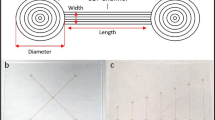
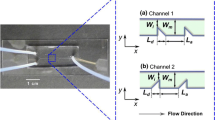
Abstract
The rapid mixing of reagents is critical to a wide range of chemical and biological reactions but is difficult to implement in microfluidic devices, particularly in capillary action/passive pumping devices or in point-of-need environments. Here, we develop a self-pumping asymmetric staggered herringbone mixer made from only laser-ablated glass and tape. This lab-on-a-chip platform is capable of rapid flow (0.14 mL min−1, 1 cm s−1) and fast mixing (< 10 s) without external forces or pumps and is amenable to the flow of non-aqueous solvents. Furthermore, the degree of mixing and flow rates are easily tunable through the length and depth of the herringbone grooves, and the thickness of the double-sided tape that defines the channel height, respectively. The device utility is demonstrated for chemical and biological assays through the reaction of Ni(II) and DMG in ethanol/water and the enzymatic reaction of o-dianisidine with peroxidase, respectively.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altundemir S, Uguz A, Ulgen K (2017) A review on wax printed microfluidic paper-based devices for international health. Biomicrofluidics 11:041501
Bayareh M, Ashani MN, Usefian A (2020) Active and passive micromixers: a comprehensive review. Chem Eng Process 147:107771
Boehle KE, Doan E, Henry S, Beveridge JR, Pallickara SL, Henry CS (2018) Single board computing system for automated colorimetric analysis on low-cost analytical devices. Anal Methods 10:5282–5290
Cai G, Xue L, Zhang H, Lin J, Cai G, Xue L, Zhang H, Lin J (2017) A review on micromixers. Micromachines 8:274–274
Capretto L, Cheng W, Hill M and Zhang X (2011) Microfluidics. In: Lin, B. (ed), Springer Berlin Heidelberg, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp. 27–68.
Cardoso TMG, De Souza FR, Garcia PT, Rabelo D, Henry CS, Coltro WKT (2017) Versatile fabrication of paper-based microfluidic devices with high chemical resistance using scholar glue and magnetic masks. Anal Chim Acta 974:63–68
Carrell C, Kava A, Nguyen M, Menger RF, Munshi Z, Call Z, Nussbaum M, Henry C (2019) Beyond the lateral flow assay: a review of paper-based microfluidics. Microelectron Eng 206:45–54
Cate DM, Noblitt SD, Volckens J, Henry CS (2015) Multiplexed paper analytical device for quantification of metals using distance-based detection. Lab Chip 15:2808–2818
Channon RB, Joseph MB, Bitziou E, Bristow AWT, Ray AD, Macpherson JV (2015) Electrochemical flow injection analysis of hydrazine in an excess of an active pharmaceutical ingredient: achieving pharmaceutical detection limits electrochemically. Anal Chem 87:10064–10071
Channon RB, Joseph MB, Macpherson JV (2016) Additive manufacturing for electrochemical (micro)fluidic platforms. Electrochem Soc Interface 25:63–68
Channon RB, Nguyen MP, Henry CS, Dandy DS (2019) Multilayered microfluidic paper-based devices: characterization, modeling, and perspectives. Anal Chem 91:8966–8972
Chen C, Zhao Y, Wang J, Zhu P, Tian Y, Xu M, Wang L, Huang X (2018) Passive Mixing inside. Microdroplets Micromachines 9:160
Chin CD, Linder V, Sia SK (2012) Commercialization of microfluidic point-of-care diagnostic devices. Lab Chip 12:2118
Choudhary R, Bhakat T, Kumar Singh R, Ghubade A, Mandal S, Ghosh A, Rammohan A, Sharma A, Bhattacharya S (2011) Bilayer staggered herringbone micro-mixers with symmetric and asymmetric geometries. Microfluid Nanofluid 10:271–286
Denkhaus E, Salnikow K (2002) Nickel essentiality, toxicity, and carcinogenicity. Crit Rev Oncol Hemat 42:35–56
