Abstract
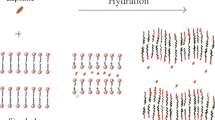
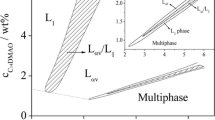
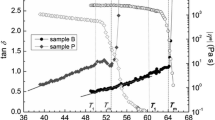
In this work, we consider a ternary system formed by a surfactant with a lamellar phase (lecithin) that was doped with a solution of Laponite at 1% by volume. The inclusion of nanoparticles in the lamellar phase was investigated by the small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) technique, which revealed three types of structures according to the observed scattering pattern. The lamellar period increased linearly with hydration up to a certain limit; this type of behavior is not the same as that found for a similar system using AOT as a surfactant. In the region that corresponds to an isotropic phase, it was observed that the period corresponds to 60 Å, and in the lamellar system of pure lecithin, with the same volumetric fraction (1/φ = 0.66), the corresponding periodicity is 62 Å, indicating that the presence of Laponite nanoparticles increases the attractive interaction, reducing the lamellar period, causing the bilayer to become more rigid, that is, with less fluctuations. In the more diluted region, the periodicity reached a limit value of 64 Å, which is slightly higher than the lamellar system in the absence of Laponite particles, so there was an expansion of the lamellar phase due to the lack of consistency of Laponite nanoparticles. In the more concentrated lamellar phase (under strong confinement), it was observed that the distance between the bilayers decreased, establishing a long-range order.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable
References
Levitz, P., Zemb, T., Grillo, I.: Insertion of small anionic particles in negatively chraged lamellar phases. Langmuir 16(11), 4830–4839 (2000)
Levitz, P., Zemb, T., Grillo, I.: Insertion of small anisotropic clay particles in swollen lamellar or sponge phases of nonionic surfactant. Langmuir 5, 377–386 (2001)
Davidson, D., Patrick, C.: Lamellar L𝛼 mesophases doped with inorganic nanoparticle. Chem. Phys. Chem. 15, 1270–1282 (2014)
Kulkarni, C.V., Engelskirchen, S.: Scattering methods applied to soft matter. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 13, 3003 (2011)
De Gennes, P.G.: Soft Matter. Science 256, 495 (1992)
Ponsinet, V., Fabre, P., Veyssie, M., Auvray, L.: A small-angle neutron scattering study of the ferrosmectic phase. J. Phys. II 3, 1021–1039 (1993)
Ménager, C., Belloni, L., Cabuil, V., Dubois, M., Gulik-Krzywicki, T., Zemb, T.: Osmotic equilibrium between an ionic magnetic fluid and an electrostatic lamlellar phase. Langmuir 12(14), 3516–3522 (1996)
Ramos, L., Fabre, P., Dubois, E.: Compatibility between solid particles and a lamelar phase: a crucial role of the membrane interactions. J. Phys. Chem. 100(11), 4533–4537 (1996)
Ponsinet, V., Fabre, P.: Modification of the interactions in a lamelar phase by the presence of nanoparticles. J. Phys. II 6, 955–960 (1996)
Salamat, G., Kaler, E.W.: Coloidal dispersions in lyotropic lamelar phases. Langmuir 15(16), 5414–5421 (1999)
Cousin, F., Cabuil, V., Levitz, P.: Magnetic coloidal particles as probes for the determinations of the structure of Laponite suspensions. Langmuir 18(5), 1466–1473 (2002)
Rubim, R.L., Ziane, N., de Oliveira, E.A., Navailles, L., Gerbelli, B.B.: Steric-induced effects on stabilizing a lamelar structure. Eur. Phys. J. E 29, 13717 (2013)
Rubim, R.L., Ziane, N., Peyencet, J., de Oliveira, E.A., Bougis, K.: Stabilising lamelar stacks of lipid bilayers with soft confinement and steric effects. Eur. Phys. J. E 38, 78 (2015)
Gerbelli, B. B.: Propriedades estruturais e elásticas de fases lamelares: O efeito da composição da membrana (2012)
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the Complex Fluids Group at UnB for letting us use the laboratory and to CAPES for the scholarship.
Code availability
Not applicable
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Leite, G.C.C., Leite, G.C.C.C. Inclusion of Laponite nanoparticles in a lyotropic lamellar phase. J Biol Phys 47, 49–59 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10867-021-09564-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10867-021-09564-x