Abstract
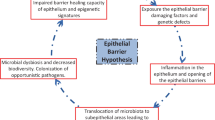
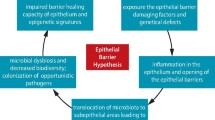
As an integral part of the innate immune system, the epithelial membrane is exposed to an array of insults that may trigger an immune response. One of the immune system’s main functions is to regulate the level of communications between the mucosa and the lumen of various tissues. While it is clear that inhaled or ingested substances, or microorganisms may induce changes that affect the epithelial barrier in various ways, the proteins involved in the signaling cascades and physiological events leading to the regulation and maintenance of the barrier are not always well characterized. We review here some of the signaling components involved in regulating the barrier’s paracellular permeability, and their potential effects on the activation of an immune response. While an effective immune response must be launched against pathogenic insults, tolerance must also be maintained for non-pathogenic antigens such as those in the commensal flora or for endogenous metabolites. Along with other members of the innate and adaptive immunity, the endocannabinoid system also plays an instrumental role in maintaining the balance between inflammation and tolerance. We discuss the potential effects of endo- and phytocannabinoids on epithelial permeability and how the dysregulation of this system could be involved in diseases and targeted for therapy.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Glencross DA, Ho T-R, Camiña N, Hawrylowicz CM, Pfeffer PE. Air pollution and its effects on the immune system. Free Radical Biol Med. 2020;151:56–68.
Chelakkot C, Ghim J, Ryu SH. Mechanisms regulating intestinal barrier integrity and its pathological implications. Exp Mol Med. 2018;50:1–9.
Ebnet K, Kummer D, Steinbacher T, Singh A, Nakayama M, Matis M. Regulation of cell polarity by cell adhesion receptors. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2018;81:2–12.
Otani T, Furuse M. Tight junction structure and function revisited. Trends Cell Biol. 2020;30:805–17.
Wang Q, Margolis B. Apical junctional complexes and cell polarity. Kidney Int. 2007;72:1448–58.
Van Itallie CM, Anderson JM. Architecture of tight junctions and principles of molecular composition. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2014;36:157–65.
Coopman P, Djiane A. Adherens junction and E-cadherin complex regulation by epithelial polarity. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2016;73:3535–53.
Rezaee F, Georas SN. Breaking barriers. New insights into airway epithelial barrier function in health and disease. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2014;50:857–69.
Campbell HK, Maiers JL, DeMali KA. Interplay between tight junctions & adherens junctions. Exp Cell Res. 2017;358:39–44.
Su W-H, Mruk DD, Wong EWP, Lui W-Y, Cheng CY. Polarity protein complex scribble/Lgl/Dlg and epithelial cell barriers. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2012;763:149–70.
Nelson WJ, Nusse R. Convergence of Wnt, [beta]-Catenin, and cadherin pathways. Science. 2004;303:1483–7.
Lee B, Moon KM, Kim CY. Tight junction in the intestinal epithelium: its association with diseases and regulation by phytochemicals [Internet]. J Immunol Res. 2018 [cited 2020 Jul 23]. https://www.hindawi.com/journals/jir/2018/2645465/
Ivanov AI, Parkos CA, Nusrat A. Cytoskeletal regulation of epithelial barrier function during inflammation. Am J Pathol. 2010;177:512–24.
Schumann M, Siegmund B, Schulzke JD, Fromm M. Celiac disease: role of the epithelial barrier. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017;3:150–62.
Michel D, Arsanto J-P, Massey-Harroche D, Béclin C, Wijnholds J, Bivic AL. PATJ connects and stabilizes apical and lateral components of tight junctions in human intestinal cells. J Cell Sci. 2005;118:4049–57.
Gao Y, Lui W, Lee WM, Cheng CY. Polarity protein Crumbs homolog-3 (CRB3) regulates ectoplasmic specialization dynamics through its action on F-actin organization in Sertoli cells. Sci Rep [Internet]. 2016 [cited 2020 Jul 28];6. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4928075/
Margolis B. The crumbs3 polarity protein. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2018;10:a027961.
Tilston-Lünel AM, Haley KE, Schlecht NF, Wang Y, Chatterton ALD, Moleirinho S, et al. Crumbs 3b promotes tight junctions in an ezrin-dependent manner in mammalian cells. J Mol Cell Biol. 2016;8:439–55.
