Abstract
Objective
The dopaminergic pathology of Parkinson’s disease (PD) impacts circuits involving GABAergic neurons, especially in the brainstem, where the disease manifests early. The aim of this study is to test the hypothesis that levels of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) in the upper brainstem are reduced in patients with PD compared to healthy controls, using edited magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS of GABA +).
Materials and methods
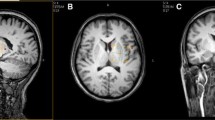
GABA + levels were examined in 18 PD patients and 18 age- and sex-matched healthy controls (HCs). GABA + -edited MRS was performed in 7.5-ml voxels in the upper brainstem, and the spectra were processed using the Gannet software. Differences in GABA + levels between the two groups were analyzed using independent t test analysis.
Results
GABA + levels were significantly lower (p < 0.05) in the upper brainstem of the patients with PD (4.57 ± 0.94 mM) than the HCs (5.89 ± 1.16 mM).
Conclusion
The lower GABA + levels in the upper brainstem of the PD patients suggest that a GABAergic deficit in the brainstem may contribute to the pathology in PD.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- PD:
-
Parkinson’s disease
- GABA:
-
Gamma-aminobutyric acid
- GABA + :
-
Gamma-aminobutyric acid plus co-edited signals
- MRS:
-
Magnetic resonance spectroscopy
- NMS:
-
Non-motor symptoms
- BG:
-
Basal ganglia
- ROI:
-
Region of interest
- NAA:
-
N-acetyl aspartate
- Cr:
-
Creatine
- Cho:
-
Choline
- Glx:
-
Glutamate + glutemine
- TR:
-
Repetition time
- TE:
-
Echo time
- MM:
-
Macromolecules
- SD:
-
Standard deviation
- HC:
-
Healthy control
- SN:
-
Substantia nigra
- GM:
-
Grey matter
- WM:
-
White matter
- MEGA-PRESS:
-
Mescher–Garwood Point Resolved Spectroscopy
- MPRAGE:
-
Magnetization-prepared rapid-acquisition gradient echo
- NMSQ:
-
Non-Motor Symptom Questionnaire
- SPSS:
-
Statistical Package for Social Sciences software
- UPDRS:
-
Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale
- H-Y stage:
-
Hoehn and Yahr Stage
- SB:
-
Sleep bruxism
- OSA:
-
Obstructive sleep apnea
References
Samii A, Nutt JG, Ransom BR (2004) Parkinson’s disease. Lancet 363(9423):1783–1793
Lee CR, Tepper JM (2009) Basal ganglia control of substantia nigra dopaminergic neurons. J Neural Transm Suppl. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-211-92660-4_6(73):71-90
Tepper JM, Lee CR (2007) GABAergic control of substantia nigra dopaminergic neurons. Prog Brain Res 160:189–208
Obeso JA, Marin C, Rodriguez-Oroz C, Blesa J, Benitez-Temino B, Mena-Segovia J, Rodriguez M, Olanow CW (2008) The basal ganglia in Parkinson’s disease: current concepts and unexplained observations. Ann Neurol 64(Suppl 2):S30-46
Braak H, Del Tredici K, Rub U, de Vos RA, Jansen Steur EN, Braak E (2003) Staging of brain pathology related to sporadic Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 24(2):197–211
Jellinger KA (2019) Is Braak staging valid for all types of Parkinson’s disease? J Neural Transmission 126(4):423–431
Beach TG, Adler CH, Lue L, Sue LI, Bachalakuri J, Henry-Watson J, Sasse J, Boyer S, Shirohi S, Brooks R, Eschbacher J, White CL 3rd, Akiyama H, Caviness J, Shill HA, Connor DJ, Sabbagh MN, Walker DG, Arizona Parkinson’s Disease C (2009) Unified staging system for Lewy body disorders: correlation with nigrostriatal degeneration, cognitive impairment and motor dysfunction. Acta Neuropathol 117(6):613–634
