Abstract
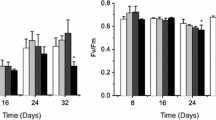
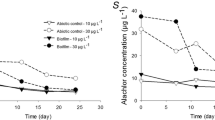
Every day, tons of caffeine is consumed by humans in beverages, medications or supplements, and a significant amount of this stimulant is released in domestic sewage. Once in aquatic environments caffeine interacts directly with the periphytic community, which is responsible for a significant part of primary production in aquatic ecosystems. However, the effects of exposure to caffeine are mostly unknown for both the periphyton and their predators. Aiming to comprehend the interaction between caffeine and the periphytic community, ecotoxicological experiments were performed by exposing a periphytic biofilm cultivated in the laboratory to different concentrations of caffeine, following concentrations found in domestic sewers. The impact of exposure to this contaminant was observed on the structure of the community through taxonomic evaluation, as well a set of physiological variables linked to primary production. After exposure to the highest caffeine concentration (300 µg L−1), the density of the genus Scenedesmus was severely affected, leading to an increase in cyanobacteria and diatoms. Both richness and diversity decreased after exposure, and there was lower photosynthetic activity, with light saturation point changing from 186 µmol m−2 s−1 in the control treatment to 108 µmol m−2 s−1 after exposure. Caffeine accumulation within the biofilm was also observed during the first 24 h, in the concentration of 0.14 µg /cm².



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abilhoa V, Valduga MO, Frehse FA, Vitule JRS (2016) Use of food resources and resource partitioning among five syntopic species of Hypostomus (Teleostei: Loricariidae) in an Atlantic Forest river in southern Brazil. Zoologia 33:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1590/s1984-4689zool-20160062
ABNT (2018) Toxicidade Aquática – Toxicidade Crônica – Método para Ensaios utilizando algas (Chlorophyceae) – Normativa Técnica NBR 12648:2018. http://www.abntcatalogo.com.br/norma.aspx?ID=391089. Accessed on 1 May 2020
Aguirre-Martínez GV, Reinardy HC, Martín-Díaz ML, Henry TB (2017) Response of gene expression in zebrafish exposed to pharmaceutical mixtures: implications for environmental risk. Ecotoxicol Environ Safety 142:471–479. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.04.038
Bicudo CEM (1990) Metodologia para estudos qualitativos do perifíton. Acta Limnol Bras 3:447–491
Bicudo CEM, Menezes M (2006) Gêneros de algas continentais no Brasil – chave para identificação e descrições. Rima, São Carlos
Bodini A, Bandavalli C, Rosseti G (2018) Ecological sucession investigated through food-web flow network. In: Moore JC, Ruiter PC, McCann KS, Wolters V (eds) Adaptive food webs – stability and transitions on real model ecosystems, 1st edn. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, p 164–177
Bonnineau C, Artigas J, Chaumet B, Dabrin A, Faburé J, Ferrari BJD, Lebrun JD, Margoum C, Mazzella N, Miège C, Morin S, Uher E, Babut M, Pesce S (2020) Role of biofilms in contaminant bioaccumulation and trophic transfer in aquatic ecosystems: current state of knowledge and future challenges. Reviews of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology (Continuation of Residue Reviews). Springer, New York, p 1–39. https://doi.org/10.1007/398_2019_39
Buerge IJ, Poiger T, Muller MD, Buser HR (2003) Caffeine: an antropoghenic marker for wastewater contamination in surface waters. Environ Sci Technol 37:691–700. https://doi.org/10.1021/es020125z
Burket SR, Wright MV, Baker LF, Chambliss CK, King RD, Matson CW, Brook BW (2020) Periphyton, bivalves and fish differentially accumulate select pharmaceuticals in effluent-dependent stream mesocosms. Sci Total Environ 745. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140882
Burliga AL (2010) Abordagem de grupos funcionais nos estudos com perifíton e fitoplâncton. In: Franceschini IM, Burliga AL, Reviers B, Prado JF, Rézig SH (eds) Algas: uma abordagem filogenética, taxonômica e ecológica, 2nd edn. Artmed, São Paulo, p 234–258
