Abstract
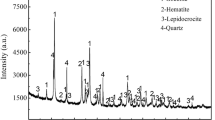
The non-isothermal magnetization roasting process and isothermal magnetization roasting process of siderite ore were investigated using thermogravimetric (TG) analysis and a real-time infrared gas analyzer. X-ray diffraction (XRD) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) with energy dispersive spectroscopy (EDS) were used to analyze the characteristics of samples. The results showed that the decomposition degree and decomposition rate of siderite ore were vitally affected by heating rate and roasting temperature. It was determined that A1 reaction model (f(α) = 1 − α) and A3/2 reaction model (f(α) = (3/2)(1 − α)[−ln(1 − α)]1/2) were the most probable mechanism function of the non-isothermal decomposition process and isothermal decomposition process, respectively. The phase transformation and decomposition mechanism during the roasting process were evaluated. Siderite decomposed in the process of magnetization roasting, released CO and CO2, and transformed into strongly magnetic magnetite. The SEM images highlighted that as the decomposition progressed, the structure of roasted samples was destroyed, and an increasing number of cracks and pores emerged on the surface, which is advantageous to the following grinding process.













Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Sun Y, Han Y, Gao P, Wei X, Li G (2015) Thermogravimetric study of coal-based reduction of oolitic iron ore: kinetics and mechanisms. Int J Min Process 143:87–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.minpro.2015.09.005
Zhang X, Han Y, Sun Y, Li Y (2019) Innovative utilization of refractory iron ore via suspension magnetization roasting: a pilot-scale study. Powder Technol 352:16–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2019.04.042
Sun Y, Gao P, Han Y, Ren D (2013) Reaction behavior of Iron minerals and metallic Iron particles growth in coal-based reduction of an Oolitic Iron ore. Indust Eng Chem Res 52(6):2323–2329. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie303233k
Tang Z, Gao P, Sun Y, Han Y, Li E, Chen J, Zhang Y (2020) Studies on the fluidization performance of a novel fluidized bed reactor for iron ore suspension roasting. Powder Technol 360:649–657. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2019.09.092
Zhao Q, Xue J, Chen W (2019) Upgrading of iron concentrate by fluidized-bed magnetizing roasting of siderite to magnetite in CO–H2–N2 atmosphere. Trans Indian Institute Metals 72(5):1381–1391. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-019-01636-w
Zhao Q, Xue J, Chen W (2020) Mechanism of improved magnetizing roasting of siderite–hematite iron ore using a synergistic CO–H2 mixture. J Iron Steel Res Int 27(1):12–21. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-019-00242-w
Luo Y, Zhu D, Pan J, Zhou X (2016) Thermal decomposition behaviour and kinetics of Xinjiang siderite ore. Min Process Extract Metallurgy 125(1):17–25. https://doi.org/10.1080/03719553.2015.1118213
Yu J, Han Y, Li Y, Gao P (2017) Beneficiation of an iron ore fines by magnetization roasting and magnetic separation. Int J Min Process 168:102–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.minpro.2017.09.012
Yuan S, Zhou W, Han Y, Li Y (2019) Selective enrichment of iron from fine-grained complex limonite using suspension magnetization roasting followed by magnetic separation. Separation Sci Technol 55(18):3427–3437. https://doi.org/10.1080/01496395.2019.1677715
Roy SK, Nayak D, Dash N, Dhawan N, Rath SS (2020) Microwave-assisted reduction roasting—magnetic separation studies of two mineralogically different low-grade iron ores. Int J Min Metallurgy Mater 27(11):1449–1461. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-020-1992-5
Li Y, Wang R, Han Y, Wei X (2015) Phase transformation in suspension roasting of oolitic hematite ore. J Central South Univ 22(12):4560–4565. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-015-3006-8
Yu J, Han Y, Li Y, Gao P, Sun Y (2017) Separation and recovery of iron from a low-grade carbonate-bearing iron ore using magnetizing roasting followed by magnetic separation. Separation Sci Technol 52(10):1768–1774. https://doi.org/10.1080/01496395.2017.1296867
Chun T, Zhu D, Pan J (2015) Simultaneously roasting and magnetic separation to treat low grade siderite and hematite ores. Min Process Extract Metallurgy Rev 36(4):223–226. https://doi.org/10.1080/08827508.2014.928620
Celikdemir M, Sarikaya M, Depci T, Aydogmus R (2016) Influence of microwave heating and thermal auxiliary on decomposition of siderite. IOP Conf Ser: Earth Environ Sci 44:052002. https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1088/1755-1315/44/5/052002
Sun Y, Zhu X, Han Y, Li Y (2019) Green magnetization roasting technology for refractory iron ore using siderite as a reductant. J Cleaner Product 206:40–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.09.113