Kalaitzakis ME, Graeber MB, Gentleman SM, Pearce RK (2008) The dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus is not an obligatory trigger site of Parkinson’s disease: a critical analysis of alpha-synuclein staging. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 34(3):284–295
Parkkinen L, Kauppinen T, Pirttila T, Autere JM, Alafuzoff I (2005) Alpha-synuclein pathology does not predict extrapyramidal symptoms or dementia. Ann Neurol 57(1):82–91
Parkkinen L, Pirttila T, Alafuzoff I (2008) Applicability of current staging/categorization of alpha-synuclein pathology and their clinical relevance. Acta Neuropathol 115(4):399–407
Burke RE, Dauer WT, Vonsattel JP (2008) A critical evaluation of the Braak staging scheme for Parkinson’s disease. Ann Neurol 64(5):485–491
Mullins PG, McGonigle DJ, O’Gorman RL, Puts NA, Vidyasagar R, Evans CJ, Cardiff Symposium on MRSoG Edden RA (2014) Current practice in the use of MEGA-PRESS spectroscopy for the detection of GABA. NeuroImage 86:43–52
Mescher M, Merkle H, Kirsch J, Garwood M, Gruetter R (1998) Simultaneous in vivo spectral editing and water suppression. NMR Biomed 11(6):266–272
Saleh MG, Oeltzschner G, Chan KL, Puts NAJ, Mikkelsen M, Schar M, Harris AD, Edden RAE (2016) Simultaneous edited MRS of GABA and glutathione. NeuroImage 142:576–582
Mikkelsen M, Barker PB, Bhattacharyya PK, Brix MK, Buur PF, Cecil KM, Chan KL, Chen DY, Craven AR, Cuypers K, Dacko M, Duncan NW, Dydak U, Edmondson DA, Ende G, Ersland L, Gao F, Greenhouse I, Harris AD, He N, Heba S, Hoggard N, Hsu TW, Jansen JFA, Kangarlu A, Lange T, Lebel RM, Li Y, Lin CE, Liou JK, Lirng JF, Liu F, Ma R, Maes C, Moreno-Ortega M, Murray SO, Noah S, Noeske R, Noseworthy MD, Oeltzschner G, Prisciandaro JJ, Puts NAJ, Roberts TPL, Sack M, Sailasuta N, Saleh MG, Schallmo MP, Simard N, Swinnen SP, Tegenthoff M, Truong P, Wang G, Wilkinson ID, Wittsack HJ, Xu H, Yan F, Zhang C, Zipunnikov V, Zollner HJ, Edden RAE (2017) Big GABA: Edited MR spectroscopy at 24 research sites. NeuroImage 159:32–45
Sanaei Nezhad F, Anton A, Michou E, Jung J, Parkes LM, Williams SR (2018) Quantification of GABA, glutamate and glutamine in a single measurement at 3 T using GABA-edited MEGA-PRESS. NMR Biomed 31:1
Elmaki EEA, Gong T, Nkonika DM, Wang G (2018) Examining alterations in GABA concentrations in the basal ganglia of patients with Parkinson’s disease using MEGA-PRESS MRS. Jap J Radiol 36(3):194–199
Gong T, Xiang Y, Saleh MG, Gao F, Chen W, Edden RAE, Wang G (2018) Inhibitory motor dysfunction in parkinson’s disease subtypes. J Magn Reson Imag JMRI 47(6):1610–1615
van Nuland AJM, den Ouden HEM, Zach H, Dirkx MFM, van Asten JJA, Scheenen TWJ, Toni I, Cools R, Helmich RC (2020) GABAergic changes in the thalamocortical circuit in Parkinson’s disease. Hum Brain Mapp 41(4):1017–1029
Delli Pizzi S, Franciotti R, Ferretti A, Edden RAE, Zollner HJ, Esposito R, Bubbico G, Aiello C, Calvanese F, Sensi SL, Tartaro A, Onofrj M, Bonanni L (2020) High gamma-aminobutyric acid content within the medial prefrontal cortex is a functional signature of somatic symptoms disorder in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Move Dis Off J Move Dis Soc. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.28221
