Abstract
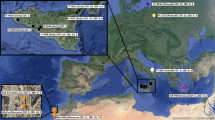
Two populations of Xiphinema persicum n. sp. belonging to the X. americanum-group, were recovered from Semnan province, and described and illustrated based upon morphological, morphometric and molecular data. The type population of the new species is characterized by 2233–2736 μm long females, offset lip region, anteriorly flat to slightly rounded and separated from the rest body by constriction, 82–87 μm long odontostyle, two equally developed genital branches with visible endosymbiont bacteria in ovaries under light microscope, vulva at 52.8–55.5%, 27–32 μm long dorsally convex and ventrally straight to slightly convex tail with a rounded tip, or having a wide mucro-like differentiation, rare male with six ventromedian supplements and four juvenile developmental stages. The new species was morphologically compared with six similar species, X. bricolense, X. californicum, X. incertum, X. pachtaicum, X. santos and X. simile. The latter species has closest morphology and phylogenetic affinities to the new species in both large subunit and internal transcribed spacer 1 (LSU and ITS1 rDNA) trees; but X. persicum n. sp. has four juvenile developmental stages (vs. three), longer odontostyle, and posteriorly located guiding ring compared to it. The phylogenetic relationships of the endosymbiont bacterium of the new species with other isolates was reconstructed using the partial sequences of 16S rDNA.






Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
The species epithet refers to Persia, the Latin name of Iran, the country of origin.
References
Barsi, L., & Lamberti, F. (2002). Morphometrics of three putative species of the Xiphinema americanum group (Nematoda: Dorylaimida) from the territory of the former Yugoslavia. Nematologia Mediterranea, 30, 59–72.
Barsi, L., & Lamberti, F. (2004). Xiphinema parasimile sp. n. from Serbia and X. simile, first record from Bosnia and Herzegovina (Nematoda, Dorylaimida). Nematologia Mediterranea, 32, 101–109.
Brosius, J., Palmer, M. L., Kennedy, P. J., & Noller, H. F. (1978). Complete nucleotide sequence of a 16S ribosomal RNA gene from Escherichia coli. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 75, 4801–4805.
Castresana, J. (2000). Selection of conserved blocks from multiple alignments for their use in phylogenetic analysis. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 17, 540–552.
Cobb, N. A. (1913). New nematode genera found inhabiting fresh water and non-brackish soils. Journal of the Washington Academy of Sciences, 3, 432–444.
Cohn, E. (1970). Observations on the feeding and symptomatology of Xiphinema and Longidorus on selected host roots. Journal of Nematology, 2, 167–173.
Coomans, A., & Heyns, J. (1997). Three species of the Xiphinema americanum-group (Nematoda: Longidoridae) from Kenya. Nematologica, 43, 259–274.
De Grisse, A. T. (1969). Redescription ou modifications de quelques techniques utilisées dans l’étude des nematodes phytoparasitaires. Mededelingen Faculteit Landbouwwetenschappen Rijksuniversiteit, Gent, 34, 351–369.
Decraemer, W., & Geraert, E. (2013). Ectoparasitic nematodes. In R. N. Perry & M. Moens (Eds.), Plant nematology (2nd ed., pp. 179–216). Wallingford: CAB International.
Di Sanzo, C. P., & Rohde, R. A. (1969). Xiphinema americanum associated with maple decline in Massachusetts. Phytopathology, 59, 279–284.
Ebsary, B. A., Vrain, T. C., & Graham, M. B. (1989). Two new species of Xiphinema (Nematoda: Longidoridae) from British Columbia vineyards. Canadian Journal of Zoology, 67, 801–804.
Folmer, M., Hoeh, W., Lutz, R., & Vrijenhoek, R. (1994). DNA primers for amplification of mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit I from diverse metazoan invertebrates. Molecular Marine Biology and Biotechnology, 3, 294–299.
Gutiérrez-Gutiérrez, C., Cantalapiedra-Navarrete, C., Decraemer, W., Vovlas, N., Prior, T., Rius, J. E. P., & Castillo, P. (2012). Phylogeny, diversity, and species delimitation in some species of the Xiphinema americanum-group complex (Nematoda: Longidoridae), as inferred from nuclear and mitochondrial DNA sequences and morphology. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 134, 561–597.
Hockland, S., Inserra, R. N., & Kohl, L. M. (2013). International plant health – Putting legislation into practice. In R. N. Perry & M. Moens (Eds.), Plant nematology (2nd ed., pp. 359–382). Wallingford: CAB International.
Huson, D. H., & Scornavacca, C. (2012). Dendroscope 3: An interactive tool for rooted phylogenetic trees and networks. Systematic Biology, 61, 1061–1067.
Jahanshahi Afshar, F., Shahryari, F., Mokhtassi-Bidgoli, A., Castillo, P., Fouladvand, Z. M., & Pedram, M. (2020). Occurrence of Xiphinema santos Lamberti, Lemos, Agostinelli & D’Addabo 1993 (Nematoda: Longidoridae), a X. americanum-group member in Iran. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 157, 281–291.