Cattaneo A, Mousseau B (1995) Empirical analysis of the removal rate of periphyton by grazers. Oecologia 103:249–254. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00329087
Dafouz R, Cáceres N, Rodríguez-Gild JL, Mastroiannie N, Aldae ML, Barceló D, Miguel AG, Valcárcel Y (2018) Does the presence of caffeine in the marine environment represent an environmental risk? A regional and global study. Sci Total Environ 615:632–642. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.09.155
Du S, Haddad SP, Scott WC, Chambliss CK, Brooks BW (2015) Pharmaceutical bioaccumulation by periphyton and snails in an effluent-dependent stream during an extreme drought. Chemosphere 119:927–934. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.08.044
Dunk B, Rodrigues L, Bicudo DC (2015) Functional diversity and functional traits of periphytic algae during a short-term successional process in a Neotropical floodplain lake. Braz J Biol 75:587–597. https://doi.org/10.1590/1519-6984.17813
Ferreira P, Soares GLG, D’ávila S, Bessa ECA (2009) The influence of caffeine and thymol on the survival, growth and reproduction of Subulina octona (Brugüière, 1789) (Mollusca, Subulinidae). Braz Arch Biol Techn 52:945–952. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1516-89132009000400018
Felisberto SA, Murakami EA (2013) O papel do perifíton na ciclagem de nutrientes e na teia trófica. In: Schwarzbold A, Burliga AL, Torgan LC (eds) Ecologia do Perifíton, 1st edn. Rima, São Carlos, p 23–44
Felisberto SA, Rodrigues L (2012) Sucessional dynamics of periphytic algae in a subtropical lotic ecosystem. Rodriguésia 63:463–473. https://doi.org/10.1590/S2175-78602012000200018
Franceschini IM (2013) Chave de identificação para algas (exceto Bacillariophyceae) comumente encontradas no perifíton de águas continentais. In: Schwarzbold A, Burliga AL, Torgan LC (eds) Ecologia do perifíton, 1st edn. Rima, São Carlos, p 245–266
Fredholm BB (2011) Notes on the History of caffeine use. In: Fredholm BB (ed) Methylxantines (Handbook of experimental pharmacology—200), 1st edn. Springer, Berlin, p 1–10
Gracia-Lor E, Rousis NI, Zuccato E, Bade R, Baz-Lomba JA, Castrignanò E, Causanilles A, Hernández F, Kasprzyk-Hordern B, Kinyua J, McCall AK, Nuijs ALN, Plósz BJ, Ramin P, Ryu Y, Santos MM, Thomas K, Voogt P, Yang Z, Castiglioni S (2017) Estimation of caffeine intake from analysis of caffeine metabolites in wastewater. Sci Total Environ 609:1582–1588. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.07.258
Gonçalves ES, Rodrigues SV, Silva-Filho EV (2017) The use of caffeine as a chemical marker of domestic wastewater contamination in surface waters: seasonal and spatial variations in Teresópolis, Brazil. Revista Ambiente & Água 12:192–202. https://doi.org/10.4136/ambi-agua.1974
Guash H, Artigas J, Bonet B, Bonineau C, Canals O, Corcoll N, Foulquier A, López-Doval J, Tiam SK, Morin S, Navarro E, Pesce S, Proia L, Salvadó H, Serra A (2016) The Use of biofilms to assess the effects of chemicals on freshwater ecosystems. In: Romaní AM, Balager MD, Guash H (eds) Aquatic biofilms: ecology, water quality and wastewater treatment, 1st edn. Caister Academic Press, Norfolk, p 125–144
Hammer Ø, Harper DAT, Ryan PD (2001) PAST: paleontological statistics software package for education and data analysis. Palaeontologia Electronica 4:9
Hill W (1996) Effects of light. In: Stevenson RJ, Bothwell ML, Lowe RL (ed) Algal ecology: freshwater benthic systems, 1st edn. Academic Press, London, p 121–148
Hommen U, Knopf B, Rudel H, Schafers C, Garman ER, Schamphalaere K, Schlekat C (2016) A microcosm study to support aquatic risk assessment of nickel: community-level effects and comparison with bioavailability-normalized species sensitivity distributions. Environ Toxicol Chem 35:1172–1182. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.3255
Jacobs LE, Weavers LK, Houtz EF, Yu-Ping C (2012) Photosensitized degradation of caffeine: role of fulvic acids and nitrate. Chemosphere 86:124–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.09.052
Johnston NK, Zhichao P, Lin J (2016) Predator identity influences metacommunity assembly. J Anim Ecol 85:1161–1170. https://doi.org/10.1111/1365-2656.12551