Pesch B, Casjens S, Woitalla D, Dharmadhikari S, Edmondson DA, Zella MAS, Lehnert M, Lotz A, Herrmann L, Muhlack S, Kraus P, Yeh CL, Glaubitz B, Schmidt-Wilcke T, Gold R, van Thriel C, Bruning T, Tonges L, Dydak U (2019) Impairment of motor function correlates with neurometabolite and brain iron alterations in Parkinson’s disease. Cells 8:2
Firbank MJ, Parikh J, Murphy N, Killen A, Allan CL, Collerton D, Blamire AM, Taylor JP (2018) Reduced occipital GABA in Parkinson disease with visual hallucinations. Neurology 91(7):e675–e685
Fan X, Qu F, Wang JJ, Du X, Liu WC (2017) Decreased gamma-aminobutyric acid levels in the brainstem in patients with possible sleep bruxism: a pilot study. J Oral Rehabil 44(12):934–940
Puts NA, Harris AD, Crocetti D, Nettles C, Singer HS, Tommerdahl M, Edden RA, Mostofsky SH (2015) Reduced GABAergic inhibition and abnormal sensory symptoms in children with Tourette syndrome. J Neurophysiol 114(2):808–817
O’Gorman Tuura RL, Baumann CR, Baumann-Vogel H (2018) Beyond dopamine: GABA, glutamate, and the axial symptoms of Parkinson disease. Front Neurol 9:806
O’Gorman Tuura RL, Baumann CR, Baumann-Vogel H (2018) Neurotransmitter activity is linked to outcome following subthalamic deep brain stimulation in Parkinson’s disease. Parkin Relat Disord 50:54–60
Emir UE, Tuite PJ, Oz G (2012) Elevated pontine and putamenal GABA levels in mild-moderate Parkinson disease detected by 7 tesla proton MRS. PLoS ONE 7(1):e30918
Dharmadhikari S, Ma R, Yeh CL, Stock AK, Snyder S, Zauber SE, Dydak U, Beste C (2015) Striatal and thalamic GABA level concentrations play differential roles for the modulation of response selection processes by proprioceptive information. NeuroImage 120:36–42
Blaszczyk JW (2016) Parkinson’s disease and neurodegeneration: GABA-collapse hypothesis. Front Neurosci 10:269
Saranza G, Lang AE (2020) Levodopa challenge test: indications, protocol, and guide. J Neurol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-020-09810-7
Song Y, Gong T, Edden RAE, Wang G (2020) Feasibility of measuring GABA levels in the upper brainstem in healthy volunteers using edited MRS. Front Psychiatry 11:813
Edden RA, Oeltzschner G, Harris AD, Puts NA, Chan KL, Boer VO, Schar M, Barker PB (2016) Prospective frequency correction for macromolecule-suppressed GABA editing at 3T. J Magn Reson Imag JMRI 44(6):1474–1482
Edden RA, Puts NA, Harris AD, Barker PB, Evans CJ (2014) Gannet: A batch-processing tool for the quantitative analysis of gamma-aminobutyric acid-edited MR spectroscopy spectra. J Magn Reson Imag JMRI 40(6):1445–1452
Near J, Edden R, Evans CJ, Paquin R, Harris A, Jezzard P (2015) Frequency and phase drift correction of magnetic resonance spectroscopy data by spectral registration in the time domain. Magn Reson Med 73(1):44–50
Vymazal J, Righini A, Brooks RA, Canesi M, Mariani C, Leonardi M, Pezzoli G (1999) T1 and T2 in the brain of healthy subjects, patients with Parkinson disease, and patients with multiple system atrophy: relation to iron content. Radiology 211(2):489–495
Sedlacik J, Boelmans K, Lobel U, Holst B, Siemonsen S, Fiehler J (2014) Reversible, irreversible and effective transverse relaxation rates in normal aging brain at 3T. NeuroImage 84:1032–1041
Mädler BHT, Mackay A (2006) 3D-relaxometry—quantitative T1 and T2 brain mapping at 3T. Proc Int Soc Magn Reson Med 14:958
