Abstract
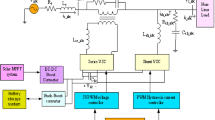
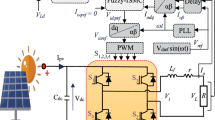
The main purpose of this paper to compare and analyze three types of controllers in the three phases DC–AC inverters in hybrid renewable energy source (HRES) systems. To achieve this, two modern controllers are developed and compared based on sliding mode control (SMC) and artificial neural network techniques. The HRESs comprise photovoltaic (PV), wind turbines, battery storage systems, and transmission lines connected to infinite bus bars via a step-up transformer. The developed controllers at the inverter side utilize both voltage control and current regulation. A DC–DC boost converter is employed to set up a voltage demand at the point of common coupling (PCC). Then, the formulation of an HRES with the developed controllers is presented. The developed controllers are considered to operate under various solar radiations, temperatures, and wind speed loading conditions. The HRESs with the developed controllers are simulated via MATLAB/Simulink to verify the effectiveness of the developed controllers. The obtained results demonstrate that adaptive SMC and artificial ANN control techniques give better results in terms of input power, output power, current, and voltage when compared to classic PI control.
































Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- I :
-
Output current of a PV module (V)
- I ph :
-
Photo-generated current (A)
- I sc :
-
PV cell short circuit current (A)
- I c :
-
PV cell output current (A)
- I o :
-
Reverse saturation current (A)
- G :
-
Solar radiation (W/m2)
- K :
-
Boltzmann’s constant (J/K)
- T :
-
PV cell temperature (K)
- T r :
-
Reference temperature (K)
- V c :
-
PV cell output voltage (V)
- R s :
-
Series resistance of a PV cell (ohm)
- R sh :
-
Shunt resistance of a PV cell (ohm)
- V :
-
PV module output voltage (V)
- V oc :
-
PV cell open-circuit voltage (V)
- P :
-
Output power of a PV module (W)
- V d and V q :
-
Stator voltages in the d-q axis (V)
- ω s :
-
Angular velocity of the synchronously rotating reference frame (rad/s)
- \({C}_{\mathrm{p}}\) :
-
Power coefficient of a wind turbine
- \({P}_{\mathrm{m}}\) :
-
Mechanical power of a wind turbine (W)
- \(\dot{m}\) :
-
Air mass (kg/s)
- \(\rho\) :
-
Air density (kg/m3)
- V w :
-
Wind speed (m/s)
- A :
-
Rotor blade area (m2)
- R :
-
Wind turbine rotor radius (m)
- λ r :
-
Tip speed ratio
- T m :
-
Mechanical torque (N·m)
- Β :
-
Pitch angle of blades (deg)
- ω m :
-
Wind turbine rotational speed (rad/s)
- K cp :
-
Power coefficient constant of a wind turbine
- N :
-
Rotational speed (rpm)
- V S :
-
Converter input voltage (V)
- V O :
-
Boost converter output voltage (V)
- D :
-
Duty cycle of a boost converter
- K p :
-
Proportional control
- K i :
-
Integral control
- G(s):
-
Functions of the variable s
- RMSE:
-
Root mean square error
- RE:
-
Relative error
- R cor :
-
Correlation coefficient
References
Lal, D.K., Dash, B.B., Akella, A.K.: Optimization of PV/wind/micro-hydro/diesel hybrid power system in HOMER for the study area. Int J Electr Eng Inf (IJEEI) 3(3), 307 (2011)
De Persis, C., Tesi, P.: Formulas for data-driven control: stabilization, optimality, and robustness. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 65(3), 909–924 (2020)
Yousef, A.M., Ebeed, M., Abo-Elyousr, F.K., Elnozohy, A., Mohamed, M., Abdelwahab, S.A.M.: Optimization of PID controller for hybrid renewable energy system using adaptive sine cosine algorithm. Int. J. Renew. Energy Res. IJRER 10(2), 670–677 (2020)
Wang, H., Hua, L., Guo, Y., Lu, C.: Control of Z-axis MEMS gyroscope using adaptive fractional order dynamic sliding mode approach. IEEE Access 7, 133008–133016 (2019)
