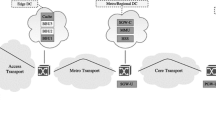
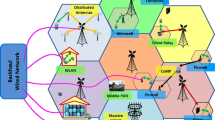
Abstract
The advanced communication networks require heterogeneous emerging technologies to be combined while enabling various future applications. The integration of 5G wireless and optical technology is considered an unavoidable approach to reach this goal. Based on 5G mobile communications and densification of cells, the upcoming idea of smart city becomes feasible and put on a lot of attention from the research community due to its effect on everyday life’s improvement and modernization. The concept of a smart city should support everything from electrical grids to traffic management and requires the transmission of a huge amount of data. Smart city planning with a reliable communication infrastructure that can provide stringent network requirements is unfeasible without the joint of optical and wireless technologies. This paper aims to provide an overview of recent developments of advanced optical networking to provide 5G transport networks and their applications in connecting a huge number of devices in future smart city infrastructures. The implementation of optical technologies in 5G core networking open numerous questions of how wireless and optical can coexist to provide sophisticated future applications, such as the smart city concept. Within this research, we will provide the answers to some of the key related questions.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kondepudi, S. N., Ramanarayanan, V., Jain, A., Singh, G. N., Agarwal, N. K. N., Kumar, R., Singh, R., Bergmark, P., Hashitani T., Gemma P., Sang, Z., Torres, D., Ospina, A., & Menon, M. (2014). A smart sustainable cities: An analysis of definitions. Technical report. ITU-T. Retrieved November 25th, 2020, from https://www.itu.int/en/ITU-T/focusgroups/ssc/Pages/default.aspx.
Silva, B. N., Khan, M., & Han, K. (2018). Towards sustainable smart cities: A review of trends, architectures, components, and open challenges in smart cities. Sustainable Cities and Society, 38, 697–713.
Aleksic, S. (2019). A survey on optical technologies for IoT, smart industry, and smart infrastructures. Journal of Sensor and Actuator Networks, 8(47), 1–18.
Miladić-Tešić, S., & Marković, G. (2020). Development of optical networking for 5G smart infrastructures. In 5th EAI international conference on management of manufacturing systems. Springer. https://www.springer.com/gp/book/9783030672409#aboutBook(in Press).
Miladić-Tešić, S., Marković, G., & Nonković, N. (2020). Optical technologies in support of the smart city concept. Tehnika, 67(2), 209–215.
ITU-T. (2012). Overview of the Internet of Things. Recommendation Y. 2060. ITU. Retrieved December 15th, 2020, from https://www.itu.int/rec/T-REC-Y.2060-201206-I.
Ortiz, R., Narvaez, W., Azurza, W., Sang, Z., Gemma, P., & Anthopoulos, L. (2015). Overview of smart sustainable cities architecture. Technical report. ITU-T. Retrieved December 30th, 2020, from https://www.itu.int/en/ITU-T/focusgroups/ssc/Pages/default.aspx.
Wey, J. S., & Zhang, J. (2018). Passive optical network for 5G transport: Technology and standards. Journal of Lightway Technology, 37(12), 2830–2837.
Doo, K.-H., Kim, K., Lee, H. H., Kim, S. H., & Park, H. (2019). Optical access and transport technologies for 5G and beyond. In 24th OptoElectronics and communications conference (OECC) and 2019 international conference on photonics in switching and computing (PSC) (pp. S1–S3). IEEE.
Silva, B. N., Khan, M., & Han, K. (2017). Big data analytics embedded smart city architecture for performance enhancement through real-time data processing and decision-making. Wireless Communication and Mobile computing, 2017, 1–12.
Shafi, M., Molisch, A. F., Smith, P. J., Haustein, T., Zhu, P., De Silva, P., Tufvesson, F., Benjebbour, A., & Wunder, G. (2017). 5G: A tutorial overview of standards, trials, challenges, deployment, and practice. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 35(6), 1201–1221.
Jaber, M., Ali Imran, M., Tafazolli, R., & Tukmanov, A. (2016). 5G backhaul challenges and emerging research directions: A survey. IEEE Access, 4, 1743–1766.
Ijaz, A., Zhang, L., Grau, M., Mohamed, A., Vural, S., Quddus, A. U., Imran, M. A., Foh, C. H., & Tafazolli, R. (2016). Enabling massive IoT in 5G and beyond systems: PHY radio frame design considerations. IEEE Access, 4, 3322–3339.
