Abstract
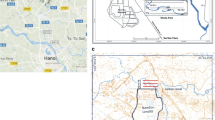
The degradation of MSW in landfills occurs naturally from the beginning of the disposal, during landfill operation and even after its closure, over a period of several years. The monitoring of closed landfills can be quite costly when done only by direct methods, especially in areas where technical and financial resources are restricted. This work presents a case study in the extreme south of Brazil that represents the vast majority of landfills in the country: public landfills, in small ditches with little resources. The geophysical survey sought to identify leachate accumulation zones and verify their chemical stability in relation to the geological environment from the joint analysis of the electrical resistivity and self-potential data. Data acquisition took place on the same date (02/2018), with results that reveal leachate generation areas (−60 mV and ~ 30 Ωm), leachate accumulation (−40 mV and ~ 20 Ωm) and areas with a predominance of inert waste (> 40 mV), where previously existing organic matter was practically degraded. The combined use of geoelectric methods to understand the degradation dynamics of organic matter in landfills allows for the recognition of active zones of leachate generation, information that supports chemical stabilization projects and site remediation.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbasi, T., Taussef, S. M., & Abbasi, S. A. (2012). Biogas energy. Springer.
ABEM. (2012). Terrameter LS, instruction manual. ABEM.
ABNT. ASSOCIAÇÃO BRASILEIRA DE NORMAS TÉCNICAS. NBR 13896. (1997). Aterros de resíduos não perigosos–Critérios para projeto, implantação e operação. ABNT.
Aizebeokhai, A. P., Olayinka, A. I., Singh, V. S., & Uhuegbu, C. C. (2011). Effectiveness of 3D geoelectrical resistivity imaging using parallel 2D profiles. Current Science, 6, 5623–5647.
Alvarez, P. J. J., & Illman, W. A. (2006). Bioremediation and natural attenuation process fundamentals and mathematical models. John Wiley and Sons.
Arora, T., Linde, N., Revil, A., & Castermant, J. (2007). Non-intrusive characterization of the redox potential of landfill leachate plumes from self-potential data. Journal of Contaminant Hydrogeology, 29, 274–292.
Ayolabi, E. A., Oluwatosin, L. B., & Ifekwuna, C. D. (2015). Integrates geopjysical and physicochemical assessment of Olushosun sanitary landfill site, southwest Nigeria. Arabian Journal of Geoscience, 8, 4101–4115.
Baird, C., & Cann, M. (2008). Environmental chemistry (4th ed.). W. H. Freeman and Company.
Beidou, X., Yonghai, J., Mingxiao, L., Yu, Y., & Caihong, H. (2016). Optimization of solid waste conversion process and risk control of groundwater pollution. Springer.
Berkowitz, B., Dror, I., & Yaron, B. (2014). Contaminant geochemistry–interaction and transport in the subsurface environment (2nd ed.). Springer.
BRASIL. (2010). Lei N° 12.305 de 02 de agosto de 2010-Política Nacional de Resíduos Sólidos. BRASIL.
Chambers, J. E., Kuras, O., Meldrum, P. I., Ogilvy, R. D., & Hollands, J. (2006). Electrical resistivity tomography applied to geologic, hydrogeologic, and engineering investigations at a former waste-disposal site. Geophysics, 71, 231–239.
Christensen, T. H. (2011). Solid waste technology and management. John Wiley and Sons.
Christensen, T. H., Kjeldsen, P., Bjerg, P. L., Jensen, D. L., Christensen, J. B., Baun, A., Albrechtsen, H. J., & Heron, G. (2001). Biogeochemistry of landfill leachate plumes. Applied Geochemistry, 16, 659.
Côrtes, A. R. P., Moreira, C. A., Veloso, D. I. K., Vieira, L. B., & Bergonzoni, F. A. (2016). Geoelectrical prospecting for a copper-sulfide mineralization in the Camaquã sedimentary basin, Southern Brazil. Geofisica Internacional. https://doi.org/10.19155/rgi20165531608
CPRM-Companhia de Pesquisa de Recursos Minerais. (1995). Geológicos Básicos do Brasil-Folha Cachoeira do Sul SH.22-Y-A. Estado do Rio Grande do Sul. Escala 1:250.000. CPRM.
