Abstract
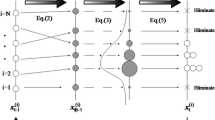
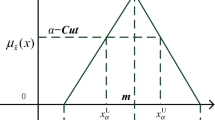
The assimilation of simulated and measured data is essential for advancing technology in NDE 4.0. In this study, a particle filter (PF) was applied to identify the geometry of flaws for ultrasonic nondestructive testing. A PF based on a probabilistic approach that allows errors in measurement and simulation models may be of great assistance for the data assimilation. In the PF, state variables are expressed by random data samples called particles, together with their associated weights. The PF estimates the probabilistic density function of the state variables by merging simulation data with measured data. Data types must be physically identical in the simulation and measurement to enhance the accuracy and to accelerate the convergence speed in the PF. Here, the scattering component, which is specific information related to the flaw geometry, was used for the likelihood evaluation in the PF. The simulation, which needed many particles, was conducted using the elastodynamic finite integration technique accelerated by parallel computing with graphics processing units. The proposed PF approach was demonstrated in ultrasonic measurement, and the geometries of artificial flaws in aluminum specimens were identified using only one pulse-echo signal at a single transducer.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Meyendorf, N.G., Bond, L.J., Curtis-Beard, J., Heilmann, S., Pal, S., Schallert, R., Scholz, H., Wunderlich, C.: NDE 4.0-NDE for the 21st century- the internet of things and cyber physical systems will revolutionize NDE, No. 117. In: Proceedings of the 15th Asia Pacific Conference for Nondestructive Testing (APCNDT2017), Singapore (2017)
Vrana, J.: NDE perception and emerging reality: NDE 4.0 value extraction. Mater. Eval. 78(7), 835–851 (2020)
Drinkwater, B.W., Wilcox, P.D.: Ultrasonic arrays for non-destructive evaluation: a review. NDT E Int. 39, 525–541 (2006)
Kouche, A.E., Hassanein, H.S.: Ultrasonic non-destructive testing (NDT) using wireless sensor networks. Procedia Comput. Sci. 10, 136–143 (2012)
Zhong, C.H., Croxford, A.J., Wilcox, P.D.: Remote inspection system for impact damage in large composite structure. Proc. R. Soc. A 471(2173), 20140631 (2015)
Liu, Z., Meyendorf, N.G., Mrad, N.: The role of data fusion in predictive maintenance using digital twin. In: Proceedings of 44th Annual Review of Progress in Quantitative Nondestructive Evaluation, AIP Conference Proceedings, Vol. 1949, 020023 (2018)
Kalman, R.E.: A new approach to linear filtering and prediction problems. Trans. ASME 82(1), 35–45 (1960)
Dobie, G.: Ultrasonic Sensor Platforms for Non-Destructive Evaluation, Ph.D. thesis, University of Strathclyde (2010)
Angrisani, L., Baccigalupi, A., Lo Moriello, R.S.: Ultrasonic time-of-flight estimation through unscented Kalman filter. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 55(4), 1077–1084 (2006)
Yoon, M.-H.: New ultrasonic signal processing techniques for NDE applications, Ph.D. thesis, Iowa State University (1994)
Engelhardt, M., Stavroulakis, G.E., Antes, H.: Crack and flaw identification in elastodynamics using Kalman filter techniques. Comput. Mech. 37(3), 249–265 (2006)
Evensen, G.: Data Assimilation, The Ensemble Kalman Filter. Springer, New York (2009)
Gordon, N.J., Salmond, D.J., Smith, A.F.M.: Novel approach to nonlinear/non-Gaussian Bayesian state estimation. IEEE Proc. F 140(2), 107–113 (1993)
Emerick, A.A., Reynolds, A.C.: Ensemble smoother with multiple data assimilation. Comput. Geosci. 55, 3–15 (2013)
Kitagawa, G.: Monte Carlo filter and smoother for non-Gaussian nonlinear state space models. J. Comput. Graph. Stat. 5(1), 1–25 (1996)
Nakamura, K., Higuchi, T., Hirose, N.: Sequential data assimilation: information fusion of a numerical simulation and large scale observation data. J. Univ. Comput. Sci. 12(6), 608–626 (2006)
