Abstract
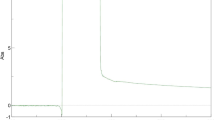
The green synthesized nanoparticles have been determined as a novel pesticide against arthropod pests. This study was designed to evaluate the in vitro acaricidal activity of green synthesized nickel oxide nanoparticles (NiO NPs) using aqueous extract of Melia azedarach ripened fruits against different developmental stages of the camel tick Hyalomma dromedarii in addition to their toxic effect on laboratory animals. The synthesized NiO NPs were characterized by UV–visible (UV–Vis) spectroscopy, Fourier transforms infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS). The UV–Vis spectra of the NiO NPs showed an absorption peak at 307 nm. FTIR analysis showed the possible functional groups used for capping and stabilization of NiO NPs with strong bands at 3416.2 and 1626.6 cm−1. The SEM images of the NiO NPs exhibited a size ranging from 21 to 35 nm. The immersion test was used for the in vitro application of the synthesized NiO NPs on the various tick stages (egg, nymph, larva, and adult). Mortality percentages and LC50 values of each tick stage were calculated. The oviposition and hatchability of the engorged females were monitored for the survived tick after treatment. The LC50 values for NiO NPs on embryonated eggs, larvae, and engorged nymphs were 5.00, 7.15, and 1.90 mg/mL, respectively. The egg productive index (EPI), egg number, and hatchability (%) were lower in females treated with the NiO NPs than in control ticks. The toxicity of the NiO NPs on laboratory animals was also investigated using Swiss albino mice by oral dose of 500 mg/kg/day administration for five consecutive days. The hematological, biochemical, and histopathological changes were evaluated. The hematological analysis showed significant increase in the level of white blood cells (WBC) and hemoglobin (Hb). Biochemical analysis showed non-significant decrease in alkaline phosphatase (ALP) and alanine amino transferase (ALT). We concluded that NiO NPs have a significant acaricidal activity as demonstrated on eggs, larvae, engorged nymphs, and fully fed females of H. dromedarii. From a toxicological point of view further in vivo investigations are needed to determine the mechanism of toxic effect of NiO NPs.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbasi BA, Iqbal J, Mahmood T, Ahmad R, Kanwal S, Afridi S (2019) Plant-mediated synthesis of nickel oxide nanoparticles (NiO) via Geranium wallichianum: characterization and different biological applications. Mater Res Express 6:0850a7
Abdel-Ghany HS, Fahmy MM, Abuowarda MM, Abdel-Shafy S, El-Khateeb RM, Hoballah EM (2019) In vitro acaricidal effect of Melia azedarach and Artemisia herba-alba extracts on Hyalomma dromedarii (Acari: Ixodidae): embryonated eggs and engorged nymphs. J Parasitic Dis 43:696–710
Abdel-Shafy S (2000). Microbiological and control studies on ticks infesting farm animals and poultry. PhD Thesis, Faculty of Agriculture, Cairo University
Abdel-Shafy S (2008) Scanning electron microscopy and comparative morphology of Hyalomma anatolicum excavatum, H. dromedarii and H. marginatum marginatum (Acari: Ixodidae) based on larvae. Acarologia 48:19–31
Abdel-Shafy S, Soliman MM, Habeeb SM (2007) In vitro acaricidal effect of some crude extracts and essential oils of wild plants against certain tick species. Acarologia 47:33–42
Abdel-Shafy S, Allam NA, Mediannikov O, Parola P, Raoult D (2012) Molecular detection of spotted fever group rickettsiae associated with ixodid ticks in Egypt. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis 12:346–359
Abdullah HH, El-Molla A, Salib FA, Allam NA, Ghazy AA, Abdel-Shafy S (2016) Morphological and molecular identification of the brown dog tick Rhipicephalus sanguineus and the camel tick Hyalomma dromedarii (Acari: Ixodidae) vectors of Rickettsioses in Egypt. Vet World 9:1087–1101
Abuowarda MM, Haleem MA, Elsayed M, Farag H, Magdy S (2020) Bio-pesticide control of the brown dog tick (Rhipicephalus sanguineus) in Egypt By Using Two Entomopathogenic Fungi (Beauveria bassiana and Metarhizium anisopliae). Int J Vet Sci 9:175–181