Misra JR, Irvine KD. The hippo signaling network and its biological functions. Annu Rev Genet. 2018;52:65–87.
Bae SJ, Luo X. Activation mechanisms of the Hippo kinase signaling cascade. Biosci Rep [Internet]. 2018 [cited 2020 Jul 24];38. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6131212/
Varelas X, Samavarchi-Tehrani P, Narimatsu M, Weiss A, Cockburn K, Larsen BG, et al. The crumbs complex couples cell density sensing to hippo-dependent control of the TGF-β-SMAD pathway. Dev Cell. 2010;19:831–44.
Szymaniak AD, Mahoney JE, Cardoso WV, Varelas X. Crumbs3-mediated polarity directs airway epithelial cell fate through the hippo pathway effector yap. Dev Cell. 2015;34:283–96.
Riga A, Castiglioni VG, Boxem M. New insights into apical-basal polarization in epithelia. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2020;62:1–8.
Suzuki A, Ohno S. The PAR-aPKC system: lessons in polarity. J Cell Sci. 2006;119:979–87.
Sumigray KD, Peifer M. Cell shape by coercion: Par1 and aPKC put the squeeze on junctions. Dev Cell. 2012;22:907–8.
Reich JD, Hubatsch L, Illukkumbura R, Peglion F, Bland T, Hirani N, et al. Regulated activation of the PAR polarity network ensures a timely and specific response to spatial cues. Curr Biol. 2019;29(1911–1923):e5.
Klunder LJ, Faber KN, Dijkstra G, van IJzendoorn SCD. Mechanisms of cell polarity–controlled epithelial homeostasis and immunity in the intestine. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol [Internet]. 2017 [cited 2020 Jun 4];9. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5495056/
Helfrich I, Schmitz A, Zigrino P, Michels C, Haase I, le Bivic A, et al. Role of aPKC isoforms and their binding partners Par3 and Par6 in epidermal barrier formation. J Investig Dermatol. 2007;127:782–91.
Mashukova A, Wald FA, Salas PJ. Tumor necrosis factor alpha and inflammation disrupt the polarity complex in intestinal epithelial cells by a posttranslational mechanism. Mol Cell Biol. 2011;31:756–65.
Etienne-Manneville S, Hall A. Cell polarity: Par6, aPKC and cytoskeletal crosstalk. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2003;15:67–72.
Gao L, Joberty G, Macara IG. Assembly of epithelial tight junctions is negatively regulated by Par6. Curr Biol. 2002;12:221–5.
Mizuno K, Suzuki A, Hirose T, Kitamura K, Kutsuzawa K, Futaki M, et al. Self-association of PAR-3-mediated by the conserved N-terminal domain contributes to the development of epithelial tight junctions. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:31240–50.
Suzuki A, Yamanaka T, Hirose T, Manabe N, Mizuno K, Shimizu M, et al. Atypical protein kinase C is involved in the evolutionarily conserved par protein complex and plays a critical role in establishing epithelia-specific junctional structures. J Cell Biol. 2001;152:1183–96.
Georgiou M, Marinari E, Burden J, Baum B. Cdc42, Par6, and aPKC regulate Arp2/3-mediated endocytosis to control local adherens junction stability. Curr Biol. 2008;18:1631–8.
Itoh N, Nakayama M, Nishimura T, Fujisue S, Nishioka T, Watanabe T, et al. Identification of focal adhesion kinase (FAK) and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3-kinase) as Par3 partners by proteomic analysis. Cytoskeleton. 2010;67:297–308.
Elias BC, Das A, Parekh DV, Mernaugh G, Adams R, Yang Z, et al. Cdc42 regulates epithelial cell polarity and cytoskeletal function during kidney tubule development. J Cell Sci. 2015;128:4293–305.
Hao Y, Du Q, Chen X, Zheng Z, Balsbaugh JL, Maitra S, et al. Par3 controls epithelial spindle orientation by aPKC-mediated phosphorylation of apical pins. Curr Biol. 2010;20:1809–18.
