Abstract
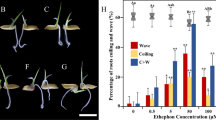
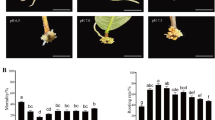
The growth of plant roots is regulated by various factors. Brassinosteroids (BRs) can induce asymmetric root growth (ARG) to form waves and coils, and this phenomenon can be eliminated by ethylene (ETH) inhibitors aminoacetic acid (AOA) or silver thiosulfate (STS), indicating this process depends on ETH pathway. Nevertheless, the research on related genes has not been reported. In this study, four treatments (Water, Brassinolide (BL), BL + AOA, and BL + STS) were set up using the seedlings of Oryza sativa as materials. The differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in BR-induced ARG via ETH pathway were identified by transcriptome sequencing, weighted gene co-expression network analysis (WGCNA), and real-time quantitative PCR (qRT-PCR). Finally, we screened 70 DEGs, including ALPHA-EXPANSINs (OsEXPAs), WALL-ASSOCIATED RECEPTOR KINASE-LIKE 16 (OsWAKL16), and TRANSMEMBRANE KINASE (OsTMK) that regulated cell elongation and expansion, as well as plant hormone synthase genes, 1-AMINO-CYCLOPROPANE-1-CARBOXYLIC ACID OXIDASEs (OsACOs), OsYUCCAs, and CYTOKININ OXIDASE(OsCKX). Most of them were up-regulated by BRs via ETH pathway. In addition, the receptor-like kinase (RLK) gene ROOT MEADNDER CURLING (OsRMC), a negative regulator in jasmonic acid-induced ARG, could be inhibited by BRs, and this process also depended on ETH pathway. The identification of the above genes provides evidence for revealing the molecular mechanism in the process.





Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The transcriptome sequencing data has been submitted to the SRA database of NCBI with the accession number of SRP278550.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Bajguz A (2007) Metabolism of brassinosteroids in plants. Plant Physiol Biochem 45:95–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2007.01.002
Beemster GTS, Dai N, Wang W, Patterson SE, Bleecker AB (2013) The TMK subfamily of receptor-like kinases in Arabidopsis display an essential role in growth and a reduced sensitivity to auxin. PLoS ONE 8:e60990. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0060990
Beyer EM (1976) A potent inhibitor of ethylene action in plants. Plant Physiol 58:268–271. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.58.3.268
Beyer EM (1979) Effect of silver ion, carbon dioxide, and oxygen on ethylene action and metabolism. Plant Physiol 63:169–173. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.63.1.169
Blancaflor EB, Masson PH (2003) Plant gravitropism. Unraveling the ups and downs of a complex process. Plant Physiol 133(4):1677–1690. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.103.032169
Buer CS, Wasteneys GO, Masle J (2003) Ethylene modulates root-wave responses in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 132(2):1085–1096. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.102.019182
Cai ZP, Yang W, Zhang HY, Luo JJ, Wu FH, Jing X, Meng SL, Wang XY, Yu XD (2018) Ethylene participates in the brassinolide-regulated asymmetric growth of O sativa root. S Afr J Bot 119:86–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sajb.2018.08.017
Cao L, Fu Y, Yu XD, Cai ZP, Luo JJ, Tang Z, Huang XW (2019) Brassinosteroid induces asymmetric growth of primary roots in Brassica chinensis L. Chin J Trop Crops 40:468–474. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1000-2561.2019.03.008
Choi D, Cho H-T, Lee Y (2006) Expansins: expanding importance in plant growth and development. Physiol Plant 126:511–518. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-3054.2005.00612.x
Clouse SD, Langford M, McMorris TC (1996) A brassinosteroid-insensitive mutant in Arabidopsis thaliana exhibits multiple defects in growth and development. Plant Physiol 111(3):671–678. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.111.3.671
Darwin C (1880) The power of movements in plants. John Murray, London
Decreux A, Messiaen J (2005) Wall-associated kinase WAK1 interacts with cell wall pectins in a calcium-induced conformation. Plant Cell Physiol 46:268–278. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pci026
Fridman Y, Elkouby L, Holland N, Vragović K, Elbaum R, Savaldi-Goldstein S (2014) Root growth is modulated by differential hormonal sensitivity in neighboring cells. Genes Dev 28:912–920. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.239335.114
