Abstract
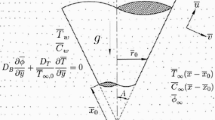
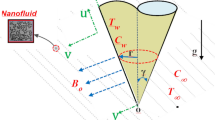
The aim of this article is to analyze the mixed convective Ostwald–de Waele power-law nanofluid flow over vertical frustum of a cone in a non-Darcy porous medium using an efficient numerical technique. The involved power-law nanofluid model utilizes water as the base fluid, and Ti-alloy (Ti6Al4V) and multi-wall carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) as the nanoparticles. The solution of resultant non-similarity equations subjected to boundary conditions is described using the local non-similarity technique along with an efficient spectral local linearization method. The error estimation is provided to show the efficiency of above-mentioned solution procedure. A detailed explanation about the impact of nanoparticle volume fraction on the dimensionless velocity and temperature profiles along with heat transfer rate and skin friction coefficient is also provided for both the opposing and aiding flow cases. On comparison of the present results in particular cases with the relevant published data, it is assured that this method gives highly accurate outcomes for this kind of very complex fluid flow problems. The domination of dilatant nanofluid over pseudo-plastic nanofluid in both the aiding and opposing flow cases is noticed for velocity profiles, and the velocity is decreased with an increment in the nanoparticle volume fraction. Also, the variation in profiles with a streamwise coordinate \(\xi\) shows non-similar nature of the problem. The use of Ti-alloy and MWCNTs in this work makes it very profitable in various important sectors like aerospace and medical sector.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
D A Nield and A Bejan Convection in Porous Media (Springer International Publishing, Berlin) (2017)
C Y Cheng Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 39 1348 (2012)
F M Hady, M R Eid, M R Abd-Elsalam and M A Ahmed IOSR J. Math. 8 51 (2013)
P V S N Murthy, Ch Ram Reddy, A J Chamkha and A M Rashad Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 47 41 (2013)
R Nandkeolyar, P K Kameswaran, S Shaw and P Sibanda J. Heat Transf. 136 122001-1 (2014)
M Khan and W A Khan AIP Adv. 6 025211 (2016)
Y Zhang, M Zhang and Y Bai J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 70 104 (2017)
P Barnoon and D Toghraie Powder Tech. 325 78 (2018)
M K Nayak, S Shaw, V S Pandey and A J Chamkha Indian J. Phys. 92 1017 (2018)
A S Dogonchi and D D Ganji Indian J. Phys. 92 757 (2018)
B Vasu, R S R Gorla, O A Beg, P V S N Murthy, V R Prasad and A Kadir J. Thermophy. Heat Transf. 33 343 (2019)
H Goodarzi, A A Omid, M M Sarafraz, M M Karcheghani, M R Safaei and G A S Shabani J. Thermal Sci. Eng. Appl. 11 061020-1 (2019)
M Dhlamini, P K Kameswaran, P Sibanda, S Motsa and H Mondal J. Comp. Des. Eng. 6 149 (2019)
A Hiremath, G J Reddy and O A Beg Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 44 7875 (2019)
M Kumar, G J Reddy, N N Kumar and O A Beg Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part N J. Nanomater. Nanoeng. Nanosyst. 233 49 (2019)
S K Das, S U S Choi, W Yu and T Pradeep Nanofluids: Science and Technology (Wiley-Interscience, New Jersey) (2007)
W J Minkowycz, E M Sparrow and J P Abraham Nanoparticle Heat Transfer and Fluid Flow (Taylor and Fracis Group, New York) (2013)
S Kakac and A Pramuanjaroenkij Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 52 3187 (2009)
J Fan and L Wang J. Heat Transf. 133 040801 (2011)
C M Hogan Phys. Rev. 188 870 (1969)
P Parayanthal and F Pollak Phys. Rev. Lett. 52 1822 (1984)
M Peters, J Kumpfert, C H Ward and C Leyens Adv. Eng. Mater. 5 419 (2003)
P Singh, H Pungotra and N S Kalsi Mater. Today Proc. 4 8971 (2017)
U Khan, A Zaib, I Khan and K S Nisar J. Mater. Res. Tech. 9 188 (2020)
S S Chougule and S K Sahu J. Thermal Sci. Eng. Appl. 6 041009-1 (2014)
X Liu, H I Mohammed, A Z Ashkezari, A Shahsavar, A K Hussein and S Rostami J. Mol. Liq. 300 112269 (2020)
P Singh, V Radhakrishnan and K A Narayan Ingenieur Archiv. 59 382 (1989)
R H Christopher and S Middleman Ind. Eng. Chem. Fund. 4 422 (1965)
R V Dharmadhikari and D D Kale Chem. Eng. Sci. 40 527 (1985)
C S K Raju, N Sandeep and V Sugunamma J. Mol. Liq. 222 1183 (2016)
S O Giwa, M Sharifur and J P Meyer Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 148 119072 (2020)
E M Sparrow and H S Yu Trans. ASME J. Heat Trans. 93 328 (1971)
S S Motsa J. Appl. Math. 2013 1 (2013)
S S Motsa and P Sibanda Comp. Math. Appl. 63 1197 (2012)
P Cheng Int. J. Heat Mass Trans. 20 807 (1977)
W Chaoyang, T Chuanjing and Z Xiaofen Acta Mechanica Sinica 6 214 (1990)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chetteti, R., Srivastav, A. Numerical study and error estimation in power-law nanofluid flow over vertical frustum of a cone. Indian J Phys 96, 1167–1179 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12648-021-02055-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12648-021-02055-8