Pallesi-Pocachard E, Bazellieres E, Viallat-Lieutaud A, Delgrossi M-H, Barthelemy-Requin M, Le Bivic A, et al. Hook2, a microtubule-binding protein, interacts with Par6α and controls centrosome orientation during polarized cell migration. Sci Rep [Internet]. 2016 [cited 2020 Jul 15];6. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5021942/
Forteza R, Wald FA, Mashukova A, Kozhekbaeva Z, Salas PJ. Par-complex aPKC and Par3 cross-talk with innate immunity NF-κB pathway in epithelial cells. Biol Open. 2013;2:1264–9.
de Vreede G, Schoenfeld JD, Windler SL, Morrison H, Lu H, Bilder D. The Scribble module regulates retromer-dependent endocytic trafficking during epithelial polarization. Development. 2014;141:2796–802.
Su W, Wong EWP, Mruk DD, Cheng CY. The Scribble/Lgl/Dlg polarity protein complex is a regulator of blood-testis barrier dynamics and spermatid polarity during spermatogenesis. Endocrinology. 2012;153:6041–53.
Sharifkhodaei Z, Gilbert MM, Auld VJ. Scribble and discs large mediate tricellular junction formation. Development [Internet]. Oxford University Press for The Company of Biologists Limited; 2019 [cited 2020 Jul 17];146. https://dev.biologists.org/content/146/18/dev174763
Ivanov AI, Young C, Beste KD, Capaldo CT, Humbert PO, Brennwald P, et al. Tumor suppressor Scribble regulates assembly of tight junctions in the intestinal epithelium. Am J Pathol. 2010;176:134–45.
Stucke VM, Timmerman E, Vandekerckhove J, Gevaert K, Hall A. The MAGUK protein MPP7 binds to the polarity protein hDlg1 and facilitates epithelial tight junction formation. Mol Biol Cell. 2007;18:1744–55.
Bilder D, Perrimon N. Localization of apical epithelial determinants by the basolateral PDZ protein Scribble. Nature. 2000;403:676–80.
Yates LL, Schnatwinkel C, Hazelwood L, Chessum L, Paudyal A, Hilton H, et al. Scribble is required for normal epithelial cell–cell contacts and lumen morphogenesis in the mammalian lung. Dev Biol. 2013;373:267–80.
Yoshihara K, Ikenouchi J, Izumi Y, Akashi M, Tsukita S, Furuse M. Phosphorylation state regulates the localization of Scribble at adherens junctions and its association with E-cadherin–catenin complexes. Exp Cell Res. 2011;317:413–22.
Awadia S, Huq F, Arnold TR, Goicoechea SM, Sun YJ, Hou T, et al. SGEF forms a complex with scribble and Dlg1 and regulates epithelial junctions and contractility. J Cell Biol. 2019;218:2699–725.
Bonello TT, Choi W, Peifer M. Scribble and discs-large direct initial assembly and positioning of adherens junctions during the establishment of apical-basal polarity. Development [Internet]. Oxford University Press for The Company of Biologists Limited; 2019 [cited 2020 Jul 19];146. https://dev.biologists.org/content/146/22/dev180976
Chalmers AD, Whitley P, Elsum I, Yates L, Humbert PO, Richardson HE. The Scribble–Dlg–Lgl polarity module in development and cancer: from flies to man. Essays Biochem. 2012;53:141–68.
Beatty A, Morton D, Kemphues K. The C. elegans homolog of Drosophila Lethal giant larvae functions redundantly with PAR-2 to maintain polarity in the early embryo. Development. 2010;137:3995–4004.
Choi J, Troyanovsky RB, Indra I, Mitchell BJ, Troyanovsky SM. Scribble, Erbin, and Lano redundantly regulate epithelial polarity and apical adhesion complex. J Cell Biol. 2019;218:2277–93.
Assémat E, Bazellières E, Pallesi-Pocachard E, Le Bivic A, Massey-Harroche D. Polarity complex proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008;1778:614–30.
Laprise P, Chailler P, Houde M, Beaulieu J-F, Boucher M-J, Rivard N. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase controls human intestinal epithelial cell differentiation by promoting adherens junction assembly and p38 MAPK activation. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:8226–34.
Hendrick J, Franz-Wachtel M, Moeller Y, Schmid S, Macek B, Olayioye MA. The polarity protein Scribble positions DLC3 at adherens junctions to regulate Rho signaling. J Cell Sci. 2016;129:3583–96.
Grzeschik NA, Parsons LM, Allott ML, Harvey KF, Richardson HE. Lgl, aPKC, and Crumbs Regulate the Salvador/Warts/Hippo pathway through two distinct mechanisms. Curr Biol. 2010;20:573–81.
