Abstract
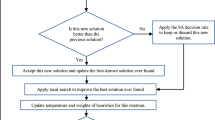
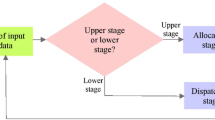
The distributed hybrid flowshop scheduling (DHFS) problem is a common scheduling problem that has been researched in both academic and industrial fields during recent years. The uncertainty levels in realistic applications are generally too high to be represented by a deterministic value or a triangular fuzzy number (TFN) value. Considering the DHFS problem with type-2 fuzzy processing time and setup time constraints, an improved version of brain storm optimization was developed, where the objective is to minimize the maximum type-2 fuzzy completion time among all factories. The main contributions of this study are as follows: (1) each solution is represented by a two vectors, i.e., a scheduling vector and a factory assignment vector; (2) two realistic constraints, i.e., the type-2 fuzzy processing time in an uncertain environment and the setup time, make the problem more realistic; (3) a novel constructive heuristic based on the Nawaz-Enscore-Ham (NEH) method, called distributed NEH, is proposed; (4) several local search heuristics considering the problem features and the objective are developed to enhance the local search abilities; and (5) a simulated-annealing-based acceptance criterion is embedded to enhance the exploration abilities. The experimental results demonstrate that the proposed algorithm is more efficient and effective for solving the considered type-2 fuzzy DHFS problems in comparison with other recently published efficient algorithms.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Naderi, B., Ruiz, R.: The distributed permutation flowshop scheduling problem. Comput. Oper. Res. 37, 754–768 (2010)
Li, J.Q., Song, M.X., Wang, L., Duan, P.Y., Han, Y.Y., Sang, H.Y., Pan, Q.K.: Hybrid artificial bee colony algorithm for a parallel batching distributed flow shop problem with deteriorating jobs. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 50, 2425–2439 (2020)
Hatami, S., Ruiz, R., Andrés-Romano, C.: The distributed assembly permutation flowshop scheduling problem. Int. J. Prod. Res. 51, 5292–5308 (2013)
Sang, H.Y., Pan, Q.K., Li, J.Q., Wang, P., Han, Y.Y., Gao, K.Z., Duan, P.: Effective invasive weed optimization algorithms for distributed assembly permutation flowshop problem with total flowtime criterion. Swarm. Evol. Comput. 44, 64–73 (2019)
Li, J.Q., Du, Y., Gao, K.Z., Duan, P.Y., Gong, D.W., Pan, Q.K., Suganthan, P.N.: A hybrid iterated greedy algorithm for a crane transportation flexible job shop problem. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. (2021). In Press.
Li, J.Q., Pan, Q.K., Tasgetiren, F.: A discrete artificial bee colony algorithm for the multi-objective flexible job-shop scheduling problem with maintenance activities. Appl. Math. Model. 38, 1111–1132 (2014)
Lin, S.W., Ying, K.C.: Minimizing makespan for solving the distributed no-wait flowshop scheduling problem. Comput. Ind. End. 99, 202–209 (2016)
Ying, K.C., Lin, S.W.: Minimizing makespan for the distributed hybrid flowshop scheduling problem with multiprocessor tasks. Expert. Syst. Appl. 92, 132–141 (2018)
Rifai, A.P., Nguyen, H.T., Dawal, S.Z.M.: Multi-objective adaptive large neighborhood search for distributed reentrant permutation flow shop scheduling. Appl. Soft. Comput. 40, 42–57 (2016)
Kacem, I., Hammadi, S., Borne, P.: Pareto-optimality approach for flexible job-shop scheduling problems: hybridization of evolutionary algorithms and fuzzy logic. Math. Comput. Simulat. 60, 245–276 (2002)
Golneshini, F.P., Fazlollahtabar, H.: Meta-heuristic algorithms for a clustering-based fuzzy bi-criteria hybrid flow shop scheduling problem. Soft. Comput. 23, 12103–12122 (2019)
Zheng, J., Wang, L., Wang, J.J.: A cooperative coevolution algorithm for multi-objective fuzzy distributed hybrid flow shop. Knowl.-Based. Syst. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2020.105536