Fujioka S, Li J, Choi Y-H, Seto H, Takatsuto S, Noguchi T, Watanabe T, Kuriyama H, Yokota T, Chory J, Sakurai A (1997) The Arabidopsis deetiolated2 mutant is blocked early in brassinosteroid biosynthesis. Plant Cell 1997(9):1951–1962. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.9.11.1951
Gudesblat GE, Russinova E (2011) Plants grow on brassinosteroids. Curr Opin Plant Biol 14:530–537. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbi.2011.05.004
Yueqing H, Shitou X, Yi S, Huiqun W, Weigui L, Shengying S, Langtao X (2016) Brassinolide increases potato root growth in vitro in a dose-dependent way and alleviates salinity stress. BioMed Res Int. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/8231873
Huang W-N, Liu H-K, Zhang H-H, Chen Z, Guo Y-D, Kang Y-F (2013) Ethylene-induced changes in lignification and cell wall-degrading enzymes in the roots of mungbean (Vigna radiata) sprouts. Plant Physiol Biochem 73:412–419. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2013.10.020
Jiang J, Li J, Xu Y, Han YE, Bai YUE, Zhou G, Lou Y, Xu Z, Chong K (2007) RNAi knockdown of Oryza sativa root meander curling gene led to altered root development and coiling which were mediated by jasmonic acid signalling in rice. Plant Cell Environ 30:690–699. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3040.2007.01663.x
Kohl M, Wiese S, Warscheid B (2011) Cytoscape: software for visualization and analysis of biological networks. Methods Mol Biol 696:291–303. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-60761-987-1_18
Kurepin LV, Bey MA, Back TG et al (2016) Structure-Function Relationships of Four Stereoisomers of a Brassinolide Mimetic on Hypocotyl and Root Elongation of the Brassinosteroid-Deficient det2-1 Mutant of Arabidopsis. J Plant Growth Regul 35:215–221. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-015-9523-8
Lally D, Ingmire P, Tong H-Y, He Z-H (2001) Antisense expression of a cell wall-associated protein kinase, WAK4, inhibits cell elongation and alters morphology. Plant Cell 13:1317–1332. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.13.6.1317
Langfelder P, Horvath S (2008) WGCNA: an R package for weighted correlation network analysis. BMC Bioinform 9:559. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-9-559
Lanza M, García-Ponce B, Castrillo G, Catarecha P, Sauer M, Rodríguez M, Paez A, Sánchez-Bermejo E, Mohan TC, Puerto Y, Sandalio L, Paz-Ares J, Leyva A (2012) Role of actin cytoskeleton in brassinosteroid signaling and in its integration with the auxin response in plants. Dev Cell 22:1275–1285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2012.04.008
Lee HY, Yoon GM (2018) Regulation of ethylene biosynthesis by phytohormones in etiolated rice (Oryza sativa L.) Seedlings. Mol Cells 41:311–319. https://doi.org/10.14348/molcells.2018.2224
Jianming L, Kyoung N (2002) Regulation of brassinosteroid signaling by GSK3/SHAGGY-like kinase. Science 295:1299–1301. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1065769
Liu G, Gao S, Tian H, Wu W, Robert HS, Ding Z (2016) Local transcriptional control of YUCCA regulates auxin promoted root-growth inhibition in response to aluminium stress in Arabidopsis. PLoS Genet 12(10):e1006360. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1006360
Lourenço TF, Serra TS, Cordeiro AM, Swanson SJ, Gilroy S, Saibo NJM, Oliveira MM (2015) The rice E3-Ubiquitin ligase HIGH EXPRESSION OF OSMOTICALLY RESPONSIVE GENE1 modulates the expression of ROOT MEANDER CURLING a gene Involved in root mechanosensing, through the interaction with two ETHYLENE-RESPONSE FACTOR transcription factors. Plant Physiol 169:2275–2287. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.15.01131
Mandava NB (1988) Plant growth-promoting brassinosteroids. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 39:23–52. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.pp.39.060188.000323
McQueen-Mason S, Durachkoand DM, Cosgrove DJ (1992) Two endogenous proteins that induce cell wall extension in plants. Plant Cell 4(11):1425–1433. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.4.11.1425
Migliaccio F, Piconese S (2001) Spiralizations and tropisms in Arabidopsis roots. Trends Plant Sci 6:561–565. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1360-1385(01)02152-5
Mori A, Toyota M, Shimada M, Mekata M, Kurata T, Tasaka M, Morita MT (2016) Isolation of new gravitropic mutants under hypergravity conditions. Front Plant Sci 7:01443. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.01443
Nymeijer K, Visser T, Brilman W, Wessling M (2004) Analysis of the complexation reaction between Ag+ and ethylene. Ind Eng Chem Res 43:2627–2635. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie0341350
Okada K, Shimura Y (1990) Reversible root tip rotation in Arabidopsis seedlings induced by obstacle-touching stimulus. Science 250(4978):274–276. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.250.4978.274
Park C-H, Seo C, Park YJ, Youn J-H, Roh J, Moon J, Kim S-K (2019) BES1 directly binds to the promoter of the ACC oxidase 1 gene to regulate gravitropic response in the roots of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Signal Behav 15:1690724. https://doi.org/10.1080/15592324.2019.1690724
Peiser GD, Wang TT, Hoffman NE, Yang SF, Liu HW, Walsh CT (1984) Formation of cyanide from carbon 1 of 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid during its conversion to ethylene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 81:3059–3063. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.81.10.3059
Pfaffl MW (2001) A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 29:45. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/29.9.e45
Robert HS, Friml J (2009) Auxin and other signals on the move in plants. Nat Chem Biol 5(5):325–332. https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.170
Roy R, Bassham DC (2014) Root growth movements: waving and skewing. Plant Sci 42–47:0168–9452. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2014.01.007
Spollen WG, LeNoble ME, Samuels TD, Bernstein N, Sharp RE (2000) Abscisic acid accumulation maintains maize primary poot elongation at low water potentials by restricting ethylene production. Plant Physiol 122:967–976. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.122.3.967
Swarup R, Perry P, Hagenbeek D, Van Der Straeten D, Beemster G, Sandberg G, Bhalerao R, Ljung K, Bennett M (2007) Ethylene upregulates auxin biosynthesis in Arabidopsis seedlings to enhance inhibition of root cell elongation. Plant Cell 19:2186–2196. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.107.052100
Tanveer M, Shahzad B, Sharma A, Biju S, Bhardwaj R (2018) 24-Epibrassinolide; an active brassinolide and its role in salt stress tolerance in plants: A review. Plant Physiol Biochem 130:69–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2018.06.035
Vragović K, Sela A, Friedlander-Shani L et al (2015) Translatome analyses capture of opposing tissue-specific brassinosteroid signals orchestrating root meristem differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 112(3):923–928. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1417947112
Wang H, Liang X, Wan Q, Wang X, Bi Y (2009) Ethylene and nitric oxide are involved in maintaining ion homeostasis in Arabidopsis callus under salt stress. Planta 230:293–307. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-009-0946-y
Wang L, Feng Z, Wang X, Wang X, Zhang X (2010) DEGseq: an R package for identifying differentially expressed genes from RNA-seq data. Bioinformatics 26:136–138. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btp612
Woods SL, Roberts JA, Taylor IB (1984) Ethylene-induced root coiling in tomato seedlings. Plant Growth Regul 2:217–225. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00124770
Funding
This work was supported by Hainan Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China [320RC508], Hainan Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China [319MS017], Hainan University Scientific Research Startup Fund Project [kyqd1620], and Innovation and entrepreneurship training program for college students [SA2000008501].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, ZC and JL; Funding acquisition, JL, ZC and XY; Investigation, ZC, ZH, CH, XJ, WY, GJ, and FW; Project administration, ZC; Resources, JL, ZC and XY. Visualization, ZC, ZH, CH, and ZW; Validation, ZC; Writing—original draft, ZC, ZH and CH; Writing—review and editing, ZC and ZH. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to Participate
The authors declare consent to participate.
Consent for Publication
The authors declare consent for publication.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cai, Z., Huang, Z., Huang, C. et al. Transcriptome Analysis on Asymmetric Root Growth of Oryza sativa Induced by Brassinosteroids via Ethylene Pathway. J. Plant Biol. 64, 349–358 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12374-021-09308-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12374-021-09308-3