Parsons LM, Grzeschik NA, Allott M, Richardson H. Lgl/aPKC and Crb regulate the Salvador/Warts/Hippo pathway. Fly. 2010;4:288–93.
Fernández BG, Gaspar P, Brás-Pereira C, Jezowska B, Rebelo SR, Janody F. Actin-Capping Protein and the Hippo pathway regulate F-actin and tissue growth in Drosophila. Development. 2011;138:2337–46.
Dow LE, Humbert PO. Polarity Regulators and the Control of Epithelial Architecture, Cell Migration, and Tumorigenesis. International Review of Cytology [Internet]. Academic Press; 2007 [cited 2020 Jul 23]; 253–302. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0074769607620063
Silvis MR, Kreger BT, Lien W-H, Klezovitch O, Rudakova GM, Camargo FD, et al. α-catenin is a tumor suppressor that controls cell accumulation by regulating the localization and activity of the transcriptional coactivator Yap1. Sci Signal. 2011;4:ra33–ra33.
Nagasaka K, Pim D, Massimi P, Thomas M, Tomaic V, Subbaiah VK, et al. The cell polarity regulator hScrib controls ERK activation through a KIM site-dependent interaction. Oncogene. 2010;29:5311–21.
Zeniou-Meyer M, Liu Y, Béglé A, Olanish M, Hanauer A, Becherer U, et al. The Coffin-Lowry syndrome-associated protein RSK2 is implicated in calcium-regulated exocytosis through the regulation of PLD1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2008;105:8434–9.
Audebert S, Navarro C, Nourry C, Chasserot-Golaz S, Lécine P, Bellaiche Y, et al. Mammalian Scribble forms a tight complex with the βPIX exchange factor. Curr Biol. 2004;14:987–95.
Reischauer S, Levesque MP, Nüsslein-Volhard C, Sonawane M. Lgl2 executes its function as a tumor suppressor by regulating ErbB signaling in the zebrafish epidermis. PLoS Genet. 2009;5:e1000720.
Wilson NR, Olm-Shipman AJ, Acevedo DS, Palaniyandi K, Hall EG, Kosa E, et al. SPECC1L deficiency results in increased adherens junction stability and reduced cranial neural crest cell delamination. Sci Rep [Internet]. 2016 [cited 2020 Jul 28];6 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4726231/
Frese KK, Latorre IJ, Chung S-H, Caruana G, Bernstein A, Jones SN, et al. Oncogenic function for the Dlg1 mammalian homolog of the Drosophila discs-large tumor suppressor. EMBO J. 2006;25:1406–17.
Willecke M, Toggweiler J, Basler K. Loss of PI3K blocks cell-cycle progression in a Drosophila tumor model. Oncogene. 2011;30:4067–74.
Li X, Yang H, Liu J, Schmidt MD, Gao T. Scribble-mediated membrane targeting of PHLPP1 is required for its negative regulation of Akt. EMBO Rep. 2011;12:818–24.
Good MC, Zalatan JG, Lim WA. Scaffold proteins: hubs for controlling the flow of cellular information. Science. 2011;332:680–6.
Romero G, von Zastrow M, Friedman PA. Role of PDZ proteins in regulating trafficking, signaling, and function of GPCRs: Means, motif, and opportunity. Adv Pharmacol [Internet]. Elsevier; 2011 [cited 2020 Jul 23]. p. 279–314. https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/B9780123859525000038
Walther C, Ferguson SSG. Minireview: Role of intracellular scaffolding proteins in the regulation of endocrine G protein-coupled receptor signaling. Mol Endocrinol. 2015;29:814–30.
Takai Y, Ikeda W, Ogita H, Rikitake Y. The immunoglobulin-like cell adhesion molecule nectin and its associated protein afadin. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2008;24:309–42.
Yoshida T, Iwata T, Takai Y, Birchmeier W, Yamato M, Okano T. Afadin requirement for cytokine expressions in keratinocytes during chemically induced inflammation in mice. Genes Cells. 2014;19:842–52.
Perez White BE, Ventrella R, Kaplan N, Cable CJ, Thomas PM, Getsios S. EphA2 proteomics in human keratinocytes reveals a novel association with afadin and epidermal tight junctions. J Cell Sci. 2017;130:111–8.
Shenolikar S, Weinman EJ. NHERF: targeting and trafficking membrane proteins. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2001;280:F389–95.
