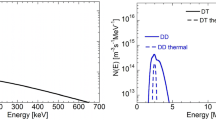
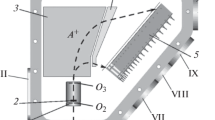
Abstract
Academician A. D. Sakharov’s idea concerning the emission of atomic flux from hot plasma (1951) inspired scientists of A. F. Ioffe Physico-Technical Institute to create the first in the world instrument called Neutral Atom Analyzer in 1960 and then in 1961 to use it successfully on the Alpha device (USSR, 1958–1963). Now the analysis of fluxes of fast atoms referred to as Neutral Particle Analysis (NPA) is one of the main diagnostic methods for the ion component of plasma in tokamaks, stellarators, and other devices. NPA provides a unique opportunity for studying the ion distribution functions, ion temperatures and hydrogen isotope ratio in hot plasma. Neutral particle analyzers developed at the Ioffe Institute were widely used in the USSR until the late 1970s, and afterwards began to be employed worldwide. Since then, most of the information on the ion distribution functions and the behavior of fast ions in fusion plasma is obtained from NPA measurements on all leading magnetic confinement fusion systems worldwide. The specialized complex of atom analyzers currently being created at the Ioffe Institute is included in the primary list of ITER diagnostics. The integration of this complex on ITER is expected to begin in 2025.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
A.D. Sakharov, Theory of the magnetic thermonuclear reactor Part II, in Plasma Physics and the Problem of Controlled Thermonuclear Reactions, vol. 1, ed. by M.A. Leontovich (Pergamon Press, Oxford, 1951). (Translated from the Russian, 1961)
V.V. Afrosimov et al., Method of investigation of the flux of atoms emitted by a plasma. Sov. Phys. Tech. Phys. 5, 1378 (1961)
V.V. Afrosimov et al., Investigation of the stream of neutral atomic particles emitted by the “Alpha” plasma. Sov. Phys. Tech. Phys. 5, 1389 (1961)
V.V. Afrosimov, Plasma diagnostic using fast neutral particles on a device with a discharge in a strong magnetic field, in ed. by B.P. Konstantinov et al., Plasma Diagnostics (Gosatomizdat, Moscow, 1963) (in Russian)
L.A. Artsimovich et al., Joule heating of plasma in the toroidal Tokamak-3 device. in Plasma Physics and Controlled Nuclear Fusion Research, Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference 6–10 September 1965, Culham, UK, vol. II (IAEA, Vienna, 1965), p. 595. http://www-naweb.iaea.org/napc/physics/FEC/STIPUB111_VOL2.pdf
Vinogradova N.D. et al., Experiments on the Tokamak-6 Device (in Russian). Plasma Physics and Controlled Nuclear Fusion Research, Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on 17–23 June 1971, Madison, Wisconsin, USA, vol. II (IAEA, Vienna, 1971). p. 441 http://www-naweb.iaea.org/napc/physics/FEC/STIPUB288_VOL2.pdf
V.V. Afrosimov et al., Multichannel energy and mass analyzer for atomic particles. Sov. Phys. Tech. Phys. 20, 33 (1975)
E.P. Gorbunov et al., 1973. Behaviour of ions in the Tokamak-4 plasma, in 6th European Conference on Controlled Fusion and Plasma Physics, vol. I (Moscow, USSR, 30 July–4 August 1973), p. 1. http://www-fusion.ciemat.es/media/EPS/EPS_06_Vol1_1973.pdf
I.P. Gladkovsky et al., A ten-channel analyzer of atomic-particle energy spectra with mass separation over a wide energy range. Nucl. Instrum. Methods 175, 441 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1016/0029-554X(80)90758-2
V.V. Afrosimov et al., Measurement of the local values of the ion temperature in a Tokamak using charge exchange of plasma ions with a jet of hydrogen atoms. JETP Lett. 18, 300 (1973)
A.B. Izvozchikov et al., The Akord-12 multichannel analyzer for simultaneous recording of the energy spectra of hydrogen and deuterium atoms. Sov. Phys. Tech. Phys. 37, 201 (1992)
F.V. Chernyshev et al., A compact neutral-particle analyzer for plasma diagnostics. Instrum. Exp. Tech. 47, 214 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:INET.0000025204.01783.1a
S.S. Medley et al., Contemporary instrumentation and application of charge exchange neutral particle diagnostics in magnetic fusion energy experiments. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 79, 011101 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2823259
A.I. Kislyakov et al., Particle diagnostics. Fusion Sci. Technol. 53, 577 (2008). https://doi.org/10.13182/FST08-A1680
L.A. Artsimovich et al., Ion energy balance in the plasma of a tokamak machine. JETP Lett. 11, 304 (1970)
L.A. Artsimovich et al., Ion lifetime in the Tokamak-3 machine. JETP Lett. 12, 62 (1970)
L.A. Artsimovich et al., Ion heating in the Tokamak-3 setup. JETP Lett. 10, 82 (1969)
L.A. Artsimovich et al., Investigation of plasma neutron radiation from the tokamak T-3A installation. JETP 34, 306 (1972)
Kreter A. et al., Optimized confinement discharges with high ion temperatures after installation of the island divertor in W7-AS, in 29th EPS Conference on Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, Europhysics Conference Abstracts vol. 26B (Montreux, Switzerland, 17–21 June 2002), p. 5.033. http://epsppd.epfl.ch/Montreux/pdf/P5_033.pdf
V.I. Afanasyev et al., Neutral particle analyzer/isotope separator for measurement of hydrogen isotope composition of JET plasmas. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 74, 2338 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1542664
