Abstract
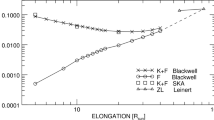
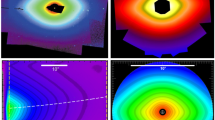
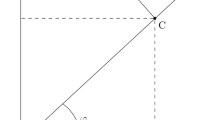
We present a photometrically accurate restoration of the K- and F-coronae from white-light images obtained over 24 years [1996 – 2019] by the Large-Angle Spectrometric COronagraph (LASCO-C2) onboard the Solar and Heliospheric Observatory (SOHO). The procedure starts with the data set of unpolarized images of 512 × 512 pixels produced by the polarimetric analysis of the routine C2 polarization sequences (Lamy et al., Solar Phys. 295, 89, 2020) in which the F-corona, the instrumental stray light, and possible remnants of the K-corona due to the imperfect polarimetric separation are entangled. Disentangling these components requires a complex procedure organized in three stages, each composed of several steps. Stage 1 establishes the distinct variations of the radiance of these components with the Sun–SOHO distance, and generate a new data set of median images calculated for each Carrington rotation. Stage 2 achieves the restoration of a set of 36 stray-light images that account for the temporal variation of the stray-light pattern, in particular those associated with the periodic roll maneuvers of SOHO, which started in 2003. Stage 3 achieves the restoration of the F-corona, and a time series of daily images is generated. Combining these images with the set of stray-light images allowed us to process the whole set of routine LASCO-C2 images of 1024 × 1024 pixels (approximately 626,000 images) and to produce calibrated, high-resolution images of the K-corona. The two sets of images of the K-corona, that produced by polarimetric separation of 512 × 512 pixels images and that presently produced by subtraction, are in excellent photometric agreement. We extend our past conclusions that the temporal variation of the integrated radiance of the K-corona tracks the solar activity over Solar Cycles 23 and 24, and that it is highly correlated with the temporal variation of the total magnetic field. The behaviors of the integrated radiance during the last few years of the declining phases of Solar Cycles 23 and 24 are remarkably similar, reaching the same base level and leading to a duration of 11.0 years for the latter cycle, in agreement with that derived from sunspots.






























Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barlyaeva, T., Lamy, P., Llebaria, A.: 2015, Mid-term quasi-periodicities and solar cycle variation of the white-light corona from 18.5 years (1996.0 - 2014.5) of LASCO observations. Solar Phys. 290, 2117. DOI. ADS.
Battams, K., Howard, R.A., Dennison, H.A., Weigel, R.S., Lean, J.L.: 2020, The LASCO coronal brightness index. Solar Phys. 295, 20. DOI. ADS.
Brueckner, G.E., Howard, R.A., Koomen, M.J., Korendyke, C.M., Michels, D.J., Moses, J.D., Socker, D.G., Dere, K.P., Lamy, P.L., Llebaria, A., Bout, M.V., Schwenn, R., Simnett, G.M., Bedford, D.K., Eyles, C.J.: 1995, The Large Angle Spectroscopic Coronagraph (LASCO). Solar Phys. 162, 357. DOI. ADS.
Burkepile, J., Boll, A., Casini, R., de Toma, G., Elmore, D.F., Gibson, K.L., Judge, P.G., Mitchell, A.M., Penn, M., Sewell, S.D., Tomczyk, S., Yanamandra-Fisher, P.A.: 2017, Polarization observations of the total solar eclipse of August 21, 2017. In: AGU Fall Meeting Abst. ADS.
Dolei, S., Spadaro, D., Ventura, R.: 2016, Mapping the coronal hydrogen temperature in view of the forthcoming coronagraph observations by Solar Orbiter. Astron. Astrophys. 592, A137. DOI. ADS.
Domingo, V., Fleck, B., Poland, A.I.: 1995, The SOHO mission: An overview. Solar Phys. 162, 1. DOI. ADS.
Fainshtein, V.G.: 2007, Some properties of the latitude brightness distributions in the K and F coronae according to SOHO/LASCO data. Astron. Rep. 51, 1026. DOI. ADS.
Fainshtein, V.G.: 2009, New method for separating K- and F-corona brightness based on LASCO/SOHO data. Geomagn. Aeron. 49, 830. DOI. ADS.
Frazin, R.A., Lamy, P., Llebaria, A., Vásquez, A.M.: 2010, Three-dimensional electron density from tomographic analysis of LASCO-C2 images of the K-corona total brightness. Solar Phys. 265, 19. DOI. ADS.
Hayes, A.P., Vourlidas, A., Howard, R.A.: 2001, Deriving the electron density of the solar corona from the inversion of total brightness measurements. Astrophys. J. 548, 1081. DOI. ADS.
Koutchmy, S., Lamy, P.L.: 1985, The f-corona and the circum-solar dust evidences and properties. In: Giese, R.H., Lamy, P. (eds.) IAU Colloq. 85: Properties and Interactions of Interplanetary Dust, Astrophys. Space Sci. Lib. 119, 63. DOI. ADS.
Lamy, P., Barlyaeva, T., Llebaria, A., Floyd, O.: 2014, Comparing the solar minima of cycles 22/23 and 23/24: The view from LASCO white light coronal images. J. Geophys. Res. 119, 47. DOI. ADS.