Zhang Q, Sun Y, Han Y, Li Y (2020) Pyrolysis behavior of a green and clean reductant for suspension magnetization roasting. J Cleaner Product 268:122173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.122173
Zhu X, Han Y, Sun Y, Li Y, Wang H (2020) Siderite as a novel reductant for clean utilization of refractory iron ore. J Cleaner Product 245:118704. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.118704
Zhu D, Luo Y, Pan J, Zhou X (2016) Reaction mechanism of siderite lump in coal-based direct reduction. High Temp Mater Process 35(2):185–194. https://doi.org/10.1515/htmp-2014-0176
Zhang X, Han Y, Li Y, Sun Y (2017) Effect of heating rate on pyrolysis behavior and kinetic characteristics of siderite. Minerals 7(11):211. https://doi.org/10.3390/min7110211
Jagtap S, Pande A, Gokarn A (1992) Kinetics of thermal decomposition of siderite: effect of particle size. Int J Min Process 36(1–2):113–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/0301-7516(92)90068-8
Zakharov VY, Adonyi Z (1986) Thermal decomposition kinetics of siderite. Thermochim Acta 102:101–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/0040-6031(86)85318-7
Alkac D, Atalay Ü (2008) Kinetics of thermal decomposition of Hekimhan–Deveci siderite ore samples. Int J Min Process 87(3–4):120–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.minpro.2008.02.007
Gotor FJ, Macias M, Ortega A, Criado JM (2000) Comparative study of the kinetics of the thermal decomposition of synthetic and natural siderite samples. Physics Chem Min 27(7):495–503. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002690000093
Yuan S, Zhou W, Han Y, Li Y (2020) Selective enrichment of iron from fine-grained complex limonite using suspension magnetization roasting followed by magnetic separation. Separation Sci Technol 55(18):3427–3437. https://doi.org/10.1080/01496395.2019.1677715
Ponomar V, Dudchenko N, Brik A (2017) Phase transformations of siderite ore by the thermomagnetic analysis data. J Magnetism Magnetic Mater 423:373–378. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2016.09.124
Lavina B, Dera P, Downs RT, Yang W, Sinogeikin S, Meng Y, Shen G, Schiferl D (2010) Structure of siderite FeCO3 to 56 GPa and hysteresis of its spin-pairing transition. Phys Rev B 82(6):064110. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.82.064110
Ponomar VP, Dudchenko NO, Brik AB (2018) Synthesis of magnetite powder from the mixture consisting of siderite and hematite iron ores. Minerals Eng 122:277–284. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2018.04.018
Sun Y, Han Y, Wei X, Gao P (2016) Non-isothermal reduction kinetics of oolitic iron ore in ore/coal mixture. J Thermal Anal Calorimetry. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-015-4863-y
Budrugeac P, Petre AL, Segal E (1996) Some problems concerning the evaluation of non-isothermal kinetic parameters: solid-gas decompositions from thermogravimetric data. J Thermal Anal Calorimetry 47(1):123–134. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf01982692
Škvára F, Šesták J (1975) Computer calculation of the mechanism and associated kinetic data using a non-isothermal integral method. J Thermal Anal Calorimetry 8(3):477–489. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01910127
Yu J, Han Y, Li Y, Gao P, Li W (2017) Mechanism and kinetics of the reduction of hematite to magnetite with CO–CO2 in a micro-fluidized bed. Minerals 7(11):209
Dhupe A, Gokarn A (1990) Studies in the thermal decomposition of natural siderites in the presence of air. Int J Mineral Process 28(3–4):209–220. https://doi.org/10.1016/0301-7516(90)90043-X
Van Siclen CD (1996) Random nucleation and growth kinetics. Phys Rev B 54(17):11845–11848. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.54.11845
Zhang Q, Sun Y, Han Y, Li Y, Gao P (2020) Effect of thermal oxidation pretreatment on the magnetization roasting and separation of refractory iron ore. Mineral Process Extractive Metallurgy Rev. https://doi.org/10.1080/08827508.2020.1837126
Funding
The authors acknowledge the financial support provided by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51874071, 51734005), the Fok Ying Tung Education Foundation for Young Teachers in the Higher Education Institutions of China (No. 161045), and Liao Ning Revitalization Talents Program (XLYC1807111).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Qiang Zhang: data curation, formal analysis, validation, writing – original draft. Yongsheng Sun: conceptualization, funding acquisition, resources, writing – review & editing. Yuexin Han: data curation, funding acquisition, project administration, resources. Peng Gao: data curation, resources, supervision. Yanjun Li: Data curation, resources, supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Q., Sun, Y., Han, Y. et al. Thermal Decomposition Kinetics of Siderite Ore during Magnetization Roasting. Mining, Metallurgy & Exploration 38, 1497–1508 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42461-021-00417-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42461-021-00417-8