Adeel M, Ma C, Ullah S, Rizwan M, Hao Y, Chen C, Tsang DC (2019) Exposure to nickel oxide nanoparticles insinuates physiological, ultrastructural and oxidative damage: a life cycle study on Eisenia fetida. Environ Pollut 254:113032
Adeel M, Tingting J, Hussain T, He X, Ahmad MA, Irshad MK, Zhiyong Z (2020) Bioaccumulation of ytterbium oxide nanoparticles insinuate oxidative stress, inflammatory, and pathological lesions in ICR mice. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:32944–32953
Ahamed M, Karns M, Goodson M, Rowe J, Hussain SM, Schlager JJ, Hong Y (2008) DNA damage response to different surface chemistry of silver nanoparticles in mammalian cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 233:404–410
Ahamed M, Ali D, Alhadlaq HA, Akhtar MJ (2013) Nickel oxide nanoparticles exert cytotoxicity viaoxidative stress and induce apoptotic response in human liver cells (HepG2). Chemosphere 93:2514–2522
Ajdari M, Ghahnavieh MZ (2014) Histopathology effects of nickel nanoparticles on lungs, liver, and spleen tissues in male mice. Int Nano Lett 4:113
Arafa WM, Mohammed AN, El-Ela FIA (2019) Acaricidal efficacy of deltamethrin-zinc oxide nanocomposite on Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) annulatus tick. Vet Parasitol 268:36–45
Aromal SA, Philip D (2012) Green synthesis of gold nanoparticles using Trigonella foenum-graecum and its size-dependent catalytic activity. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 97:1–5
Banumathi B, Malaikozhundan B, Vaseeharan B (2016) In vitro acaricidal activity of ethnoveterinary plants and green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles against Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus. Vet Parasitol 216:93–100
Baun A, Hartmann NB, Grieger K, Kusk KO (2008) Ecotoxicity of engineered nanoparticles to aquatic invertebrates: a brief review and recommendations for future toxicity testing. Ecotoxicology 17:387–395
Benelli G, Maggi F, Pavela R, Murugan K, Govindarajan M, Vaseeharan B, Petrelli R, Cappellacci L, Kumar S, Hofer A, Youssefi MR, Alarfaj AA, Hwang JS, Higuchi A (2017) Mosquito control with green nanopesticides: towards the One Health approach? A review of non-target effects. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:10184–10206
Bhakyaraj K, Kumaraguru S, Gopinath K, Sabitha V, Kaleeswarran PR, Karthika V, Arumugam A (2017) Eco-friendly synthesis of palladium nanoparticles using Melia azedarach leaf extract and their evaluation for antimicrobial and larvicidal activities. J Cluster Sci 28:463–476
Chandler D, Davidson G, Pell JK, Ball BV, Shaw K, Sunderland KD (2000) Fungal biocontrol of acari. Biocontrol Sci Technol 10:357–384
Chandrasekaran R, Gnanasekar S, Seetharaman P, Keppanan R, Arockiaswamy W, Sivaperumal S (2016) Formulation of Carica papaya latex-functionalized silver nanoparticles for its improved antibacterial and anticancer applications. J Mol Liq 219:232–238
Chen HW, Su SF, Chien CT, Lin WH, Yu SL, Chou CC, Chen JJ, Yang PC (2006) Titanium dioxide nanoparticles induce emphysema-like lung injury in mice. FASEB J 20:2393–2395
Chinnasamy G, Chandrasekharan S, Bhatnagar S (2019) Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles from Melia azedarach: Enhancement of antibacterial, wound healing, antidiabetic and antioxidant activities. Int J Nanomed 14:9823
Dhandapani P, Siddarth AS, Kamalasekaran S, Maruthamuthu S, Rajagopal G (2014) Bio-approach: ureolytic bacteria mediated synthesis of ZnO nanocrystals on cotton fabric and evaluation of their antibacterial properties. Carbohydr Polym 103:448–455
Drummond RO, Ernst SE, Trevino JL, Gladney WJ, Graham OH (1973) Boophilus annulatus and B. microplus: laboratory tests of insecticides. J Econ Entomol 66:130–133
Dumala N, Mangalampalli B, Kalyan Kamal SS, Grover P (2018) Biochemical alterations induced by nickel oxide nanoparticles in female Wistar albino rats after acute oral exposure. Biomarkers 23:33–43
Dumala N, Mangalampalli B, Kalyan Kamal SS, Grover P (2019) Repeated oral dose toxicity study of nickel oxide nanoparticles in Wistar rats: a histological and biochemical perspective. J Appl Toxicol 39:1012–1029