L. Ballabio et al., \(\alpha \)-particle knock-on signature in the neutron emission of DT plasmas. Phys. Rev. E 55, 3358 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevE.55.3358
A.I. Kislyakov et al., High energy neutral particle analyzer. Fusion Eng. Des. 34–35, 107 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0920-3796(96)00668-0
M.P. Petrov et al., Neutral particle analysis in the MeV range in JET, in 19th EPS Conference on Controlled Fusion and Plasma Physics, Europhysics Conference Abstracts, vol. 16C part II (Innsbruck, Austria, 29 June–3 July 1992), p. 1031. http://libero.ipp.mpg.de/libero/PDF/EPS_19_Vol2_1992.pdf
V.I. Afanassiev et al., Neutral particle analysis in MeV energy range and relative role of He\(^{+}\) and C\(^{5+}\) ions in fast proton neutralization in ICRF and combined ICRF/NBI-heated JT-60U plasmas. Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 39, 1509 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1088/0741-3335/39/10/002
S.E. Sharapov et al., Energetic particle physics in JET. Nucl. Fusion 40, 1363 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1088/0029-5515/40/7/307
V.I. Afanasyev et al., Neutral particle measurements of fusion tritons in JET. Plasma Phys. Rep. 36, 659 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063780X10080027
M.P. Petrov et al., Effective temperatures, sawtooth mixing, and stochastic diffusion ripple loss of fast H\(^{+}\) minority ions driven by ion cyclotron heating in the Tokamak fusion test reactor. Phys. Plasmas 6, 2430 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.873539
H.H. Duong et al., Radio frequency-driven energetic tritium ion tail measurements in the tokamak fusion test reactor using the pellet charge exchange diagnostic. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 68, 340 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1148060
Y. Kusama et al., Charge-exchange neutral particle measurement in MeV energy range on JT-60U. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 66, 339 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1146405
F.V. Tchernychev et al., Charge-exchange measurements of d-d triton distribution functions in high-power neutral beam heating on JT-60U. Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 41, 1291 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1088/0741-3335/41/10/306
R.K. Fisher et al., Alpha particle diagnostics using impurity pellet injection. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 63, 4499 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1143705
S.S. Medley et al., Design and operation of the pellet charge exchange diagnostic for measurement of energetic confined \(\alpha \) particles and tritons on the tokamak fusion test reactor. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 67, 3122 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1147419
S.S. Medley et al., Measurements of confined alphas and tritons in the MHD quiescent core of TFTR plasmas using the pellet charge exchange diagnostic. Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 38, 1779 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1088/0741-3335/38/10/006
N.N. Gorelenkov et al., Alpha-particle neoclassical distribution function in the TSP tokamak. Sov. J. Plasma Phys. 15, 80 (1989)
V.I. Afanasyev et al., Neutral particle analysis on ITER: present status and prospects. Nucl Instrum Meth Phys Res A 621, 456 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nima.2010.06.201
S.Y. Petrov et al., Design features of the neutral particle diagnostic system for the ITER tokamak. Phys. Atom. Nucl. 80, 1268 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063778817070109
M. Petrov et al., Fuel monitoring in ITER plasma with the use of neutral particle analysis. PoS (ECPD2015) (2015). https://doi.org/10.22323/1.240.0153
M.I. Mironov et al., Sawtooth mixing of alphas, knock-on D, and T ions, and its influence on NPA spectra in ITER plasma. Nucl. Fusion 58, 082030 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1088/1741-4326/aab678
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the State Assignment on the topic No. 0040-2019-0023. The authors express their gratitude to Prof. Dr. F. Wagner of Max-Planck-Institute for Plasma Physics who was the first outside the USSR to use Ioffe atom analyzers in IPP (Garching) on the tokamaks Pulsator and ASDEX. His successful experiments contributed to the international reputation of the Ioffe instruments. On the basis of that he also initiated scientific exchange and many Russian scientists had the possibility to work in IPP. This cooperation was maintained over decades also during politically difficult periods. We also thank Prof. Dr. F. Wagner for his help in the preparation of this paper for publication.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Petrov, M.P., Afanasyev, V.I., Chernyshev, F.V. et al. 60 Years of neutral particle analysis: from early tokamaks to ITER. EPJ H 46, 5 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjh/s13129-021-00009-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjh/s13129-021-00009-6