Gao, P., Zhang, G., Ouyang, H., Mei, L.: An adaptive super twisting nonlinear fractional order PID sliding mode control of permanent magnet synchronous motor speed regulation system based on extended state observer. IEEE Access 8, 53498–53510 (2020)
Xu, S.S., Chen, C., Wu, Z.: Study of nonsingular fast terminal sliding-mode fault-tolerant control. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 62(6), 3906–3913 (2015)
Zhang, X., Zhou, Z.: Integrated fault estimation and fault tolerant attitude control for rigid spacecraft with multiple actuator faults and saturation. IET Control Theory Appl. 13(15), 2365–2375 (2019)
Syafaruddin, E., Karatepe, T.H.: Artificial neural network-polar coordinated fuzzy controller based maximum power point tracking control under partially shaded conditions. IET Renew. Power Gener. 3(2), 239–253 (2009)
H. Khorashadi-Zadeh: Power transformer differential protection scheme based on symmetrical component and artificial neural network. 7th Seminar on neural network applications in electrical engineering, 2004. NEUREL, Belgrade, Serbia, pp. 261–265, (2004)
Voloshin, E. A., Voloshin, A. A., Usachev, S. S., Ententeev, A. R., Maksudov B. T., Livshits, S. A.: Increase of efficiency of relay protection reliability in modes with deep saturation of current transformers using the methodology based on the application of Artificial Neural Networks. 2018 International youth scientific and technical conference relay protection and automation (RPA), Moscow, pp. 1–14, (2018)
Kalaam, R.N., Muyeen, S.M., Al-Durra, A., Hasanien, H.M., Al-Wahedi, K.: Optimisation of controller parameters for grid-tied photovoltaic system at faulty network using artificial neural network-based cuckoo search algorithm. IET Renew. Power Gener. 11(12), 1517–1526 (2017)
Yoo, H., Nguyen, T., Kim, H.: Consensus-based distributed coordination control of hybrid AC/DC microgrids. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 11(2), 629–639 (2020)
Abdelwahab, S.A.M., Abdellatif, W.S.E., Hamada, A.M.: Comparative analysis of the modified perturb and observe with different MPPT techniques for PV grid connected systems. Int. J. Renew. Energy Res. IJRER 10(1), 156–164 (2020)
Ayvaz, E., Kaplan, K., Kuncan, M.: An integrated LSTM neural networks approach to sustainable balanced scorecard-based early warning system. IEEE Access 8, 37958–37966 (2020)
Chen, J., Park, J.H., Xu, S.: Stability analysis for neural networks with time-varying delay via improved techniques. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 49(12), 4495–4500 (2019)
Yousef, A.M., Ibrahem, H.A., Abo-elyousr, F.K., Mohamed, M.: Sliding mode control for three phase PV grid connected energy system using LCL filter. Minia J Eng. Technol. (MJET) 36(2), 1 (2017)
Zhang, H., Yue, D., Xie, X.: Distributed model predictive control for hybrid energy resource system with large-scale decomposition coordination approach. IEEE Access 4, 9332–9344 (2016)
Lubbad, M. M., El-Amary, N. H., Abdelaziz A. Y.: Sliding mode control for hybrid power sources micro-grid. 2019 21st International middle east power systems conference (MEPCON), Cairo, Egypt, pp. 650–655 (2019)
Qi, G., Chen, A., Chen, J.: Improved control strategy of interlinking converters with synchronous generator characteristic in islanded hybrid AC/DC microgrid. CPSS Trans. Power Electron. Appl. 2(2), 149–158 (2017)
Awad H., Abdalfatah, S., Hegazy H., Elkholy E. E.: Hybrid PV/FC system design and simulation. 2019 21st international middle east power systems conference (MEPCON), Cairo, Egypt, pp. 1025–1030 (2019)
Rmili, L., Hamouda, M., Rahmani, S., Fortin, H., Al-Haddad, B.K.: PWM-based integral sliding-mode controller for unity input power factor operation of indirect matrix converter. J. Power Electron. 17(4), 1048–1057 (2017)