El-Hadidi MN, Boulos L (1988). The street trees of Egypt, no. revised edn. American University in Cairo Press, Cairo
Esmaeillou M, Moharamnejad M, Hsankhani R, Tehrani AA, Maadi H (2013) Toxicity of ZnO nanoparticles in healthy adult mice. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 35:67–71
Ezhilarasi AA, Vijaya JJ, Kaviyarasu K, Maaza M, Ayeshamariam A, Kennedy LJ (2016) Cytotoxicity effect of nanoparticles against HT-29 cancer cells. J Photochem Photobiol B Biol 164:352–360
Finney DJ (1962) Probit analysis a statistical treatment of the response curve. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Gandhi PR, Jayaseelan C, Mary RR, Mathivanan D, Suseem SR (2017) Acaricidal, pediculicidal and larvicidal activity of synthesized ZnO nanoparticles using Momordica charantia leaf extract against blood feeding parasites. Exp Parasitol 181:47–56
Guglielmone AA, Robbins RG, Apanaskevich DA, Petney TN, Estrada Pena A, Horak IG (2014) Hard ticks (Acari: Ixodida: Ixodidae) of the world. Springer, Heidelberg
Gui S, Zhang Z, Zheng L, Cui Y, Liu X, Li N, Sang X, Sun Q, Gao G, Cheng Z, Cheng J, Wang L, Tang M, Hong F (2011) Molecular mechanism of kidney injury of mice caused by exposure to titanium dioxide nanoparticles. J Hazard Mater 195:365–370
Handa SS, Rakesh DD, Vasisht K (2006). Compendium of medicinal and aromatic plants. United Nations Industrial Development Organization and the International Centre for Science and High Technology, pp 16–286
Hassan MI, Gabr HSM, Abdel-Shafy S, Hammad KM, Mokhtar MM (2017) Molecular detection of Borrelia sp. In Ornithodoros savignyi and Rhipicephalus annulatus by flab gene and Babesia bigemina in R. annulatus by 18s rRNA gene. J Egypt Soc Parasitol 47:403–414
Hillyer JF, Albrecht RM (2001) Gastrointestinal persorption and tissue distribution of differently sized colloidal gold nanoparticles. J Pharm Sci 90:1927–1936
Horie M, Nishio K, Fujita K, Kato H, Nakamura A, Kinugasa S, Endoh S, Miyauchi A, Yamamoto K, Murayama H (2009) Ultrafine NiO particles induce cytotoxicity in vitro by cellular uptake and subsequent Ni (II) release. Chem Res Toxicol 22:1415–1426
Horie M, Fukui H, Nishio K, Endoh S, Kato H, Fujita K, Miyauchi A, Nakamura A, Shichiri M, Ishida N (2011) Evaluation of acute oxidative stress induced by NiO nanoparticles in vivo and in vitro. J Occup Health 53(2):64–74
Iqbal J, Abbasi BA, Mahmood T, Hameed S, Munir A, Kanwal S (2019) Green synthesis and characterizations of Nickel oxide nanoparticles using leaf extract of Rhamnus virgata and their potential biological applications. Appl Organomet Chem 33:e4950
Irache JM, Esparza I, Gamazo C, Agueros M, Espuelas S (2011) Nanomedicine: novel approaches in human and veterinary therapeutics. Vet Parasitol 180:47–71
Jayaseelan C, Rahuman AA (2012) Acaricidal efficacy of synthesized silver nanoparticles using aqueous leaf extract of Ocimum canum against Hyalomma anatolicum anatolicum and Hyalomma marginatum isaaci (Acari: Ixodidae). Parasitol Res 111:1369–1378
Jebril S, Dridi C (2020) Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Melia azedarach leaf extract and their antifungal activities: in vitro and in vivo. Mater Chem Phys 248:122898
Khan TM, Mateen A (2018) Synthesis of CuO nanoparticles by using leaf extracts of Melia azedarach and Morusnigra and their antibacterial activity. J Innov Sci 4:120–129
Kirthi AV, Rahuman AA, Rajakumar G, Marimuthu S, Santhoshkumar T, Jayaseelan C, Velayutham K (2011) Acaricidal, pediculocidal and larvicidal activity of synthesized ZnO nanoparticles using wet chemical route against blood feeding parasites. Parasitol Res 109:461–472
Kohler D, Dellweg D (2010) Polycythemia. Dtsch Med Wochenschr 135:2300–2303
Kong B, Seog JH, Graham LM, Lee SP (2011) Experimental considerations on the cytotoxicity of nanoparticles. Nanomed J 6:929–941
Kumar S (2010) Nanotechnology and animal health. Vet World 3:567–569
Litvin VA, Minaev BF (2013) Spectroscopy study of silver nanoparticles fabrication using synthetic humic substances and their antimicrobial activity. Spectrochim Acta Part A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 108:115–122