Muir, J.B., Tsai, V.C.: Geometric and level set tomography using ensemble Kalman inversion. Geophys. J. Int. 220, 967–980 (2020)
Evensen, N.: The Ensemble Kalman Filter: theoretical formulation and practical implementation. Ocean Dyn. 53, 343–367 (2003)
Potthast, R., Walter, A., Rhodin, A.: A localized adaptive particle filter within an operational NWP framework. Mon. Weather Rev. 147(1), 345–362 (2019)
Schmerr, L.W.: Fundamentals of ultrasonic nondestructive evaluation. Plenum Press, New York (1998)
Schmerr, L.W., Song, S.-J.: Ultrasonic Nondestructive Evaluation Systems. Models and Measurement. Springer, New York (2007)
Dassios, G., Kiriaki, K., Polyzos, D.: On the scattering amplitudes for elastic waves. J. Appl. Math. Phys. 38, 856–873 (1987)
Schafbuch, P.J.: Application of the boundary element method to elastic wave scattering problems in ultrasonic nondestructive evaluation, Ph.D. thesis, Iowa State University (1991)
Fellinger, P., Marklein, R., Langenberg, K.J., Klaholz, S.: Numerical modeling of elastic wave propagation and scattering with EFIT-elastodynamic finite integration technique. Wave Motion 21, 47–66 (1995)
Terada, K., Miura, T., Kikuchi, N.: Digital image-based modeling applied to the homogenization analysis of composite materials. Comput. Mech. 20, 331–346 (1997)
Taheri, S.: A review on five key sensors for monitoring of concrete structures. Construct. Build. Mater. 204, 492–509 (2019)
Nakahata, K., Chang, J., Takahashi, M., Ohira, K., Ogura, Y.: Finite integration technique for coupled acoustic and elastic wave simulation and its application to noncontact ultrasonic testing. Acoust. Sci. Technol. 35(5), 260–268 (2014)
Murakami, A., Shuku, T., Nishimura, S., Fujisawa, K., Nakamura, K.: Data assimilation using the particle filter for identifying the elastoplastic material properties of geomaterials. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Methods Geomech. 37, 1642–1669 (2013)
Myers, M.R.: Parameter estimation using extended Kalman filter and ultrasonic pulse time of flight to locate transient, concentrated heating sources, Ph.D. thesis, Vanderbilt University (2012)
Courant, P., Friedrichs, K., Lewy, H.: On the partial difference equations of mathematical physics. IBM J. Res. Dev. 11(2), 215–234 (1967)
Schubert, F., Koehler, B.: Three-dimensional time domain modeling of ultrasonic wave propagation in concrete in explicit consideration of aggregates and porosity. J. Comput. Acoust. 9(4), 1543–1560 (2011)
Ricker, N.: The computation of output disturbance from amplifiers for true wavelet inputs. Geophysics 10, 207–220 (1945)
Collino, F., Tsogka, C.: Application of the PML absorbing layer model to the linear elastodynamic problem in anisotropic heterogeneous media, Rapport de Recherche. INRIA N3471 (1998)
Li, T., Sun, S., Sattar, T.P., Corchado, J.M.: Fight sample degeneracy and impoverishment in particle filters: a review of intelligent approaches. Expert Syst. Appl. 41, 3944–3954 (2014)
Nguyen, V.P., Anitescu, C., Bordas, S., Rabczuk, T.: Isogeometric analysis: an overview and computer implementation aspects. Math. Comput. Simul. 117, 89–116 (2015)
Jones, B., Johnson, R.T.: Design and analysis for the Gaussian process model. Qual. Reliab. Eng. Int. 25, 515–524 (2009)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by JSPS KAKENHI Grant Numbers 19K21987 and 20H02230.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nakahata, K., Maruyama, T. & Hirose, S. Application of a Particle Filter to Flaw Identification for Ultrasonic Nondestructive Evaluation: Assimilation of Simulated and Measured Data. J Nondestruct Eval 40, 34 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10921-021-00765-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10921-021-00765-x