CPRM-Companhia de Pesquisa de Recursos Minerais. (2000). Mapa de Geodiversidade do Estado do Rio Grande do Sul. CPRM.
De Carlo, L., Perri, M. T., Caputo, M. C., Deiana, R., Vurro, M., & Cassiani, G. (2013). Characterization of a dismissed landfill via electrical resistivity tomography and mise-à-lamasse method. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 98, 1.
Erdogan, R., & Zaimoglu, Z. (2015). The characteristics of phytoremediation of soil and leachate polluted by landfills. In N. Shiomi (Ed.), Advances in bioremediation of wastewater and polluted soil. Intech.
GEOSOFT. (2014). Oasis Montaj How to Guide. 2014. http://updates.geosoft.com/downloads/files/how-to-guides/Oasis_montaj_Gridding.pdf. Accessed 18 Mar 2018.
Giang, N. V., Kochanek, K., Vu, N. T., & Duan, N. B. (2018). Landfill leachate assessment by hidrological and geophysical data: case study NamSon, Hanoi, Vietnam. Journal of Material Cycles and Waste Management, 20, 1648–1662.
Helene, L. P. I., Moreira, C. A., & Carrazza, L. P. (2016). Applied geophysics on a soil contaminated site by chromium of a tannery in Motuca (SP). Revista Brasileira de Geofísica. https://doi.org/10.22564/rbgf.v34i3.825
Hung, T.-Y., Wang, L. K., & Shammas, N. K. (2014). Handbook of environment and waste management: land and groundwater pollution control. World Scientific.
IBGE. INSTITUDO BRASILEIRO DE GEOGRAFIA E ESTATÍSTICA. (2010). Demográfico 2010–Características Gerais da População. IBGE.
INMET. INSTITUTO NACIONAL DE METEOROLOGIA. (2018). Estação Meteorológica de Observação de Superfície Automática. Disponível em: http://www.inmet.gov.br/portal/index.php?r=estacoes/estacoesautomaticas. Accessed 18 Mar 2018.
Jouniaux, L., & Ishido, T. (2012). Electrokinetics in earth science. International Journal of Geophysics. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/286107
Justus, J. O., de Machado, M. L. A., & Franco, M. S. M. (1986). Geomorfologia. Folha SH22 Porto Alegre e parte das folhas SH21 Uruguaiana e SI22 Lagoa Mirim (pp. 313–404). IBGE.
Kearey, P., Brooks, M., & Hill, I. (2002). An introduction to geophysical exploration (3rd ed.). Wiley-Blackwell Science.
Knödel, K., Lange, G., & Voigt, H. J. (2007). Enviromental Geology: Handbook of fields methods and case studies. In M. Chi (Ed.), Hannover federal institute for geosciences and natural resources (p. 1357). Springer.
Loke, M. H., & Baker, R. D. (1996). Rapid least-squares inversion of apparent resistivity pseudosections by quasi-newton method. Geophysical Prospecting, 44, 131–152.
Machado, J. L. F., & Freitas, M. A. (2005). Projeto mapa hidrogeológico do Rio Grande do Sul: relatório final (p. 1). CPRM.
Maineult, A., Bernabé, Y., & Ackerer, P. (2006). Detection of advected, reacting redox fronts from self-potential measurements. Journal of Contaminant Hydrogeology, 86, 32–52.
Maurya, P. K., Ronde, V. K., Fiandaca, G., Balbarini, N., Auken, E., Bjerg, P. L., & Christensen, A. V. (2017). Detailed landfill leachate plume mapping using 2D and 3D electrical resistivity tomography–with correlation to ionic strength measured in screens. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 138, 1–8.
Meju, M. A. (2000). Geoelectrical investigation of old/abandoned, covered landfill sites in urban areas: model development with a genetic diagnosis approach. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 44(1), 115–150.