Jeger, M., Bragard, C., Caffier, D., Candresse, T., Chatzivassiliou, E., Dehnen-Schmutz, K., Gilioli, G., Grégoire, J. C., Miret, J. A. J., MacLeod, A., & Navarro, M. N. (2018). Pest categorisation of Xiphinema americanum sensu lato. EFSA Journal, 16, 5298.
Katoh, K., & Standley, D. M. (2013). MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: Improvements in performance and usability. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 30, 772–780.
Kiontke, K., Gavin, N. P., Raynes, Y., Roehrig, C., Piano, F., & Fitch, D. H. (2004). Caenorhabditis phylogeny predicts convergence of hermaphroditism and extensive intron loss. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 101, 9003–9008.
Kirjanova, E. S. (1951). Soil nematodes in cotton fields and in virgin soil of Golodnaya steppe (Uzbekistan). [In Russian]. Trudy Zoologicheskogo Instituta Akademiya Nauk SSSR, 9, 625–657.
Kumari, S. (2006). Xiphinema simile (Nematoda: Longidoridae) in the Czech Republic and a note on other Xiphinema species. Helminthologia, 43, 43–50.
Lamberti, F., & Bleve-Zacheo, T. (1979). Studies on Xiphinema americanum sensu lato with descriptions of fifteen new species (Nematoda, Longidoridae). Nematologia Mediterranea, 7, 51–106.
Lamberti, F., & Martelli, G. P. (1971). Notes on Xiphinema mediterraneum (Nematoda: Longidoridae). Nematologica, 17, 75–81.
Lamberti, F., Choleva, B., & Agostinelli, A. (1983). Longidoridae from Bulgaria (Nematoda, Dorylaimida) with description of three new species of Longidorus and two new species of Xiphinema. Nematologia Mediterranea, 11, 49–72.
Lamberti, F., Lemos, R. M., Agostinelli, A., & D’addabo, T. (1993). The Xiphinema americanum-group in the vineyards of the Dao and Douro regions (Portugal) with description of two new species (Nematoda, Dorylaimida). Nematologia Mediterranea, 21, 215–225.
Lamberti, F., Molinari, S., Moens, M., & Brown, D. J. F. (2000). The Xiphinema americanum group. I. Putative species, their geographical occurrence and distribution, and regional polytomous identification keys for the group. Russian Journal of Nematology, 8, 65–84.
Lamberti, F., Hockland, S., Agostinelli, A., Moens, M., & Brown, D. J. F. (2004). The Xiphinema americanum group. III. Keys to species identification. Nematologia Mediterranea, 32, 53–56.
Larget, B., & Simon, D. L. (1999). Markov chain Monte Carlo algorithms for the Bayesian analysis of phylogenetic trees. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 16, 750–759.
Lazarova, S. S., Malloch, G., Oliveira, C. M., Hübschen, J., & Neilson, R. (2006). Ribosomal and mitochondrial DNA analyses of Xiphinema americanum-group populations. Journal of Nematology, 38, 404–410.
Lazarova, S., De Luca, F., & Peneva, V. (2008). On two closely related species of Xiphinema americanum-group: X. simile Lamberti, Choleva & Agostinelli, 1983 and X. parasimile Barsi & Lamberti, 2004 (Longidoridae), with a description of the male of X. parasimile. ZooKeys, 3, 29–50.
Lazarova, S. S., Brown, D. J., Oliveira, C. M. G., Fenton, B., MacKenzie, K., Wright, F., Gaynor, M., & Neilson, R. (2016a). Diversity of endosymbiont bacteria associated with a non-filarial nematode group. Nematology, 18, 615–623.
Lazarova, S., Peneva, V., & Kumari, S. (2016b). Morphological and molecular characterisation, and phylogenetic position of X. browni sp. n., X. penevi sp. n. and two known species of Xiphinema americanum-group (Nematoda, Longidoridae). ZooKeys, 574, 1–42.
Lazarova, S., Oliveira, C. M. G., Prior, T., Peneva, V., & Kumari, S. (2019). An integrative approach to the study of Xiphinema brevicolle Lordello and Da Costa 1961, supports its limited distribution worldwide (Nematoda: Longidoridae). European Journal of Plant Pathology, 153, 441–464.
Lordello, L. G., & Da Costa, C. P. (1961). A new nematode parasite of coffee roots in Brazil. Revista Brasileira de Biologia, 21, 363–366.
Miller, P. M. (1980). Reproduction and survival of Xiphinema americanum on selected woody plants, crops, and weeds. Plant Disease, 64, 174–175.
Mobasseri, M., Hutchinson, M. C., Jahanshahi Afshar, F., & Pedram, M. (2019). New evidence of nematode-endosymbiont bacteria coevolution based on one new and one known dagger nematode species of Xiphinema americanum-group (Nematoda, Longidoridae). PLoS One, 14, e0217506.
Nunn, G.B. (1992). Nematode molecular evolution: an investigation of evolutionary patterns among nematodes based upon DNA sequences. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Nottingham, Nottingham.
