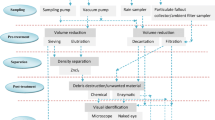
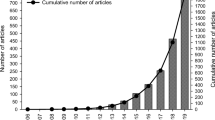
Abstract
As emerging environmental contaminants, microplastics may cause potential hazard to global ecosphere (including water, soil and air) and human health. To date, the occurance and ecological effects of microplastics in water and soil were systematically summarized. However, there are few reviews of microplastics in air (i.e. airborne microplastics). Recently, microplastics have been observed in atmospheric fallout collected from some areas. Although the studies are limited, most of the researches showed that synthetic textiles are the main source of airborne microplastics, and fibers are the dominant shape. Airborne microplastics are contributors to microplastic pollution in aquatic and soil environments. In addition, airborne microplastics can be directly inhaled and posed health risks to humans. Therefore, this review summarized the current knowledge and provide insights into further research to better understand airborne microplastics and their risks to human.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbasi S, Keshavarzi B, Moore F et al (2019) Distribution and potential health impacts of microplastics and microrubbers in air and street dusts from Asaluyeh County, Iran. Environ Pollut 244:153–164
Allen S, Allen D, Phoenix VR et al (2019) Atmospheric transport and deposition of microplastics in a remote mountain catchment. Nat Geosci 12:679
Auta HS, Emenike CU, Fauziah SH (2017) Distribution and importance of microplastics in the marine environment: a review of the sources, fate, effects, and potential solutions—ScienceDirect. Environ Int 102:165–176
Bergmann M, Mützel S, Primpke S et al (2019) White and wonderful? Microplastics prevail in snow from the Alps to the Arctic. Sci Adv 5:1157
Browne MA, Galloway T, Thompson R (2007) Microplastic—an emerging contaminant of potential concern? Integr Environ Assess Manag 3:559–561
Cai LQ, Wang JD, Peng JP et al (2017) Characteristic of microplastics in the atmospheric fallout from Dongguan City, China: preliminary research and first evidence. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:24928–24935
Chen G, Feng Q, Wang J (2020) Mini-review of microplastics in the atmosphere and their risks to humans. Sci Total Environ 703:135504
Dehghani S, Moore F, Akhbarizadeh R (2017) Microplastic pollution in deposited urban dust, Tehran metropolis, Iran. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:20360–20371
Deng Y, Zhang Y, Lemos B et al (2017) Tissue accumulation of microplastics in mice and biomarker responses suggest widespread health risks of exposure. Sci Rep 7:46687
Dris R, Gasperi J, Rocher V et al (2015) Microplastic contamination in an urban area: a case study in Greater Paris. Environ Chem 12:2015
Dris R, Gasperi J, Saad M et al (2016) Synthetic fibers in atmospheric fallout: a source of microplastics in the environment? Mar Pollut Bull 104:290–293
Dris R, Gasperi J, Mirande C et al (2017) A first overview of textile fibers, including microplastics, in indoor and outdoor environments. Environ Pollut 221:453–458
Gasperi J, Wright SL, Dris R et al (2018) Microplastics in air: are we breathing it in? Curr Opin Environ Sci Health 1:1–5
Haiyan X, David D, Benoit N et al (2003) Role of residual additives in the cytotoxicity and cytokine release caused by polyvinyl chloride particles in pulmonary cell cultures. Toxicol Sci 72:1
Klein M, Fischer EK (2019) Microplastic abundance in atmospheric deposition within the Metropolitan area of Hamburg, Germany. Sci Total Environ 685:96–103
Liu C, Li J, Zhang Y et al (2019a) Widespread distribution of PET and PC microplastics in dust in urban China and their estimated human exposure. Environ Int 128:116–124
Liu K, Wang X, Fang T et al (2019b) Source and potential risk assessment of suspended atmospheric microplastics in Shanghai. Sci Total Environ 675:462–471
Liu K, Wang X, Wei N et al (2019c) Accurate quantification and transport estimation of suspended atmospheric microplastics in megacities: implications for human health. Environ Int 132:105127
Liu K, Wu T, Wang X et al (2019d) Consistent transport of terrestrial microplastics to the ocean through atmosphere. Environ Sci Technol 53:10612–10619
Napper IE, Thompson RC (2016) Release of synthetic microplastic plastic fibres from domestic washing machines: effects of fabric type and washing conditions. Mar Pollut Bull 112:39–45
Pauly JL, Stegmeier SJ, Allaart HA et al (1998) Inhaled cellulosic and plastic fibers found in human lung tissue. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark Prev 7:419–428
Prata JC (2018) Airborne microplastics: consequences to human health? Environ Pollut 234:115–126
Prata JC, da Costa JP, Lopes I et al (2020) Environmental exposure to microplastics: an overview on possible human health effects. Sci Total Environ 702:134455
Song Y, Li X, Du X (2009) Exposure to nanoparticles is related to pleural effusion, pulmonary fibrosis and granuloma. Eur Respir J 34:559
Thompson RC (2004) Lost at Sea: where is all the plastic? Science 304:838
Vianello A, Jensen RL, Liu L et al (2019) Simulating human exposure to indoor airborne microplastics using a Breathing Thermal Manikin. Sci Rep 9:8670
Wang X, Li C, Liu K et al (2020) Atmospheric microplastic over the South China Sea and East Indian Ocean: abundance, distribution and source. J Hazard Mater 389:121846
Wright SL, Ulke J, Font A et al (2020) Atmospheric microplastic deposition in an urban environment and an evaluation of transport. Environ Int 136:105411
Yukioka S, Tanaka S, Nabetani Y et al (2020) Occurrence and characteristics of microplastics in surface road dust in Kusatsu (Japan), Da Nang (Vietnam), and Kathmandu (Nepal). Environ Pollut 256:113447
Zhang J, Wang L, Kannan K (2020a) Microplastics in house dust from 12 countries and associated human exposure. Environ Int 134:105314–105320
Zhang Q, Zhao Y, Du F et al (2020b) Microplastic fallout in different indoor environments. Environ Sci Technol 54:6530–6539
Zhang Y, Kang S, Allen S et al (2020c) Atmospheric microplastics: a review on current status and perspectives. Earth Sci Rev 203:103118
Zhou Q, Tian C, Luo Y (2017) Various forms and deposition fluxes of microplastics identified in the coastal urban atmosphere. Chin Sci Bull 62:3902–3909
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by National Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 22006066) and the Talent-Recruiting Program of Nanjing Institute of Technology (Grant No. YKJ2019100).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Huang, J., Zhu, F. et al. Airborne Microplastics: A Review on the Occurrence, Migration and Risks to Humans. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 107, 657–664 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-021-03180-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-021-03180-0