Magaye RR, Yue X, Zou B, Shi H, Yu H, Liu K, Zhao J (2014) Acute toxicity of nickel nanoparticles in rats after intravenous injection. Int J Nanomed 9:1393
Makarov VV, Love AJ, Sinitsyna OV, Makarova SS, Yaminsky IV, Taliansky ME, Kalinina NO (2014) Green nanotechnologies: synthesis of metal nanoparticles using plants. Acta Nat 6:20
Mamuru SA, Jaji N (2015) Voltammetric and impedimetric behaviour of phytosynthesized nickel nanoparticles. J Nanostruct Chem 5:347–356
Manokari M, Ravindran CP, Shekhawat MS (2016) Biosynthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Melia azedarach L. extracts and their characterization. Int J Pharm Sci Res 1:31–36
Marimuthu S, Rahuman AA, Rajakumar G, Santhoshkumar T, Kirthi AV, Jayaseelan C, Bagavan A, Zahir AA, Elango G, Kamaraj C (2011) Evaluation of green synthesized silver nanoparticles against parasites. Parasitol Res 108:1541–1549
Marimuthu S, Rahuman AA, Jayaseelan C, Kirthi AV, Santhoshkumar T, Velayutham K, Bagavan A, Kamaraj C, Elango G, Iyappan M, Siva C, Karthik L, Rao KV (2013) Acaricidal activity of synthesized titanium dioxide nanoparticles using Calotropis gigantea against Rhipicephalus microplus and Haemaphysalis bispinosa. Asian Pac J Trop Med 6:682–688
Massoud AM, Kutkat MA, Abdel-Shafy S, El-Khateeb RM, Labib IM (2005) Acaricidal efficacy of Myrrh (Commiphora molmol) on the fowl tick Argas persicus (Acari: Argasidae). J Egypt Soc Parasitol 35:667–686
Mehmood A, Murtaza G, Bhatti TM, Kausar R (2017) Phyto-mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles from Melia azedarach L. leaf extract: characterization and antibacterial activity. Arab J Chem 10:S3048–S3053
Nasseri MA, Ahrari F, Zakerinasab B (2016) Synthesis of nano-spherical nickel by templating hibiscus flower petals. J Nanosci Nanotechnol Appl Organomet Chem 30:978–984
Norouzi R, Ataei A, Hejazy M, Shahbazi P (2019) Acaricidal activity of zinc oxide nanoparticles against Hyalomma spp. in vitro. Nanomed Res J 4:234–238
Osuntokun J, Onwudiwe DC, Ebenso EE (2019) Green synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles using aqueous Brassica oleracea L. var. italica and the photocatalytic activity. Green Chem Lett Rev 12:444–457
Rai M, Ingle A (2012) Role of nanotechnology in agriculture with special reference to management of insect pests. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 94:287–293
Rajakumar G, Rahuman AA, Velayutham K, Ramyadevi J, Jeyasubramanian K, Marikani A, Zahir AA (2013) Novel and simple approach using synthesized nickel nanoparticles to control blood-sucking parasites. Vet Parasitol 191:332–339
Rajakumar G, Rahuman AA, Roopan SM, Chung IM, Anbarasan K, Karthikeyan V (2015) Efficacy of larvicidal activity of green synthesized titanium dioxide nanoparticles using Mangifera indica extract against blood-feeding parasites. Parasitol Res 114:571–581
Ramyadevi J, Jeyasubramanian K, Marikani A, Rajakumar G, Rahuman AA, Santhoshkumar T, Kirthi AV, Jayaseelan C, Marimuthu S (2011) Copper nanoparticles synthesized by polyol process used to control hematophagous parasites. Parasitol Res 109:1403–1415
Rastogi L, Arunachalam J (2011) Sunlight based irradiation strategy for rapid green synthesis of highly stable silver nanoparticles using aqueous garlic (Allium sativum) extract and their antibacterial potential. Mat Chem Phys 129:558–563
Rubae AAY (2009) The potential uses of Melia azedarach L. as pesticidal and medicinal plant, review. Am Eurasian J Sustain Agric 3:185–195
Saquib Q, Attia SM, Ansari SM, Al-Salim A, Faisal M, Alatar AA, Al-Khedhairy AA (2017) p53, MAPKAPK-2 and caspases regulate nickel oxide nanoparticles induce cell death and cytogenetic anomalies in rats. Int J Biol Macromol 105:228–237
Sathishkumar M, Sneha K, Won WS, Cho CW, Kim S, Yun YS (2009) Cynamon zeylanicum bark extract and powder mediated green synthesis of nanocrystalline silver particles and its bactericidal activity. Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces 73:332–338
Sharmila G, Thirumarimurugan M, Muthukumaran C (2019) Green synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles using Tecoma castanifolia leaf extract: characterization and evaluation of its antioxidant, bactericidal and anticancer activities. Microchem J 145:578–587