Korekar G, Kumar A, Ugale C (2019) Occurrence, fate, persistence and remediation of caffeine: a review. Environ Sci Poll Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06998-8
Kumar J, Singh VP, Prasad SM (2017) An investigation on involvement of the ascorbate-glutathione cycle in modulating NaCl toxicity in two cyanobacteria photoacclimatized to different photosynthetic active radiation. Algal Res 32:70–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.algal.2017.10.019
Kumar KS, Dahms HU, Lee JS, Kim HC, Lee WC, Shin KH (2014) Algal photosynthetic responses to toxic metals and herbicides assessed by chlorophyll a fluorescence. Ecotox Environ Safe 104:51–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2014.01.042
Lamparelli MC, Tucci A, Sant’Anna C, Pires DA, Lerche LHM, Carvalho MC, Rosal C (2014) Atlas de Cianobactérias na bacia do Alto Tietê. CETESB, São Paulo
Lawrence JR, Bin Z, Swerhone GDW, Roy J, Tumber V, Waiser MJ, Topp E, Korber DR (2012) Molecular and microscopic assessment of the effects of caffeine, acetaminophen, diclofenac and other mixtures on river biofilm communities. Environ Toxicol Chem 31:508–517. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.1723
Lei X, Cruz JA, Savage LJ, Kramer DM, Chen J (2015) Plant photosynthesis phenomics data quality control. Bioinformatics 31:1796–1804. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btu854
Liess A, Hillebrand H (2004) Invited review: direct and indirect effects in herbivore—periphyton interactions. Arch Hydrobiol 159:433–453. https://doi.org/10.1127/0003-9136/2004/0159-0433
Ludwig TAV, Tremarin PI (2013) Chave de identificação para Diatomae-Ochrophyta comumente encontradas no perifíton de águas continentais. In: Schwarzbold A, Burliga AL, Torgan LC (eds) Ecologia do Perifíton, 1st edn. Rima, São Carlos, p 267–330
Montagner CC, Vidal C, Sodré FF, Pescara IC, Jardim WF (2014) Cafeina no meio ambiente. In: Canela MC, Jardim WF, Sodré FF, Grassi MT (ed) Cafeina em águas de abastecimento public no Brasil, 1st edn. Cubo, São Carlos, p 11–18
Moraes MFPG, Barbola IF, Guedes EAC (1997) Alimentação e relações morfológicas com o aparelho digestivo do “Curimbatá”, Prochilodus llneatus (valenciennes) (osteichthyes, prochilodontidae), de uma lagoa do sul do Brasil. Revta Bras Zool 14:169–180
Ningyuan Z, Sichu W, Tang C, Pengfei D, Lunguang Y, Jun T, Po KW, Taicheng A, Dionysiou D.D, Yonghong W. (2019) Protection mechanisms of periphytic biofilm to photocatalytic nanoparticles (PNPs) exposure. Environ Sci Technol https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.8b04923
Ondarza PM, Haddad SP, Avigliano E, Miglioranza KSB, Brooks BW (2019) Pharmaceuticals, illicit drugs and their metabolites in fish from Argentina: implications for protected areas influenced by urbanization. Sci Total Environ 649:1029–1037. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.08.383
Potvin C (2001) ANOVA: experimental layout and analysis. In: Schneider SM, Gurevitch J (ed) Design and analysis of ecological experiments, 2nd edn. Oxford university press, New York, NY, p 63–77
Roberts MJ, Long SP, Tieszen LL, Beadle CL (2014) Measurement of plant biomass and net primary production. In: Coombs J, Hall DO, Long SP, Scurlock JMO (ed) Techniques in bioproductivity and photosynthesis, 2nd ed. Pergamon Press, Oxford, p 1–19
Rosi-Marshall EJ, Kincaid DW, Bechtold HA, Royer TV, Rojas M, Kelly JJ (2013) Pharmaceuticals suppress algal growth and microbial respiration and alter bacterial communities in stream biofilms. Ecol Appl 23:583–593. https://doi.org/10.1890/12-0491.1
Ruhí A, Acuña V, Barceló D, Huerta B, Mor JR, Rodríguez-Mozaz S, Sabater S (2016) Bioaccumulation and trophic magnification of pharmaceuticals and endocrine disruptors in a Mediterranean river food web. Sci Total Environ 540:250–259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.06.009
Serra A, Corcoll N, Guash H (2011) Cooper acumullation and toxycity in fluvial periphyton: the influence of exposal history. Chemosphere 74(5):633–641
Shaw L, Phung C, Grace M (2015) Pharmaceuticals and personal care products alter growth and function in lentic biofilms. Environ Chem 12:301–306. https://doi.org/10.1071/EN14141