Voltz JW, Weinman EJ, Shenolikar S. Expanding the role of NHERF, a PDZ-domain containing protein adapter, to growth regulation. Oncogene. 2001;20:6309–14.
Georgescu M-M, Yell P, Mobley BC, Shang P, Georgescu T, Wang S-HJ, et al. NHERF1/EBP50 is an organizer of polarity structures and a diagnostic marker in ependymoma. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2015;3:11.
Mangia A, Saponaro C, Malfettone A, Bisceglie D, Bellizzi A, Asselti M, et al. Involvement of nuclear NHERF1 in colorectal cancer progression. Oncol Rep. 2012;28:889–94.
Oh Y-S, Heo K, Kim E-K, Jang J-H, Bae SS, Park JB, et al. Dynamic relocalization of NHERF1 mediates chemotactic migration of ovarian cancer cells toward lysophosphatidic acid stimulation. Exp Mol Med. 2017;49:e351–e351.
Castellani S, Guerra L, Favia M, Di Gioia S, Casavola V, Conese M. NHERF1 and CFTR restore tight junction organisation and function in cystic fibrosis airway epithelial cells: role of ezrin and the RhoA/ROCK pathway. Lab Invest. 2012;92:1527–40.
Acharya N, Penukonda S, Shcheglova T, Hagymasi AT, Basu S, Srivastava PK. Endocannabinoid system acts as a regulator of immune homeostasis in the gut. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2017;114:5005–10.
Almogi-Hazan O, Or R. Cannabis, the endocannabinoid system and immunity—the journey from the bedside to the bench and back. IJMS. 2020;21:4448.
Pandey R, Mousawy K, Nagarkatti M, Nagarkatti P. Endocannabinoids and immune regulation☆. Pharmacol Res. 2009;60:85–92.
Howlett AC. International union of pharmacology. XXVII. Classification of cannabinoid receptors. Pharmacol Rev. 2002;54:161–202.
De Petrocellis L, Nabissi M, Santoni G, Ligresti A. Actions and regulation of ionotropic cannabinoid receptors. Adv Pharmacol. 2017;80:249–89.
Lauckner JE, Jensen JB, Chen H-Y, Lu H-C, Hille B, Mackie K. GPR55 is a cannabinoid receptor that increases intracellular calcium and inhibits M current. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2008;105:2699–704.
Ryberg E, Larsson N, Sjögren S, Hjorth S, Hermansson N-O, Leonova J, et al. The orphan receptor GPR55 is a novel cannabinoid receptor. Br J Pharmacol. 2007;152:1092–101.
McHugh D, Page J, Dunn E, Bradshaw HB. Δ(9) -Tetrahydrocannabinol and N-arachidonyl glycine are full agonists at GPR18 receptors and induce migration in human endometrial HEC-1B cells. Br J Pharmacol. 2012;165:2414–24.
Lee J-W, Huang BX, Kwon H, Rashid MA, Kharebava G, Desai A, et al. Orphan GPR110 (ADGRF1) targeted by N-docosahexaenoylethanolamine in development of neurons and cognitive function. Nat Commun. 2016;7:13123.
Brown AJ. Novel cannabinoid receptors. Br J Pharmacol. 2007;152:567–75.
Di Marzo V. Biosynthesis and inactivation of endocannabinoids: relevance to their proposed role as neuromodulators. Life Sci. 1999;65:645–55.
Bisogno T, Melck D, De Petrocellis L, Di Marzo V. Phosphatidic acid as the biosynthetic precursor of the endocannabinoid 2-arachidonoylglycerol in intact mouse neuroblastoma cells stimulated with ionomycin. J Neurochem. 1999;72:2113–9.
Stella N, Schweitzer P, Piomelli D. A second endogenous cannabinoid that modulates long-term potentiation. Nature. 1997;388:773–8.
Deutsch DG, Chin SA. Enzymatic synthesis and degradation of anandamide, a cannabinoid receptor agonist. Biochem Pharmacol. 1993;46:791–6.
Bisogno T, Maurelli S, Melck D, De Petrocellis L, Di Marzo V. Biosynthesis, uptake, and degradation of anandamide and palmitoylethanolamide in leukocytes. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:3315–23.