Feeny RM, Puissant NL, Henry CS (2016) Degassed PDMS pump for controlled extraction from dried filter samples in microfluidic devices. Anal Methods 8:8243–8370
Feng X, Ren Y, Hou L, Tao Y, Jiang T, Li W, Jiang H (2019) Tri-fluid mixing in a microchannel for nanoparticle synthesis. Lab Chip 19:2936–2946
Gervais L, Hitzbleck M, Delamarche E (2011) Capillary-driven multiparametric microfluidic chips for one-step immunoassays. Biosens Bioelectron 27:64–70
Glavan AC, Martinez RV, Maxwell EJ, Subramaniam AB, Nunes RMD, Soh S, Whitesides GM (2013) Rapid fabrication of pressure-driven open-channel microfluidic devices in omniphobic RF paper. Lab Chip 13:2922
Hama B, Mahajan G, Fodor PS, Kaufman M, Kothapalli CR (2018) Evolution of mixing in a microfluidic reverse-staggered herringbone micromixer. Microfluid Nanofluid 22:1–14
Hempen C, Karst U (2006) Labeling strategies for bioassays. Anal Bioanal Chem 384:572–583
Hossain S, Husain A, Kim K-Y (2010) Shape optimization of a micromixer with staggered-herringbone grooves patterned on opposite walls. Chem Eng J 162:730–737
Hossain S, Husain A, Kim KY (2011) Optimization of micromixer with staggered herringbone grooves on top and bottom walls. Eng Appl Comp Fluid Mech 5:506–516
Iliescu C, Taylor H, Avram M, Miao J, Franssila S (2012) A practical guide for the fabrication of microfluidic devices using glass and silicon. Biomicrofluidics 6:016505
Illa X, Ordeig O, Snakenborg D, Romano-Rodríguez A, Compton RG, Kutter JP (2010) A cyclo olefin polymer microfluidic chip with integrated gold microelectrodes for aqueous and non-aqueous electrochemistry. Lab Chip 10:1254
Jeong GS, Chung S, Kim C-B, Lee S-H (2010) Applications of micromixing technology. Analyst 135:460
Lago S, Nadai M, Rossetto M, Richter SN (2018) Surface plasmon resonance kinetic analysis of the interaction between G-quadruplex nucleic acids and an anti-G-quadruplex monoclonal antibody. Biochim Biophys Act Gen Subj 1862:1276–1282
Lee JN, Park C, Whitesides GM (2003) Solvent compatibility of Poly(dimethylsiloxane)-based microfluidic devices. Anal Chem 75:6544–6554
Lillehoj PB, Wei F, Ho C-M (2010) A self-pumping lab-on-a-chip for rapid detection of botulinum toxin. Lab Chip 10:2265
Lin D, He F, Liao Y, Lin J, Liu C, Song J, Cheng Y (2013) Three-dimensional staggered herringbone mixer fabricated by femtosecond laser direct writing. J Opt 15:025601–025601
Liu B, Wu T, Yang X, Wang Z, Du Y (2014) Portable microfluidic chip based surface-enhanced raman spectroscopy sensor for crystal violet. Anal Lett 47:2682–2690
Lynn NS, Henry CS, Dandy DS (2008) Microfluidic mixing via transverse electrokinetic effects in a planar microchannel. Microfluid Nanofluid 5:493–505
Mentele MM, Cunningham J, Koehler K, Volckens J, Henry CS (2012) Microfluidic paper-based analytical device for particulate metals. Anal Chem 84:4474–4480
Movafaghi S, Cackovic MD, Wang W, Vahabi H, Pendurthi A, Henry CS, Kota AK (2019) Superomniphobic papers for on-paper pH sensors. Adv Mater Interfaces 6:1900232
Nahavandi S, Baratchi S, Soffe R, Tang S-Y, Nahavandi S, Mitchell A, Khoshmanesh K (2014) Microfluidic platforms for biomarker analysis. Lab Chip 14:1496–1514
Park J, Park J-K (2019) Integrated microfluidic pumps and valves operated by finger actuation. Lab Chip 19:5
Park SH, Maruniak A, Kim J, Yi G-R, Lim SH (2016) Disposable microfluidic sensor arrays for discrimination of antioxidants. Talanta 153:163–169
Regnault C, Dheeman D, Hochstetter A (2018) Microfluidic Devices for Drug Assays. High-Throughput 7:18
