Abstract
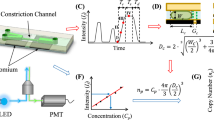
Measurements of single-cell proteins provide key insights in studies related to cellular heterogeneities, while the absolute quantification of single-cell non-surface proteins remains elusive. This paper presents a droplet-based microfluidic flow cytometry enabling high-throughput quantification of both surface and intracellular proteins of single cell. Gradient solutions of fluorescently labeled proteins were first flushed into constriction channels with fluorescence signals detected to obtain calibration curves. Then, droplets encapsulating single cells stained with fluorescently labeled proteins were aspirated into constriction channels with excited fluorescence signals detected and translated into numbers of proteins based on the calibration curves. Based on this approach, both suspended and adherent cells with both surface and intracellular staining were processed. More specifically, the numbers of ConA binding sites of K562 cells, anti-β-actin antibody binding sites of A549 and HeLa cells were quantified as 3.43 ± 4.07 × 106/cell (Nc = 530); 9.20 ± 5.21 × 105/cell (Nc = 1073); and 1.44 ± 0.75 × 106/cell (Nc = 1138), respectively. As a high-throughput microfluidic platform, this technique can add a quantitative approach to measure single-cell proteins with arbitrary distributions within cells.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not available.
Code availability
The code used during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Armbruster DA, Pry T (2008) Limit of blank, limit of detection and limit of quantitation. Clin Biochem Rev 29(Suppl 1):S49-52
Chattopadhyay PK, Roederer M (2012) Cytometry: today’s technology and tomorrow’s horizons. Methods 57:251–258. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymeth.2012.02.009
Chen J et al (2011) Classification of cell types using a microfluidic device for mechanical and electrical measurement on single cells. Lab Chip 11:3174–3181. https://doi.org/10.1039/c1lc20473d
Chen W, Huang NT, Li X, Yu ZT, Kurabayashi K, Fu J (2013) Emerging microfluidic tools for functional cellular immunophenotyping: a new potential paradigm for immune status characterization. Front Oncol 3:98. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2013.00098
Chokkalingam V et al (2013) Probing cellular heterogeneity in cytokine-secreting immune cells using droplet-based microfluidics. Lab Chip 13:4740–4744. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3lc50945a
Cole RH et al (2017) Printed droplet microfluidics for on demand dispensing of picoliter droplets and cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 114:8728–8733. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1704020114
Darmanis S et al (2016) Simultaneous Multiplexed Measurement of RNA and Proteins in Single Cells. Cell Rep 14:380–389. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2015.12.021
Doerr A (2019) Single-cell proteomics. Nat Methods 16:20. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41592-018-0273-y
Fan B, Li X, Chen D, Peng H, Wang J, Chen J (2016) Development of microfluidic systems enabling high-throughput single-cell protein characterization. Sensors 16:232. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16020232
Fan B et al (2018) Absolute copy numbers of β-actin proteins collected from 10,000 single cells. Micromachines 9:254. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi9050254
Gratama JW et al (1998) Flow cytometric quantitation of immunofluorescence intensity: problems and perspectives. Cytometry 33:166–178. https://doi.org/10.1002/(sici)1097-0320(19981001)33:2%3c166::Aid-cyto11%3e3.0.Co;2-s
Hoffman RA, Wang L, Bigos M, Nolan JP (2012) NIST/ISAC standardization study: variability in assignment of intensity values to fluorescence standard beads and in cross calibration of standard beads to hard dyed beads. Cytometry A 81:785–796. https://doi.org/10.1002/cyto.a.22086
Kang D-K, Monsur Ali M, Zhang K, Pone EJ, Zhao W (2014) Droplet microfluidics for single-molecule and single-cell analysis for cancer research, diagnosis and therapy. Trends Anal Chem 58:145–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2014.03.006
Konry T, Dominguez-Villar M, Baecher-Allan C, Hafler DA, Yarmush ML (2011) Droplet-based microfluidic platforms for single T cell secretion analysis of IL-10 cytokine. Biosens Bioelectron 26:2707–2710. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2010.09.006
Li X et al (2017) A microfluidic flow cytometer enabling absolute quantification of single-cell intracellular proteins. Lab Chip 17:3129–3137. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7lc00546f
Li W et al (2018a) Microfluidic fabrication of microparticles for biomedical applications. Chem Soc Rev 47:5646–5683. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7cs00263g
Li X et al (2018b) A microfluidic fluorescent flow cytometry capable of quantifying cell sizes and numbers of specific cytosolic proteins. Sci Rep 8:14299. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-32333-1