Shan, Y., Hu, J., Chan, K.W., Fu, Q., Guerrero, J.M.: Predictive control of bidirectional DC–DC converters and AC/DC interlinking converters—a new control method for PV-wind-battery microgrids. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 10(4), 1823–1833 (2019)
Elbaset, A.A., Abdelwahab, S.A.M., Ibrahim, H.A., Eid, M.A.E.: Performance analysis of photovoltaic systems with energy storage systems. Renewable and Green Energy. Springer, Berlin (2019)
Pradhan, S., Singh, B., Panigrahi, B.K., Murshid, S.: A composite sliding mode controller for wind power extraction in remotely located solar PV–wind hybrid system. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 66(7), 5321–5331 (2019)
Baghaee, H. R., Mirsalim, M., Gharehpetian G. B., Talebi, H. A.: Decentralized sliding mode control of WG/PV/FC microgrids under unbalanced and nonlinear load conditions for on- and off-grid modes. IEEE Syst J. 12(4):3108–3119, (2018)
Alaboudy, A.H.K., Elbaset, A.A., Abdelwahab, S.A.M.: Effect of dc link capacitance on stand-alone PV system operation with fluctuated dc resistive loads. Port. Said Eng. Res. J. 19(1), 121–128 (2015)
Dessouky, S. S., Abdellatif, W. S.E., Abdelwahab S. A. M., Ali M. A.: Maximum power point tracking achieved of DFIG-based wind turbines using perturb and observant method. IEEE international middle-east power systems conference, December 18–20 (2018)
Polinder, H., van der Pijl, F.F.A., de Vilder, G., Tavner, P.J.: Comparison of direct-drive and geared generator concepts for wind turbines. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 21(3), 725–733 (2006)
Yousef, A.M., Abo-Elyousr, F.K., Elnozohy, A., Mohamed, M., Abdelwahab, S.A.M.: Fractional order PI control in hybrid renewable power generation system to three phase grid connection. Int. J. Elect. Eng. Inf. 12(3), 1 (2020)
Eid, M. A. E., Elbaset, A. A., Ibrahim H. A., Abdelwahab S. A. M.: Modelling, simulation of MPPT using perturb and observe and incremental conductance techniques for stand-alone PV Systems. 2019 21st international middle east power systems conference, Cairo, Egypt, pp. 429–434 (2019)
Kwonhue C., Huaping L.: Phase-locked loop and synchronization. problem-based learning in communication systems using MATLAB and Simulink, IEEE, pp.135–150 (2016)
Seidi Khorramabadi, S., Bakhshai, A.: Critic-based self-tuning PI structure for active and reactive power control of VSCs in microgrid systems. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid. 6(1), 92–103 (2015)
Souza de Santana, E., Jesus Fiais Cerqueira, J., Silva Flanklin, T.: Fuzzy and PI controllers in pumping water system using photovoltaic electric generation. IEEE Latin Am. Trans. 12(6), 1049–1054 (2014)
Yang, C., Jiang, Y., He, W., Na, J., Li, Z., Xu, B.: Adaptive parameter estimation and control design for robot manipulators with finite-time convergence. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 65(10), 8112–8123 (2018)
Leland, R.P.: Adaptive control of a MEMS gyroscope using Lyapunov methods. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 14(2), 278–283 (2006)
Paiva, G. M. D., Pimentel, S. P., Marra, E. G., Alvarenga, B. P. D., Mussetta M., Leva, S.: Intra-day forecasting of building-integrated PV systems for power systems operation using ANN ensemble. 2019 IEEE Milan PowerTech, Milan, Italy, pp. 1–5, (2019)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Elnozahy, A., Yousef, A.M., Abo-Elyousr, F.K. et al. Performance improvement of hybrid renewable energy sources connected to the grid using artificial neural network and sliding mode control. J. Power Electron. 21, 1166–1179 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43236-021-00242-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s43236-021-00242-8