Maccarrone M, Bab I, Bíró T, Cabral GA, Dey SK, Di Marzo V, et al. Endocannabinoid signaling at the periphery: 50 years after THC. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2015;36:277–96.
Martínez V, Iriondo De-Hond A, Borrelli F, Capasso R, Del Castillo MD, Abalo R. Cannabidiol and other non-psychoactive cannabinoids for prevention and treatment of gastrointestinal disorders: useful nutraceuticals? Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21.
Cravatt BF, Giang DK, Mayfield SP, Boger DL, Lerner RA, Gilula NB. Molecular characterization of an enzyme that degrades neuromodulatory fatty-acid amides. Nature. 1996;384:83–7.
Maurelli S, Bisogno T, De Petrocellis L, Di Luccia A, Marino G, Di Marzo V. Two novel classes of neuroactive fatty acid amides are substrates for mouse neuroblastoma “anandamide amidohydrolase.” FEBS Lett. 1995;377:82–6.
Laezza C, Pagano C, Navarra G, Pastorino O, Proto MC, Fiore D, et al. The endocannabinoid system: A target for cancer treatment. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21.
Joshi N, Onaivi ES. Endocannabinoid system components: overview and tissue distribution. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019;1162:1–12.
McAllister SD, Glass M. CB1 and CB2 receptor-mediated signalling: a focus on endocannabinoids. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2002;66:161–71.
Patel KD, Davison JS, Pittman QJ, Sharkey KA. Cannabinoid CB(2) receptors in health and disease. Curr Med Chem. 2010;17:1393–410.
Sugiura T, Kondo S, Kishimoto S, Miyashita T, Nakane S, Kodaka T, et al. Evidence that 2-arachidonoylglycerol but not N-palmitoylethanolamine or anandamide is the physiological ligand for the cannabinoid CB2 receptor. Comparison of the agonistic activities of various cannabinoid receptor ligands in HL-60 cells. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:605–12.
Parolaro D, Massi P, Rubino T, Monti E. Endocannabinoids in the immune system and cancer. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2002;66:319–32.
Suárez J, Romero-Zerbo SY, Rivera P, Bermúdez-Silva FJ, Pérez J, De Fonseca FR, et al. Endocannabinoid system in the adult rat circumventricular areas: An immunohistochemical study. J Comp Neurol. 2010;518:3065–85.
Turcotte C, Chouinard F, Lefebvre JS, Flamand N. Regulation of inflammation by cannabinoids, the endocannabinoids 2-arachidonoyl-glycerol and arachidonoyl-ethanolamide, and their metabolites. J Leukoc Biol. 2015;97:1049–70.
Turcotte C, Archambault A, Dumais É, Martin C, Blanchet M, Bissonnette E, et al. Endocannabinoid hydrolysis inhibition unmasks that unsaturated fatty acids induce a robust biosynthesis of 2-arachidonoyl-glycerol and its congeners in human myeloid leukocytes. FASEB J. 2020;34:4253–65.
Angelina A, Pérez-Diego M, López-Abente J, Palomares O. The role of cannabinoids in allergic diseases. IAA. 2020;1–20.
Cabral GA, Ferreira GA, Jamerson MJ. Endocannabinoids and the immune system in health and disease. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2015;231:185–211.
Turcotte C, Blanchet M-R, Laviolette M, Flamand N. Impact of cannabis, cannabinoids, and endocannabinoids in the lungs. Front Pharmacol. 2016;7:317.
Hoggatt J, Pelus LM. Eicosanoid regulation of hematopoiesis and hematopoietic stem and progenitor trafficking. Leukemia. 2010;24:1993–2002.
Khuja I, Yekhtin Z, Or R, Almogi-Hazan O. Cannabinoids reduce inflammation but inhibit lymphocyte recovery in murine models of bone marrow transplantation. IJMS. 2019;20:668.
Robinson RH, Meissler JJ, Breslow-Deckman JM, Gaughan J, Adler MW, Eisenstein TK. Cannabinoids inhibit T-cells via cannabinoid receptor 2 in an in vitro assay for graft rejection, the mixed lymphocyte reaction. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2013;8:1239–50.
Eisenstein T, Meissler J, Wilson Q, Gaughan J, Adler M. Anandamide and Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol directly inhibit cells of the immune system via CB2 receptors. J Neuroimmunol. 2007;189:17–22.