Moreira, C. A., Braga, A. C. O., Godoy, L. H., & Sardinha, D. S. S. (2013). Relationship between age of waste and natural electric potential generation in Sanitary Landfill. Geofísica Internacional, 52(4), 375–383.
Moreira, C. A., Helene, L. P. I., Nogara, P., & Ilha, L. M. (2018). Analysis of leaks from geomembrane in a sanitary landfill through models of electrical resistivity thomography in South Brazil. Environmental Earth Science, 77, 7.
Moreira, C. A., Lapola, M. M., & Carrara, A. (2016). Comparative analyzes among electrical resistivity tomography arrangements in the characterization of flow structure in free aquifer. Geofísica Internacional, 55(2), 119–129.
Morita, A. K. M., de Souza, P. N., Elis, V. R., & Wendland, E. (2020). Longterm geophysical monitoring of an abandoned dumpsite area in a Guarani Aquifer recharge zone. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconhyd.2020.103623
Naudet, V., Revil, A., & Bottero, J.-Y. (2003). Relationship between self-potential (SP) signals and redox conditions in contaminated groundwater. Geophysical Research Letters. https://doi.org/10.1029/2003GL018096
Nyquist, J. E., & Corry, C. E. (2002). Self-potential: The ugly duckling of environmental geophysics. The Leading Edge, 21(5), 446–451.
Park, S., Myeong-jong, Y., Jung-Ho, K., & Seung-Wook, S. (2016). Electrical resistivity imaging (ERI) monitoring for groundwater contamination in an uncontrolled landfill, South Korea. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 135, 1–7.
Porowska, D. (2016). Assessment of a degree of geochemical maturation and activity of a closed landfill site in Poland. Environmental Earth Science, 75, 331.
Raji, W. O., & Adeyoe, T. O. (2017). Geophysical mapping of contaminant leachate around a reclaimed open dumpsite. Journal of King Saud University Science, 29, 348–3359.
Rao, G. T., Rao, V. V. S. G., Padalu, G., Dhakate, R., & Sarma, V. S. (2014). Application of electrical resistivity tomography methods for delineation of groundwater contamination and potential zones. Arabian Journal Geoscience, 7, 1373–1384.
Reddy, P. J. (2011). Municipal solid waste management: processing, energy recovery, global examples. CRC Press.
Reinhart, D. R., & Al-Yousfi, B. A. (1996). The impact of leachate recirculation on municipal solid waste landfill operating characteristics. Waste Management, 4, 337–346.
Revil, A., Troland, F., Bourrié, G., Castermant, J., Jardani, A., & Mendonça, C. A. (2009). Ionic contribution to the self-potential signals associated with a redox front. Journal of Contaminant Hydrogeology, 109, 27–39.
Reynolds, J. N. (1997). An introduction to applied and environmental geophysics. John Wiley and Sons.
Sara, M. (2003). Site assessment and remediation handbook (2nd ed.). Lewis Publishers.
Sasaki, Y. (1992). Resolution of resistivity tomography inferred from numerical simulation. Geophysical Prospecting. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2478.1992.tb00536.x
Schuring, J., Schulz, H. D., Fischer, W. R., Bottcher, J., & Duijnisveld, W. H. M. (2000). Redox fundamentals processes and applications. Springer.
Tchobanoglous, G., & Kreith, F. (2002). Handbook of solid waste management. McGraw Hill Professional.
Telford, W. M. W., Geldart, L. P., & Sheriff, R. E. (1990). Applied geophysics. Cambridge University Press.
Williams, P. T. (2005). Waste treatment and disposal. John Wiley and Sons.
Acknowledgements
This research was funded by the National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq) and the equipment used was loaned by the Geology Department, São Paulo State University (UNESP)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Helene, L.P.I., Moreira, C.A. Analysis of Leachate Generation Dynamics in a Closed Municipal Solid Waste Landfill by Means of Geophysical Data (DC Resistivity and Self-Potential Methods). Pure Appl. Geophys. 178, 1355–1367 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00024-021-02700-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00024-021-02700-7