Mirsanei, H.S., Zandieh, M., Moayed, M.J., Khabbazi, M.R.: A simulated annealing algorithm approach to hybrid flow shop scheduling with sequence-dependent setup times. J. Intell. Manuf. 22, 965–978 (2011)
Schulz, S., Neufeld, J.S., Buscher, U.: A multi-objective iterated local search algorithm for comprehensive energy-aware hybrid flow shop scheduling. J. Clean. Prod. 224, 421–434 (2019)
Shao, W., Shao, Z., Pi, D.: Modeling and multi-neighborhood iterated greedy algorithm for distributed hybrid flow shop scheduling problem. Knowl.-Based. Syst. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2020.105527
Sukkerd, W., Wuttipornpun, T.: Hybrid genetic algorithm and tabu search for finite capacity material requirement planning system in flexible flow shop with assembly operations. Comput. Ind. Eng. 97, 157–169 (2016)
Liao, C.J., Tjandradjaja, E., Chung, T.P.: An approach using particle swarm optimization and bottleneck heuristic to solve hybrid flow shop scheduling problem. Appl. Soft. Comput. 12, 1755–1764 (2012)
Li, J.Q., Tao, X.R., Jia, B.X., Han, Y.Y., Liu, C., Duan, P., Zheng, Z.X., Sang, H.Y.: Efficient multi-objective algorithm for the lot-streaming hybrid flowshop with variable sub-lots. Swarm. Evol. Comput. 52, 100600 (2020)
Li, J.Q., Pan, Q.K., Duan, P.Y.: An improved artificial Bee Colony Algorithm for solving hybrid flexible flowshop with dynamic operation skipping. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 46, 1311–1324 (2016)
Yu, C., Semeraro, Q., Matta, A.: A genetic algorithm for the hybrid flow shop scheduling with unrelated machines and machine eligibility. Comput. Oper. Res. 100, 211–229 (2018)
Tao, X., Li, J., Huang, T., Duan, P.: Discrete imperialist competitive algorithm for the resource-constrained hybrid flowshop problem with energy consumption. Complex Intell. Syst. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40747-020-00193-w
Yu, H., Li, J.Q., Zhang, L.J., Duan, P.: An imperialist competition algorithm using a global search strategy for physical examination scheduling. Appl. Intell. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-020-01975-y
Lei, D., Gao, L., Zheng, Y.: A novel teaching-learning-based optimization algorithm for energy-efficient scheduling in hybrid flow shop. IEEE. Trans. Eng. Manag. 65, 330–340 (2017)
Gao, J., Chen, R., Deng, W.: An efficient tabu search algorithm for the distributed permutation flowshop scheduling problem. Int. J. Prod. Res. 51, 641–651 (2013)
Wang, S.Y., Wang, L., Liu, M., Xu, Y.: An effective estimation of distribution algorithm for solving the distributed permutation flow-shop scheduling problem. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 145, 387–396 (2013)
Naderi, B., Ruiz, R.: A scatter search algorithm for the distributed permutation flowshop scheduling problem. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 239, 323–334 (2014)
Fernandez-Viagas, V., Perez-Gonzalez, P., Framinan, J.M.: The distributed permutation flow shop to minimize the total flowtime. Comput. Ind. Eng. 118, 464–477 (2018)
Ruiz, R., Pan, Q.K., Naderi, B.: Iterated Greedy methods for the distributed permutation flowshop scheduling problem. Omega 83, 213–222 (2018)
Bargaoui, H., Belkahla Driss, O., Ghédira, K.: A novel chemical reaction optimization for the distributed permutation flowshop scheduling problem with makespan criterion. Comput. Ind. Eng. 111, 239–250 (2017)
Li, Y., Li, X., Gao, L., et al.: A discrete artificial bee colony algorithm for distributed hybrid flowshop scheduling problem with sequence-dependent setup times. Int. J. Prod. Res. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1080/00207543.2020.1753897
Zare, H.K., Fakhrzad, M.B.: Solving flexible flow-shop problem with a hybrid genetic algorithm and data mining: A fuzzy approach. Expert. Syst. Appl. 38, 7609–7615 (2011)
Behnamian, J., Ghomi, S.M.T.F.: Hybrid flowshop scheduling with machine and resource-dependent processing times. