Abstract
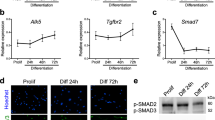
Although originally discovered inducing important biological functions in the nervous system, repulsive guidance molecule a (RGMa) has now been identified as a player in many other processes and diseases, including in myogenesis. RGMa is known to be expressed in skeletal muscle cells, from somites to the adult. Functional in vitro studies have revealed that RGMa overexpression could promote skeletal muscle cell hypertrophy and hyperplasia, as higher efficiency in cell fusion was observed. Here, we extend the potential role of RGMa during C2C12 cell differentiation in vitro. Our results showed that RGMa administrated as a recombinant protein during late stages of C2C12 myogenic differentiation could induce myoblast cell fusion and the downregulation of different myogenic markers, while its administration at early stages induced the expression of myogenic markers with no detectable morphological effects. We also found that RGMa effects on skeletal muscle hyperplasia are performed via neogenin receptor, possibly as part of a complex with other proteins. Additionally, we observed that RGMa-neogenin is not playing a role as an inhibitor of the BMP signalling in skeletal muscle cells. This work contributes to placing RGMa as a component of the mechanisms that determine skeletal cell fusion via neogenin receptor.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abmayr SM, Zhuang S, Geisbrecht ER (2008) Myoblast fusion in Drosophila. Methods Mol Biol 475:75–97
Agley CC, Velloso CP, Lazarus NR, Harridge SD (2012) An image analysis method for the precise selection and quantitation of fluorescently labeled cellular constituents: application to the measurement of human muscle cells in culture. J Histochem Cytochem 60:428–438
Akiyama S, Katagiri T, Namiki M, Yamaji N, Yamamoto N, Miyama K, Shibuya H, Ueno N, Wozney JM, Suda T (1997) Constitutively active BMP type I receptors transduce BMP-2 signals without the ligand in C2C12 myoblasts. Exp Cell Res 235:362–369
Asfour HA, Allouh MZ, Said RS (2018) Myogenic regulatory factors: the orchestrators of myogenesis after 30 years of discovery. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 243:118–128
Babai F, Musevi-Aghdam J, Schurch W, Royal A, Gabbiani G (1990) Coexpression of alpha-sarcomeric actin, alpha-smooth muscle actin and desmin during myogenesis in rat and mouse embryos I. Skeletal muscle. Differentiation 44:132–142
Babitt JL, Zhang Y, Samad TA, Xia Y, Tang J, Campagna JA, Schneyer AL, Woolf CJ, Lin HY (2005) Repulsive guidance molecule (RGMa), a DRAGON homologue, is a bone morphogenetic protein co-receptor. J Biol Chem 280:29820–29827
Bae GU, Yang YJ, Jiang G, Hong M, Lee HJ, Tessier-Lavigne M, Kang JS, Krauss RS (2009) Neogenin regulates skeletal myofiber size and focal adhesion kinase and extracellular signal-regulated kinase activities in vivo and in vitro. Molecular Biology of the Cell 20, 4920–4931
Bai G, Pfaff SL (2011) Protease regulation: the Yin and Yang of neural development and disease. Neuron 72:9–21
Bentzinger CF, Wang YX, Rudnicki MA (2012) Building muscle: molecular regulation of myogenesis. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 4
Berger S, Schafer G, Kesper DA, Holz A, Eriksson T, Palmer RH, Beck L, Klambt C, Renkawitz-Pohl R, Onel SF (2008) WASP and SCAR have distinct roles in activating the Arp2/3 complex during myoblast fusion. J Cell Sci 121:1303–1313
Bergstrom DA, Penn BH, Strand A, Perry RL, Rudnicki MA, Tapscott SJ (2002) Promoter-specific regulation of MyoD binding and signal transduction cooperate to pattern gene expression. Mol Cell 9:587–600
Berkes CA, Tapscott SJ (2005) MyoD and the transcriptional control of myogenesis. Semin Cell Dev Biol 16:585–595
Boergermann JH, Kopf J, Yu PB, Knaus P (2010) Dorsomorphin and LDN-193189 inhibit BMP-mediated Smad, p38 and Akt signalling in C2C12 cells. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 42:1802–1807
Brown S, Jayachandran P, Negesse M, Olmo V, Vital E, Brewster R (2019) Rgma-induced Neo1 proteolysis promotes neural tube morphogenesis. J Neurosci 39:7465–7484
Campbell DS, Holt CE (2003) Apoptotic pathway and MAPKs differentially regulate chemotropic responses of retinal growth cones. Neuron 37:939–952
Chal J, Pourquie O (2017) Making muscle: skeletal myogenesis in vivo and in vitro. Development 144:2104–2122
Corradini E, Babitt JL, Lin HY (2009) The RGM/DRAGON family of BMP co-receptors. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 20:389–398
Dahlqvist C, Blokzijl A, Chapman G, Falk A, Dannaeus K, Ibanez CF, Lendahl U (2003) Functional Notch signaling is required for BMP4-induced inhibition of myogenic differentiation. Development 130:6089–6099
De Vries M, Cooper HM (2008) Emerging roles for neogenin and its ligands in CNS development. J Neurochem 106:1483–1492
Demicheva E, Cui YF, Bardwell P, Barghorn S, Kron M, Meyer AH, Schmidt M, Gerlach B, Leddy M, Barlow E, O’Connor E, Choi CH, Huang L, Veldman GM, Rus H, Shabanzadeh AP, Tassew NG, Monnier PP, Muller T, Calabresi PA, Schoemaker H, Mueller BK (2015) Targeting repulsive guidance molecule A to promote regeneration and neuroprotection in multiple sclerosis. Cell Rep 10:1887–1898
Feng J, Wang T, Li Q, Wu X, Qin X (2012) RNA interference against repulsive guidance molecule A improves axon sprout and neural function recovery of rats after MCAO/reperfusion. Exp Neurol 238:235–242
Fujita Y, Yamashita T (2017) The roles of RGMa-neogenin signaling in inflammation and angiogenesis. Inflamm Regen 37:6
Galbiati F, Volonte D, Engelman JA, Scherer PE, Lisanti MP (1999) Targeted down-regulation of caveolin-3 is sufficient to inhibit myotube formation in differentiating C2C12 myoblasts. Transient activation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase is required for induction of caveolin-3 expression and subsequent myotube formation. J Biol Chem 274:30315–30321
Graef IA, Wang F, Charron F, Chen L, Neilson J, Tessier-Lavigne M, Crabtree GR (2003) Neurotrophins and netrins require calcineurin/NFAT signaling to stimulate outgrowth of embryonic axons. Cell 113:657–670
Hagihara M, Endo M, Hata K, Higuchi C, Takaoka K, Yoshikawa H, Yamashita T (2011) Neogenin, a receptor for bone morphogenetic proteins. J Biol Chem 286:5157–5165
Halbrooks PJ, Ding R, Wozney JM, Bain G (2007) Role of RGM coreceptors in bone morphogenetic protein signaling. J Mol Signal 2:4
Harada K, Fujita Y, Yamashita T (2016) Repulsive guidance molecule A suppresses angiogenesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 469:993–999
Hata K, Fujitani M, Yasuda Y, Doya H, Saito T, Yamagishi S, Mueller BK, Yamashita T (2006) RGMa inhibition promotes axonal growth and recovery after spinal cord injury. J Cell Biol 173:47–58
Healey EG, Bishop B, Elegheert J, Bell CH, Padilla-Parra S, Siebold C (2015) Repulsive guidance molecule is a structural bridge between neogenin and bone morphogenetic protein. Nat Struct Mol Biol 22:458–465
Horbelt D, Boergermann JH, Chaikuad A, Alfano I, Williams E, Lukonin I, Timmel T, Bullock AN, Knaus P (2015) Small molecules dorsomorphin and LDN-193189 inhibit myostatin/GDF8 signaling and promote functional myoblast differentiation. J Biol Chem 290:3390–3404
Jorge EC, Ahmed MU, Bothe I, Coutinho LL, Dietrich S (2012) RGMa and RGMb expression pattern during chicken development suggest unexpected roles for these repulsive guidance molecules in notochord formation, somitogenesis, and myogenesis. Dev Dyn 241:1886–1900
Kang JS, Yi MJ, Zhang W, Feinleib JL, Cole F, Krauss RS (2004) Netrins and neogenin promote myotube formation. J Cell Biol 167:493–504
Katagiri T, Akiyama S, Namiki M, Komaki M, Yamaguchi A, Rosen V, Wozney JM, Fujisawa-Sehara A, Suda T (1997) Bone morphogenetic protein-2 inhibits terminal differentiation of myogenic cells by suppressing the transcriptional activity of MyoD and myogenin. Exp Cell Res 230:342–351
Kee N, Wilson N, De Vries M, Bradford D, Key B, Cooper HM (2008) Neogenin and RGMa control neural tube closure and neuroepithelial morphology by regulating cell polarity. J Neurosci 28:12643–12653
Kim JH, Jin P, Duan R, Chen EH (2015) Mechanisms of myoblast fusion during muscle development. Curr Opin Genet Dev 32:162–170
Kislinger T, Gramolini AO, Pan Y, Rahman K, MacLennan DH, Emili A (2005) Proteome dynamics during C2C12 myoblast differentiation. Mol Cell Proteomics 4:887–901
Krauss RS (2010) Regulation of promyogenic signal transduction by cell-cell contact and adhesion. Exp Cell Res 316:3042–3049
Lee NK, Fok KW, White A, Wilson NH, O’Leary CJ, Cox HL, Michael M, Yap AS, Cooper HM (2016) Neogenin recruitment of the WAVE regulatory complex maintains adherens junction stability and tension. Nat Commun 7:11082
Lyons GE, Buckingham ME, Mannherz HG (1991) alpha-Actin proteins and gene transcripts are colocalized in embryonic mouse muscle. Development 111:451–454
Malekzadeh A, Leurs C, van Wieringen W, Steenwijk MD, Schoonheim MM, Amann M, Naegelin Y, Kuhle J, Killestein J, Teunissen CE (2019) Plasma proteome in multiple sclerosis disease progression. Ann Clin Transl Neurol 6:1582–1594
Martins AF, Xavier Neto J, Azambuja A, Sereno ML, Figueira A, Campos-Junior PH, Rosario MF, Toledo CB, Silva GA, Kitten GT, Coutinho LL, Dietrich S, Jorge EC (2015) Repulsive guidance molecules a, b and c are skeletal muscle proteins, and repulsive guidance molecule a promotes cellular hypertrophy and is necessary for myotube fusion. Cells Tissues Organs 200:326–338
Matsunaga E, Tauszig-Delamasure S, Monnier PP, Mueller BK, Strittmatter SM, Mehlen P, Chedotal A (2004) RGM and its receptor neogenin regulate neuronal survival. Nat Cell Biol 6:749–755
Matsunaga E, Nakamura H, Chedotal A (2006) Repulsive guidance molecule plays multiple roles in neuronal differentiation and axon guidance. J Neurosci 26:6082–6088
McKinnell IW, Ishibashi J, Le Grand F, Punch VG, Addicks GC, Greenblatt JF, Dilworth FJ, Rudnicki MA (2008) Pax7 activates myogenic genes by recruitment of a histone methyltransferase complex. Nat Cell Biol 10:77–84
Millay DP, O’Rourke JR, Sutherland LB, Bezprozvannaya S, Shelton JM, Bassel-Duby R, Olson EN (2013) Myomaker is a membrane activator of myoblast fusion and muscle formation. Nature 499:301–305
Monnier PP, Sierra A, Macchi P, Deitinghoff L, Andersen JS, Mann M, Flad M, Hornberger MR, Stahl B, Bonhoeffer F, Mueller BK (2002) RGM is a repulsive guidance molecule for retinal axons. Nature 419:392–395
Mueller TD (2015) RGM co-receptors add complexity to BMP signaling. Nat Struct Mol Biol 22:439–440
Muller T, Trommer I, Muhlack S, Mueller BK (2016) Levodopa increases oxidative stress and repulsive guidance molecule A levels: a pilot study in patients with Parkinson’s disease. J Neural Transm (Vienna) 123:401–406
Musumeci G, Castrogiovanni P, Coleman R, Szychlinska MA, Salvatorelli L, Parenti R, Magro G, Imbesi R (2015) Somitogenesis: from somite to skeletal muscle. Acta Histochem 117:313–328
O’Leary C, Cole SJ, Langford M, Hewage J, White A, Cooper HM (2013) RGMa regulates cortical interneuron migration and differentiation. PLoS One 8:e81711
Olguin HC, Pisconti A (2012) Marking the tempo for myogenesis: Pax7 and the regulation of muscle stem cell fate decisions. J Cell Mol Med 16:1013–1025
Pfaffl MW (2001) A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 29:e45
Pfaffl MW, Horgan GW, Dempfle L (2002) Relative expression software tool (REST) for group-wise comparison and statistical analysis of relative expression results in real-time PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 30:e36
Rajagopalan S, Deitinghoff L, Davis D, Conrad S, Skutella T, Chedotal A, Mueller BK, Strittmatter SM (2004) Neogenin mediates the action of repulsive guidance molecule. Nat Cell Biol 6:756–762
Rochlin K, Yu S, Roy S, Baylies MK (2010) Myoblast fusion: when it takes more to make one. Dev Biol 341:66–83
Rosen GD, Sanes JR, LaChance R, Cunningham JM, Roman J, Dean DC (1992) Roles for the integrin VLA-4 and its counter receptor VCAM-1 in myogenesis. Cell 69:1107–1119
Samad TA, Rebbapragada A, Bell E, Zhang Y, Sidis Y, Jeong SJ, Campagna JA, Perusini S, Fabrizio DA, Schneyer AL, Lin HY, Brivanlou AH, Attisano L, Woolf CJ (2005) DRAGON, a bone morphogenetic protein co-receptor. J Biol Chem 280:14122–14129
Satoh J, Tabunoki H, Ishida T, Saito Y, Arima K (2013) Accumulation of a repulsive axonal guidance molecule RGMa in amyloid plaques: a possible hallmark of regenerative failure in Alzheimer’s disease brains. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 39:109–120
Schwander M, Leu M, Stumm M, Dorchies OM, Ruegg UT, Schittny J, Muller U (2003) Beta1 integrins regulate myoblast fusion and sarcomere assembly. Dev Cell 4:673–685
Shabanzadeh AP, Tassew NG, Szydlowska K, Tymianski M, Banerjee P, Vigouroux RJ, Eubanks JH, Huang L, Geraerts M, Koeberle PD, Mueller BK, Monnier PP (2015) Uncoupling neogenin association with lipid rafts promotes neuronal survival and functional recovery after stroke. Cell Death Dis 6:e1744
Shi S, Hoogaars WM, de Gorter DJ, van Heiningen SH, Lin HY, Hong CC, Kemaladewi DU, Aartsma-Rus A, ten Dijke P, t Hoen PA (2011) BMP antagonists enhance myogenic differentiation and ameliorate the dystrophic phenotype in a DMD mouse model. Neurobiol Dis 41:353–360
Siebold C, Yamashita T, Monnier PP, Mueller BK, Pasterkamp RJ (2017) RGMs: structural insights, molecular regulation, and downstream signaling. Trends Cell Biol 27:365–378
Tanabe S, Fujita Y, Ikuma K, Yamashita T (2018) Inhibiting repulsive guidance molecule-a suppresses secondary progression in mouse models of multiple sclerosis. Cell Death Dis 9:1061
Xia Y, Babitt JL, Bouley R, Zhang Y, Da Silva N, Chen S, Zhuang Z, Samad TA, Brenner GJ, Anderson JL, Hong CC, Schneyer AL, Brown D, Lin HY (2010) Dragon enhances BMP signaling and increases transepithelial resistance in kidney epithelial cells. J Am Soc Nephrol 21:666–677
Xia Y, Yu PB, Sidis Y, Beppu H, Bloch KD, Schneyer AL, Lin HY (2007) Repulsive guidance molecule RGMa alters utilization of bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) type II receptors by BMP2 and BMP4. J Biol Chem 282:18129–18140
Zhang G, Wang R, Cheng K, Li Q, Wang Y, Zhang R, Qin X (2017) Repulsive guidance molecule a inhibits angiogenesis by downregulating VEGF and phosphorylated focal adhesion kinase in vitro. Front Neurol 8:504
Zhao ZW, Lian WJ, Chen GQ, Zhou HY, Wang GM, Cao X, Yang HJ, Hou YP (2012) Decreased expression of repulsive guidance molecule member A by DNA methylation in colorectal cancer is related to tumor progression. Oncol Rep 27:1653–1659
Zhou Z, Xie J, Lee D, Liu Y, Jung J, Zhou L, Xiong S, Mei L, Xiong WC (2010) Neogenin regulation of BMP-induced canonical Smad signaling and endochondral bone formation. Dev Cell 19:90–102
Acknowledgements
We want to thank Dr. Alain Chédotal (Institute De La Vision, Paris, France) for the neogenin construction and Dr. Antonio Figueira from Centro de Energia Nuclear na Agricultura (Universidade de São Paulo, Piracicaba, Brazil) for financing part of this work.
This research was supported by the Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq), the Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES) and the Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de Minas Gerais (FAPEMIG). Alinne do Carmo Costa, Aline Gonçalves Lio Copola and Júlia Meireles Nogueira were supported by Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES) – Financial Code 001. Erika C Jorge received a scholarship from CNPq.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Editor: Tetsuji Okamoto.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
(PNG 2068 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
do Carmo Costa, A., Copola, A.G.L., Carvalho e Souza, C. et al. RGMa can induce skeletal muscle cell hyperplasia via association with neogenin signalling pathway. In Vitro Cell.Dev.Biol.-Animal 57, 415–427 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-021-00555-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-021-00555-9