Xiang W, Shi R, Kang X, Zhang X, Chen P, Zhang L, et al. Monoacylglycerol lipase regulates cannabinoid receptor 2-dependent macrophage activation and cancer progression. Nat Commun. 2018;9:2574.
Szabady RL, Louissaint C, Lubben A, Xie B, Reeksting S, Tuohy C, et al. Intestinal P-glycoprotein exports endocannabinoids to prevent inflammation and maintain homeostasis. J Clin Investig. 2018;128:4044–56.
Karwad MA, Couch DG, Theophilidou E, Sarmad S, Barrett DA, Larvin M, et al. The role of CB1 in intestinal permeability and inflammation. FASEB J. 2017;31:3267–77.
Alhamoruni A, Wright K, Larvin M, O’Sullivan S. Cannabinoids mediate opposing effects on inflammation-induced intestinal permeability: Cannabinoids and intestinal permeability. Br J Pharmacol. 2012;165:2598–610.
Karwad MA, Couch DG, Wright KL, Tufarelli C, Larvin M, Lund J, et al. Endocannabinoids and endocannabinoid-like compounds modulate hypoxia-induced permeability in CaCo-2 cells via CB1, TRPV1, and PPARα. Biochem Pharmacol. 2019;168:465–72.
Karwad MA, Macpherson T, Wang B, Theophilidou E, Sarmad S, Barrett DA, et al. Oleoylethanolamine and palmitoylethanolamine modulate intestinal permeability in vitro via TRPV1 and PPARα. FASEB J. 2017;31:469–81.
Zoppi S, Madrigal JL, Pérez-Nievas BG, Marín-Jiménez I, Caso JR, Alou L, et al. Endogenous cannabinoid system regulates intestinal barrier function in vivo through cannabinoid type 1 receptor activation. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2012;302:G565–71.
Muccioli GG, Naslain D, Bäckhed F, Reigstad CS, Lambert DM, Delzenne NM, et al. The endocannabinoid system links gut microbiota to adipogenesis. Mol Syst Biol. 2010;6:392.
Shang VCM, O’Sullivan SE, Kendall DA, Roberts RE. The endogenous cannabinoid anandamide increases human airway epithelial cell permeability through an arachidonic acid metabolite. Pharmacol Res. 2016;105:152–63.
Gu L, Wang G, Li R, Feng Y, Qian Y. Cranberry juice phytochemicals attenuated ethanol-induce epithelial barrier dysfunction on Caco-2 monolayers (P06–094–19). Curr Dev Nutr [Internet]. 2019 [cited 2020 Jul 23];3. https://academic.oup.com/cdn/article/3/Supplement_1/nzz031.P06-094-19/5517550
Hossen I, Hua W, Ting L, Mehmood A, Jingyi S, Duoxia X, et al. Phytochemicals and inflammatory bowel disease: a review. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2020;60:1321–45.
Perisetti A. Role of cannabis in inflammatory bowel diseases. Ann Gastroenterol [Internet]. 2020 [cited 2020 Jul 23].http://www.annalsgastro.gr/files/journals/1/earlyview/2020/ev-02-2020-03-AG4866-0452.pdf
Izzo AA, Sharkey KA. Cannabinoids and the gut: New developments and emerging concepts. Pharmacol Ther. 2010;126:21–38.
Alhamoruni A, Lee AC, Wright KL, Larvin M, O’Sullivan SE. Pharmacological effects of cannabinoids on the Caco-2 cell culture model of intestinal permeability. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2010;335:92–102.
Milian L, Mata M, Alcacer J, Oliver M, Sancho-Tello M, de Llano JJM, et al. Cannabinoid receptor expression in non-small cell lung cancer. Effectiveness of tetrahydrocannabinol and cannabidiol inhibiting cell proliferation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in vitro. PLoS ONE. 2020;15:e0228909.
Hohmann T, Feese K, Ghadban C, Dehghani F, Grabiec U. On the influence of cannabinoids on cell morphology and motility of glioblastoma cells. PLoS ONE. 2019;14:e0212037.
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by Dalhousie University Faculty of Medicine Bridge Funding. L.F.O. and A.M.T. were supported by Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada undergraduate student research awards.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: John Di Battista.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
O’Leary, L.F., Tomko, A.M. & Dupré, D.J. Polarity scaffolds signaling in epithelial cell permeability. Inflamm. Res. 70, 525–538 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-021-01454-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-021-01454-1