Shimizu S, Nojiri K, Matsunaga N, Yamanea I, Minamia T (2000) Reduction in tick numbers (Haemaphysalis longicornis), mortality and incidence of Theileria sergenti infection in field-grazed calves treated with flumethrin pour-on. Vet Parasitol 92:129–138
Siddiqui MA, Ahamed M, Ahmad J, Khan MM, Musarrat J, Al-Khedhairy AA, Alrokayan SA (2012) Nickel oxide nanoparticles induce cytotoxicity, oxidative stress and apoptosis in cultured human cells that is abrogated by the dietary antioxidant curcumin. Food Chem Toxicol 50:641–647
Singh N, Manshian B, Jenkins GJ, Griffiths SM, Williams PM, Maffeis TG, Wright CJ, Doak SH (2009) Nano Genotoxicology: the DNA damaging potential of engineered nanomaterials. Biomaterials 30:3891–3914
Sone BT, Fuku XG, Maaza M (2016) Physical and electrochemical properties of green synthesized bunsenite NiO nanoparticles via Callistemon viminalis’ extracts. Int J Electrochem Sci 11:8204–8220
Sousa LA, Soares SF, Pires Junior HB, Ferri PH, Borges LMF (2008) Evaluation of efficacy of ripe and unripe fruit oil extracts of Melia azedarach against Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus (Acari: ixodidae). Rev Bras DE Parasitol Vet 17:36–40
Sousa LAD, Junior HBP, Soares SF, Ferri PH, Ribas P, Lima EM, Borges LMF (2011) Potential synergistic effect of Melia azedarach fruit extract and Beauveria bassiana in the control of Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus (Acari: Ixodidae) in cattle infestations. Vet Parasitol 175:320–324
Underwood C, Van Eps AW (2012) Nanomedicine and veterinary science: The reality and the practicality. Vet J 193:12–23
Walker AR, Bouattour A, Camicas JL, Estrada-Pena A, Horak IG, Latif AA, Pegram RG, Preston PM (2003). Ticks of domestic animals in Africa: a guide to identification of species. Bio Science Reports, Edinburgh, pp 3:210
Wandscheer CB, Duque JE, da Silva MA, Fukuyama Y, Wohlke JL, Adelmann J, Fontana JD (2004) Larvicidal action of ethanolic extracts from fruit endocarps of Melia azedarach and Azadirachta indica against the dengue mosquito Aedes aegypti. Toxicon 44:829–835
Wang J, Zhou G, Chen C, Yu H, Wang T, Ma Y, Li Y (2007) Acute toxicity and biodistribution of different sized titanium dioxide particles in mice after oral administration. Toxicol Lett 168:176–185
Yuvakkumar R, Suresh J, Nathanael AJ, Sundrarajan M, Hong SI (2014) A green biosynthesis of NiO nanoparticles using aqueous extract of Tamarix serotina and their characterization and application. Mater Lett 128:170–174
Acknowledgements
This study is a part of a PhD thesis to be submitted to the Department of Parasitology, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Cairo University. The study was financially supported by the National Research Centre as a part of PhD Thesis No. 12/2/19.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MMF, SA, MMA, RME, and HSMA designed the experiments. EMH and HSMA participated in the preparation of Nickel oxide nanoparticles. MMF, SA, MMA, RME, AMH and HSMA shared in bioassay of the NiO NPs against various developmental stages of H. dromedarii and evaluation the toxic effect of NiO NPs on Swiss albino mice. SA and HSMA analyzed and tabulated the data. MMF, SA, MMA, and HSMA wrote the draft of the manuscript. All authors revised and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This study was approved by Ethical Committee for Medical and Veterinary Research at the National Research Centre (NRC), Egypt in accordance with local laws and regulations (Approval Protocol No. 20148). Consent was obtained from the owners of camels included in this study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abdel-Ghany, H.S.M., Abdel-Shafy, S., Abuowarda, M.M. et al. In vitro acaricidal activity of green synthesized nickel oxide nanoparticles against the camel tick, Hyalomma dromedarii (Ixodidae), and its toxicity on Swiss albino mice. Exp Appl Acarol 83, 611–633 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10493-021-00596-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10493-021-00596-5