Liu L, Chen D, Wang J, Chen J (2020a) Advances of single-cell protein analysis. Cells. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9051271
Liu L et al (2020b) Development of microfluidic platform capable of high-throughput absolute quantification of single-cell multiple intracellular proteins from tumor cell lines and patient tumor samples. Biosens Bioelectron 155:112097. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2020.112097
Maher KJ, Fletcher MA (2005) Quantitative flow cytometry in the clinical laboratory. Clin Appl Immunol Rev 5:353–372. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cair.2005.10.001
Marti GE, Zenger VE, Vogt R, Gaigalas A (2002) Quantitative flow cytometry: history, practice, theory, consensus, inter-laboratory variation and present status. Cytotherapy 4:97–98. https://doi.org/10.1080/146532402317251626
Martino C, Zagnoni M, Sandison ME, Chanasakulniyom M, Pitt AR, Cooper JM (2011) Intracellular protein determination using droplet-based immunoassays. Anal Chem 83:5361–5368. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac200876q
Perfetto SP, Chattopadhyay PK, Roederer M (2004) Seventeen-colour flow cytometry: unravelling the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol 4:648–655. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri1416
Peterson VM et al (2017) Multiplexed quantification of proteins and transcripts in single cells. Nat Biotechnol 35:936. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.3973
Shahi P, Kim SC, Haliburton JR, Gartner ZJ, Abate AR (2017) Abseq: Ultrahigh-throughput single cell protein profiling with droplet microfluidic barcoding. Sci Rep 7:44447. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep44447
Shelby JP, White J, Ganesan K, Rathod PK, Chiu DT (2003) A microfluidic model for single-cell capillary obstruction by Plasmodium falciparum infected erythrocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:14618–14622. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2433968100
Spitzer MH, Nolan GP (2016) Mass cytometry: single cells, many features. Cell 165:780–791. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2016.04.019
Telford WG, Hawley T, Subach F, Verkhusha V, Hawley RG (2012) Flow cytometry of fluorescent proteins. Methods 57:318–330. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymeth.2012.01.003
Wei S-C, Hsu MN, Chen C-H (2019) Plasmonic droplet screen for single-cell secretion analysis. Biosens Bioelectron. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2019.111639
Wen N, Zhao Z, Fan B, Chen D, Men D, Wang J, Chen J (2016) Development of droplet microfluidics enabling high-throughput single-cell analysis. Molecules 21:881. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21070881
Wolfert MA, Boons G-J (2013) Adaptive immune activation: glycosylation does matter. Nat Chem Biol 9:776–784. https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.1403
Woo J, Baumann A, Arguello V (2014) Recent advancements of flow cytometry: new applications in hematology and oncology. Expert Rev Mol Diagn 14:67–81. https://doi.org/10.1586/14737159.2014.862153
Zenger VE, Vogt R, Mandy F, Schwartz A, Marti GE (1998) Quantitative flow cytometry: inter-laboratory variation. Cytometry 33:138–145. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1097-0320(19981001)33:2%3c138::AID-CYTO8%3e3.0.CO;2-F
Zhang XL (2006) Roles of glycans and glycopeptides in immune system and immune-related diseases. Curr Med Chem 13:1141–1147. https://doi.org/10.2174/092986706776360897
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge financial supports from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 61825107, 61922079, 62001042); Key Project (QYZDB-SSW-JSC011), Instrument Development GJJSTD20210004), Youth Innovation Promotion Association and Interdisciplinary Innovation Team of Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Funding
Financial supports from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 61825107, 61922079, 62001042); Key Project (QYZDB-SSW-JSC011), Instrument Development (GJJSTD20210004), Youth Innovation Promotion Association and Interdisciplinary Innovation Team of Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: JC, JW, HY; data curation: HY, YW, BF; methodology: HY, YW, BF, TZ; formal analysis and investigation: HY, YW, BF, LL, TZ; writing—original draft preparation: HY; writing—review and editing: JC, JW; funding acquisition: JW, DC; resources: YW, LL, TZ; software, validation and visualization: DC, LL, TZ; supervision and project administration: JW, JC, DC.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, H., Wei, Y., Fan, B. et al. A droplet-based microfluidic flow cytometry enabling absolute quantification of single-cell proteins leveraging constriction channel. Microfluid Nanofluid 25, 30 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-021-02427-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-021-02427-w