Nylander, J. A. A. (2004). MrModeltest v2. Program distributed by the author. Evolutionary Biology Centre: Uppsala University.
Orlando, V., Chitambar, J. J., Dong, K., Chizhov, V. N., Mollov, D., Bert, W., & Subbotin, S. A. (2016). Molecular and morphological characterisation of Xiphinema americanum-group species (Nematoda: Dorylaimida) from California, USA, and other regions, and co-evolution of bacteria from the genus Candidatus Xiphinematobacter with nematodes. Nematology, 18, 1015–1043.
Palomares-Rius, J. E., Archidona-Yuste, A., Cantalapiedra-Navarrete, C., Prieto, P., & Castillo, P. (2016). Molecular diversity of bacterial endosymbionts associated with dagger nematodes of the genus Xiphinema (Nematoda: Longidoridae) reveals a high degree of phylogenetic congruence with their host. Molecular Ecology, 25, 6225–6247.
Pedram, M. (2018). Nematodes of the family Longidoridae. In: Ghaderi, R., Kashi, L. & Karegar, A. (Eds). Plant-parasitic nematodes in Iran. Science reference in collaboration with the Iranian Society of Nematology, pp. 627–67. (In Persian).
Peneva, V., & Choleva, B. (1992). Nematodes of the family Longidoridae from forest nurseries in Bulgaria. II. The genus Xiphinema Cobb, 1913. Helminthology, 32, 46–58.
Repasi, V., Agostinelli, A., Nagy, P., Coiro, M. I., Hecker, K., & Lamberti, F. (2008). Distribution and morphometrical characterization of Xiphinema pachtaicum, X. simile and X. brevicollum from Hungary. Helminthologia, 45, 96–102.
Robbins, R. T., Brown, D. J. F., Halbrendt, J. M., & Vrain, T. C. (1996). Compendium of juvenile stages of Xiphinema species (Nematoda: Longidoridae). Russian Journal of Nematology, 4, 163–171.
Ronquist, F., & Huelsenbeck, J. P. (2003). MrBayes 3: Bayesian phylogenetic inference under mixed models. Bioinformatics, 19, 1572–1574.
Subbotin, S., Perry, R., Warry, A., & Halford, P. (2000). Variations in ribosomal DNA sequences and phylogeny of Globodera parasitising solanaceous plants. Nematology, 2, 591–604.
Subbotin, S. A., Vierstraete, A., De Ley, P., Rowe, J., Waeyenberge, L., Moens, M., & Vanfleteren, J. R. (2001). Phylogenetic relationships within the cyst-forming nematodes (Nematoda, Heteroderidae) based on analysis of sequences from the ITS regions of ribosomal DNA. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 21, 1–16.
Tulaganov, A. T. (1938). The fauna of nematodes of cotton and surrounding soil in Katta-Kurgan district of the Uzbek SSR. Trudy Uzbekskogo Gosudarstvennogo Universiteta, 12, 1–25.
Tzortzakakis, E. A., Archidona-Yuste, A., Cantalapiedra-Navarrete, C., Nasiou, E., Lazanaki, M. S., Kabourakis, E. M., Palomares-Rius, J. E., & Castillo, P. (2014). Integrative diagnosis and molecular phylogeny of dagger and needle nematodes of olives and grapevines in the island of Crete, Greece, with description of Xiphinema cretense n. sp. (Nematoda, Longidoridae). European Journal of Plant Pathology, 140, 563–590.
Vandekerckhove, T. T., Willems, A., Gillis, M., & Coomans, A. (2000). Occurrence of novel verrucomicrobial species, endosymbiotic and associated with parthenogenesis in Xiphinema americanum-group species (Nematoda, Longidoridae). International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 50, 2197–2205.
Williams, B. D., Schrank, B., Huynh, C., Shownkeen, R., & Waterston, R. H. (1992). A genetic mapping system in Caenorhabditis elegans based on polymorphic sequence-tagged sites. Genetics, 131, 609–624.
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge Tarbiat Modares University and Iranian National Science Foundation (INSF) for the financial supports. The authors appreciate valuable technical helps of Dr. Mohammad Reza Atighi.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All the authors certify that they do not have any conflict of interest, the presented data are original and the presented data are not published, and are not under evaluation for publication elsewhere, all prevailing local, national and international regulations and conventions, and normal scientific ethical practices, have been respected. They also certify that the final version of this manuscript has been reviewed by all authors.
Research involving human participants and/or animals
In this study, the soil samples were collected in forest park which are not under protection.
Informed consent
The authors certify that they have accepted the principles of ethical standards and that guidelines of professional conduct have been followed.
The funders had no role in designing of this study, collecting and analyzing of the data, preparing the manuscript and are not involved in evaluating or publishing process of this research.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jahanshahi Afshar, F., Pedram, M. & Mobasseri, M. Description of Xiphinema persicum n. sp. (Nematoda: Longidoridae), a X. americanum-group species from Iran. Eur J Plant Pathol 159, 783–797 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-021-02201-2
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-021-02201-2