Gasparovic C, Song T, Devier D, Bockholt HJ, Caprihan A, Mullins PG, Posse S, Jung RE, Morrison LA (2006) Use of tissue water as a concentration reference for proton spectroscopic imaging. Magn Reson Med 55(6):1219–1226
ErnstRoss TKTBD (1993) Absolute quantitation of water and metabolites in the human brain I compartments and water. J Magn Reson 102(1):1–8
Romenets SR, Wolfson C, Galatas C, Pelletier A, Altman R, Wadup L, Postuma RB (2012) Validation of the non-motor symptoms questionnaire (NMS-Quest). Parkin Relat Disord 18(1):54–58
Politis M, Wu K, MolloyGB SP, Chaudhuri KR, Piccini P (2010) Parkinson’s disease symptoms: the patient’s perspective. Move Disord Off J Move Disord Soc 25(11):1646–1651
Mazuel L, Chassain C, Jean B, Pereira B, Cladiere A, Speziale C, Durif F (2016) Proton MR spectroscopy for diagnosis and evaluation of treatment efficacy in Parkinson disease. Radiology 278(2):505–513
Tritsch NX, Granger AJ, Sabatini BL (2016) Mechanisms and functions of GABA co-release. Nat Rev Neurosci 17(3):139–145
Oz G, Terpstra M, Tkac I, Aia P, Lowary J, Tuite PJ, Gruetter R (2006) Proton MRS of the unilateral substantia nigra in the human brain at 4 tesla: detection of high GABA concentrations. Magn Reson Med 55(2):296–301
Macey PM, Sarma MK, Prasad JP, Ogren JA, Aysola R, Harper RM, Thomas MA (2017) Obstructive sleep apnea is associated with altered midbrain chemical concentrations. Neuroscience 363:76–86
Soares DP, Law M (2009) Magnetic resonance spectroscopy of the brain: review of metabolites and clinical applications. Clin Radiol 64(1):12–21
Chaudhuri KR, Schapira AH (2009) Non-motor symptoms of Parkinson’s disease: dopaminergic pathophysiology and treatment. Lancet Neurol 8(5):464–474
Jellinger KA (2015) Neuropathobiology of non-motor symptoms in Parkinson disease. J Neural Transmiss 122(10):1429–1440
Grinberg LT, Rueb U, Alho AT, Heinsen H (2010) Brainstem pathology and non-motor symptoms in PD. J Neurol Sci 289(1–2):81–88
Funding
This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health [Grant numbers R01 EB016089; P41 EB015909 and Grant K99 EB028828]; National Natural Science Foundation of China [Grant number 81671668; 81371534]; Major research project of Shandong province [Grant number 2016ZDJS07A16]; and Natural Science Foundation of Shandong [Grant No. ZR2020QH267].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: YS, TG. Methodology: YS, TG, MG.S, MM, RA.E.E. Formal analysis and investigation: YS, MM. Write—original draft preparation: YS, TG. Write—reviewing and editing: RA.E.E, MG.S. Funding acquisition: RA.E.E, GW. Supervision: GW.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval
Approval was obtained from the ethics committee of Shandong University. The procedures used in this study adhere to the tenets of the Declaration of Helsinki.
Consent to participate
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Consent to publish
Patients signed informed consent regarding publishing their data and photographs.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, Y., Gong, T., Saleh, M.G. et al. Upper brainstem GABA levels in Parkinson’s disease. Magn Reson Mater Phy 34, 689–696 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10334-021-00910-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10334-021-00910-7