Renckens TJA, Janeliunas D, Van Vliet H, Van Esch JH, Mul G, Kreutzer MT (2011) Micromolding of solvent resistant microfluidic devices. Lab Chip 11:2035
Seong GH, Crooks RM (2002) Efficient mixing and reactions within microfluidic channels using microbead-supported catalysts. J Am Chem Soc 124:13360–13361
Shanko E-S, Van De Burgt Y, Anderson PD, Den Toonder JMJ (2019) Microfluidic magnetic mixing at low reynolds numbers and in stagnant fluids. Micromachines 10:731
Srinivasan V, Pamula VK, Fair RB (2004) An integrated digital microfluidic lab-on-a-chip for clinical diagnostics on human physiological fluids. Lab Chip 4:310–315
Stroock AD, McGraw GJ (2004) Investigation of the staggered herringbone mixer with a simple analytical model. Phil Trans R Soc Lond A 362:971–986
Stroock AD, Dertinger SKW, Ajdari A, Mezic I, Stone HA, Whitesides GM (2002) Chaotic mixer for microchannels. Science 295:647–651
Taher AJ, Benjamin FP, Lagae L (2017) A valveless capillary mixing system using a novel approach for passive flow control. Microfluid Nanofluid 21:10
Ugarova NN, Lebedeva OV, Berezin IV (1981) Horseradish peroxidase catalysis I. Steady-state kinetics of peroxidase-catalyzed individual and co-oxidation of potassium ferrocyanide and o-dianisidine by hydrogen peroxide. J Mol Catal 13:215–225
Vahabi H, Wang W, Davies S, Mabry JM, Kota AK (2017) Coalescence-induced self-propulsion of droplets on superomniphobic surfaces. ACS Appl Mater 9:29328–29336
Vahabi H, Wang W, Mabry JM, Kota AK (2018) Coalescence-induced jumping of droplets on superomniphobic surfaces with macrotexture. Sci Adv 4:3488
Wang S, Thomas A, Lee E, Yang S, Cheng X, Liu Y (2016) Highly efficient and selective isolation of rare tumor cells using a microfluidic chip with wavy-herringbone micro-patterned surfaces. Analyst 141:2228–2237
Wang J, Zhang N, Chen J, Rodgers VGJ, Brisk P, Grover WH (2019a) Finding the optimal design of a passive microfluidic mixer. Lab Chip 19:3618–3627
Wang W, Du X, Vahabi H, Zhao S, Yin Y, Kota AK, Tong T (2019b) Trade-off in membrane distillation with monolithic omniphobic membranes. Nat Comm 10:1–9
Wang W, Vahabi H, Movafaghi S, Kota AK (2019c) Superomniphobic surfaces with improved mechanical durability: synergy of hierarchical texture and mechanical interlocking. Adv Mater Interfaces 6:1900538
Ward K, Fan ZH (2015) Mixing in microfluidic devices and enhancement methods. J Micromech Microeng 25:094001
Williams MS, Longmuir KJ, Paul Y (2008) A practice guide to the staggered herringbone mixer. Lab Chip 8:1121–1129
Zhang X, Xia K, Ji A (2020) A portable plug-and-play syringe pump using passive valves for microfluidic applications. Sens Actuators B Chem 304:127331
Acknowledgements
A.K.K. acknowledges financial support under award 1751628 from the National Science Foundation and under awards R01HL135505 and R21HL139208 from the National Institutes of Health. C.S.H. acknowledges support under R33ES024719. Additional support was provided by Colorado State University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary file2 (MP4 685 KB)
Supplementary file3 (MP4 462 KB)
Supplementary file4 (MP4 482 KB)
Supplementary file5 (MP4 747 KB)
Supplementary file6 (MP4 488 KB)
Supplementary file7 (MP4 817 KB)
Supplementary file8 (MP4 721 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Channon, R.B., Menger, R.F., Wang, W. et al. Design and application of a self-pumping microfluidic staggered herringbone mixer. Microfluid Nanofluid 25, 31 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-021-02426-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-021-02426-x