Shulan L, Jing W, Bingshu H, Jun W, Xianmin H, Juan L (2020a) Occurrence of caffeine in the freshwater environment: implications for ecopharmacovigilance. Environ Pollut https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114371
Shulan L, Bingshu H, Jun W, Juan L, Xianmin H (2020b) Risks of caffeine residues in the environment: necessity for a targeted ecopharmacovigilance program. Chemosphere https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125343
Silant’eva DI, Gainutdinova TK, Andrianov VV, Gainutdinov KL (2009) Electrophysiological studies of the effects of chronic administration of caffeine on the formation of a conditioned defensive reflex in the common Snail. Neurosci Behav Physiol 39:403–407. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11055-009-9136-4
Sodré FF, Locatelli MAF, Jardim WF (2010) Occurrence of emerging contaminants in Brazilian drinking waters: a sewage-to-tap issue. Water Air Soil Pollut 206: 57–67. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-009-0086-9
Sousa ML, Chow F, Pompêo MLM (2019) Community-level changes in periphytic biofilm caused by copper contamination. J Appl Phycol 31:2401–2410. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-019-1734-0
Stoler AB, Relyea RA(2015) Leaf litter species identity alters the structure of pond communities Oikos 125:179–191. https://doi.org/10.1111/oik.02480
Torgan LC, Bertolli LM, Talgatti DM, Salmoni S (2013) Colonization and succession in periphyton. In: Schwazbold A, Burliga AL, Torgan LC (ed) Periphyton ecology. 1st edn. Rima, São Carlos, p 4558
Torres PB, Chow F, Furlan CM, Mandelli F, Mercadante A, Santos DYAC (2014) Standardization of a protocol to extract and analyze chlorophyll a and carotenoids in Gracilaria tenuistipitata Var. Liui. Zhang and Xia (Rhodophyta). Braz J Oceanogr Ol 62:57–63. https://doi.org/10.1590/s1679-87592014068106201
Torres JLT, Hiley SL, Lorimor SP, Rhoad JS, Caldwell BD, Zweerink GL, Ducey M (2015) Separation of caffeine from beverages and analysis using thin-layer chromatography and gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. J Chem Educ 92:900–902. https://doi.org/10.1021/ed500977r
Uhlenbrook S, Ortigara ARC, Connor R, Zadeh SM (2017) State of water resources: quality and availability. In: WWAP (United Nations World Water Assessment Programme) The United Nations World Water Development Report 2017—Wastewater: the untapped resource. UNESCO, Paris, p 9–15
Wetzel RG, Likens GE (1991) Limnological Analyses. Springer, New York, NY
Weyer KM, Bush DR, Darzins A, Wilson BD (2010) Theoretical maximum algal oil production. Bioenerg Res 3:204–213. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12155-009-9046-x
Yonghong W (2016) Periphyton: functions and application in environmental remediation. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Yonghong W, Junzhuo L, Eldon RR (2017) Periphytic biofilms: a promising nutrient utilization regulator in wetlands. Bioresource Technol 248 B:44–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.07.081
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior—Brasil (CAPES) - Finance Code 001 and Fundação de Amparo á Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo (FAPESP)—research grant (2014/22581-8). Fungyi Chow thanks Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq) for the productivity fellowship (303937/2015-7).
Funding
Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior—Brasil (CAPES)—Finance Code 001, Fundação de Amparo á Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo (FAPESP)—research grant (2014/22581-8), and Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq) (303937/2015-7).
Author contributions
SML and PMLM were responsible for experimental design, writing and main idea. CF was responsible for statistical support, and analysis using the fluorometer. SDYAC was responsible for GC/MS analysis and caffeine extraction procedures.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Sousa, M.L., dos Santos, D.Y.A.C., Chow, F. et al. Caffeine as a contaminant of periphyton: ecological changes and impacts on primary producers. Ecotoxicology 30, 599–609 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-021-02381-x
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-021-02381-x