Lamy, P., Boclet, B., Wojak, J., Vibert, D.: 2017, Anomalous surge of the white-light corona at the onset of the declining phase of solar cycle 24. Solar Phys. 292, 60. DOI. ADS.
Lamy, P., Llebaria, A., Boclet, B., Gilardy, H., Burtin, M., Floyd, O.: 2020, Coronal photopolarimetry with the LASCO-C2 coronagraph over 24 years [1996 - 2019] – Application to the K/F separation and to the determination of the electron density. Solar Phys. 295, 89. DOI. ADS.
Lamy, P., Gilardy, H., Llebaria, A., Quémerais, E., Ernandez, F.: 2021, LASCO-C3 observations of the K and F coronae over 24 years (1996–2019): photopolarimetry and electron density distribution. Solar Phys. (accepted).
Lamy, P., Gilardy, H., Llebaria, A.: 2021, The F-corona from 24 years of LASCO Observations, Solar Phys. (in preparation).
Leinert, C., Grun, E.: 1990, In: Schwenn, R., Marsch, E. (eds.) Interplanetary Dust, Springer, Berlin, 207. ADS.
Leinert, C., Richter, I., Pitz, E., Planck, B.: 1981, The zodiacal light from 1.0 to 0.3 A.U. as observed by the HELIOS space probes. Astron. Astrophys. 103, 177. ADS.
Llebaria, A., Lamy, P., Bout, M.: 2004, Lessons learnt from the soho lasco-c2 calibration. In: Proc. Soc. Photo-Opt. Instrum. Eng. (SPIE) 5171, 27. DOI.
Llebaria, A., Lamy, P., Koutchmy, S.: 1999, The global activity of the solar corona. In: Vial, J.-C., Kaldeich-Schü, B. (eds.) 8th SOHO Workshop: Plasma Dynamics and Diagnostics in the Solar Transition Region and Corona, ESA SP 446, ESA, Noordwijk, 441. ADS.
Llebaria, A., Loirat, J., Lamy, P.: 2012, In-orbit determination of the straylight in the SOHO/LASCO-C2 coronagraph and its temporal evolution. In: Clampin, M.C., Fazio, G.G., MacEwen, H.A., Oschmann, J.M. Jr. (eds.) Space Telescopes and Instrumentation 2012: Optical, Infrared, and Millimeter Wave, Proc. SPIE 8442, 844226. DOI. ADS.
Llebaria, A., Thernisien, A.: 2001, Highly accurate photometric equalization of long sequences of coronal images. In: Starck, J.-L., Murtagh, F.D., (eds.) Astronomical Data Analysis, Proc. Soc. Photo-Opt. Instrum. Eng. (SPIE) 4477, 265. DOI.
Morgan, H., Habbal, S.R.: 2007, The long-term stability of the visible f corona at heights of 3 to 6 solar radii. Astron. Astrophys. 471, L47.
Munro, R.H., Jackson, B.V.: 1977, Physical properties of a polar coronal hole from 2 to 5 solar radii. Astrophys. J. 213, 874. DOI. ADS.
Pagot, E., Lamy, P., Llebaria, A., Boclet, B.: 2014, Automated processing of lasco coronal images: Spurious point-source-filtering and missing-blocks correction. Solar Phys. 289, 1433. DOI.
Quémerais, E., Lamy, P.: 2002, Two-dimensional electron density in the solar corona from inversion of white light images-application to soho/lasco-c2 observations. Astron. Astrophys. 393, 295. DOI.
Saito, K., Poland, A.I., Munro, R.H.: 1977, A study of the background corona near solar minimum. Solar Phys. 55, 121.
Stenborg, G., Howard, R.A.: 2017, The evolution of the surface of symmetry of the interplanetary dust from 24∘ to 5∘ elongation. Astrophys. J. 848, 57. DOI. ADS.
Van de Hulst, H.C.: 1947, Zodiacal light in the solar corona. Astrophys. J. 105, 471. DOI. ADS.
Von Klüber, H.: 1958, Intensities, polarization and electron density of the solar corona from photographs taken at the total solar eclipse of 1952 February 25. Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 118, 201.
Vorobiev, D., Ninkov, Z., Bernard, L., Brock, N.: 2017, Imaging polarimetry of the 2017 solar eclipse with the RIT polarization imaging camera. arXiv.
Wang, Y.-M., Sheeley, N.R.: 2003, On the fluctuating component of the Sun’s large-scale magnetic field. Astrophys. J. 590, 1111. DOI. ADS.
Acknowledgments
We thank Y.-M. Wang for providing the Total Magnetic Field (TMF) data. The LASCO-C2 project at the Laboratoire d’Astrophysique de Marseille and the Laboratoire Atmosphères, Milieux et Observations Spatiales is funded by the Centre National d’Etudes Spatiales (CNES). LASCO was built by a consortium of the Naval Research Laboratory, USA, the Laboratoire d’Astrophysique de Marseille (formerly Laboratoire d’Astronomie Spatiale), France, the Max-Planck-Institut für Sonnensystemforschung (formerly Max Planck Institute für Aeronomie), Germany, and the School of Physics and Astronomy, University of Birmingham, UK. SOHO is a project of international cooperation between ESA and NASA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Llebaria, A., Lamy, P., Gilardy, H. et al. Restoration of the K and F Components of the Solar Corona from LASCO-C2 Images over 24 Years [1996 – 2019]. Sol Phys 296, 53 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-021-01800-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-021-01800-w