Gao, Y. (2020). Deep multi-view enhancement hashing for image retrieval. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence.
Yang, H., Xu, H., Li, Q., Jin, Y., Jiang, W., Wang, J., Wu, Y., Li, W., Yang, C., Li, X., & et al. (2019). Study of brain morphology change in Alzheimer’s disease and amnestic mild cognitive impairment compared with normal controls. General Psychiatry, 32(2).
Zhang, Y., Brady, M., & Smith, S. (2001). Segmentation of brain mr images through a hidden markov random field model and the expectation-maximization algorithm. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 20 (1), 45–57.
Zhou, C., Guan, X. -J., Guo, T., Zeng, Q. -L., Gao, T., Huang, P. -Y., Xuan, M., Gu, Q. -Q., Xu, X. -J., & Zhang, M. -M. (2020). Progressive brain atrophy in parkinson’s disease patients who convert to mild cognitive impairment. CNS Neuroscience & Therapeutics, 26(1), 117–125.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the generous persons that volunteered to participate in the study and Fundación Reina Sofía for their support. The authors acknowledge funding from Ministerio de Ciencia, Innovación y Universidades (CONNECT-AD) RTI2018-098762-B-C31 and and Structural Funds ERDF (INTERREG V-A Spain-Portugal (POCTEP) Grant: 0348CIE6E).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Information Sharing Statement
Code and all data used in this research are publicly available on the Github repository under an Apache 2.0 license at https://github.com/grjd/automaticsegmentation. Part of the pre-processing code depends on FSL and FreeSurfer. Both software libraries are only licensed for non-commercial use and are freely available.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gomez-Ramirez, J., Quilis-Sancho, J. & Fernandez-Blazquez, M.A. A Comparative Analysis of MRI Automated Segmentation of Subcortical Brain Volumes in a Large Dataset of Elderly Subjects. Neuroinform 20, 63–72 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12021-021-09520-z
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12021-021-09520-z