Liu, X., & Effenberger, F. (2016). Emerging optical acces network technologies for 5G wireless [Invited]. Journal of Optical Communication and Networking, 8(12), B70–B79.
Parvez, I., Rahmati, A., Guvenc, I., Sarwat, A. I., & Dai, H. (2018). A survey on low latency towards 5G: RAN, core network and caching solutions. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 20(4), 3098–3130.
Iovanna, P., Bottari, G., Ponzini, F., & Contreras, L. M. (2018). Latency-driven transport for 5G. Journal of Optical Communications and Networking, 10(8), 695–702.
Fiorani, M., Tombaz, S., Mårtensson, J., Skubic, B., Wosinska, L., & Monti, P. (2016). Modeling energy performance of C-RAN with optical transport in 5G network scenarios. Journal of Optical Communications and Networking, 8(11), B21–B34.
Talebi, S., Alam, F., Katib, I., Khamis, M., Salama, R., & Rouskas, G. N. (2014). Spectrum management techniques for elastic optical networks: A survey. Optical Switching and Networking, 13, 34–48.
Chowdhury, M. Z., Shahjalah, M., Hasan, M. K., & Jang, Y. M. (2019). The role of optical wireless communication in 5G/6G and IoT solutions: Prospects, directions and challenges. Applied Sciences, 9(20), 4367.
Alimi, I. A., Tavares, A., Pinho, C., Abdalla, A. M., Monteiro, P. P., & Teixeira, A. L. (2019). Enabling optical wired and wireless technologies for 5G and beyond networks. In I. A. Alimi, P. P. Monteiro, & A. L. Teixeira (Eds.), Telecommunication systems-principles and applications of wireless-optical technologies. IntechOpen.
Abbas, H. S., & Gregory, M. A. (2016). The next generation of passive optical networks: A review. Journal of Network and Computing Applications, 67, 53–74.
Houtsma, V., & Van Veen, D. (2018). Bi-directional 25G/50G TDM-PON with extended power budget using 25G APD and coherent detection. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 36(1), 122–127.
Hatta, S., Tanaka, N., & Sakamoto, T. (2017). Low latency dynamic bandwidth allocation method with high bandwidth efficiency for TDM-PON. Ntt Technical Review, 15(4), 1–7.
Yen, C.-T., & Chen, C.-M. (2015). A study of three-dimensional optical code-division multipleaccess for optical fiber sensor networks. Computers and Electrical Engineering, 49, 136–145.
Shaddad, R. Q., Mohammad, A. B., Al-Gailani, S. A., Al-hetar, A. M., & Elmagzoub, M. A. (2014). A survey on access technologies for broadband optical and wireless networks. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 41, 459–472.
Bindhaiq, S., Supa, A. S. M., Zulkifli, N., Mohammad, A. B., Shaddad, R. Q., Elmagzoub, M. A., & Faisal, A. (2015). Recent development on time and wavelength-division multiplexed passive optical network (TWDM-PON) for next-generation passive optical network stage 2 (NG-PON2). Optical Switching and Networking, 15, 53–66.
Peters, A., Hugues-Salas, E., Gunkel, M., & Zervas, G. (2017). Key performance indicators for elastic optical transponders and ROADMs: The role of flexibility. Optical Switching and Networking, 25, 1–12.
ITU-T. (2012). Spectral grids for WDM applications: DWDM frequency grid. v2.0. Recommendation G.694.1. ITU. Retrieved December 15th, 2020, from https://www.itu.int/rec/T-REC-G.694.1/en.
Boutaba, R., Shahriar, N., & Fathi, S. (2017). Elastic optical networking for 5G transport. Journal of Network and System Management, 25(4), 819–847.
Sócrates-Dantas, J., Careglio, D., Perelló, J., Silveira, R. M., Ruggiero, W. V., & Solè-Pareta, J. (2014). Challenges and requirements of a control plane for elastic optical networks. Computer Networks, 72, 156–171.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miladić-Tešić, S., Marković, G., Peraković, D. et al. A review of optical networking technologies supporting 5G communication infrastructure. Wireless Netw 28, 459–467 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-021-02582-6
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-021-02582-6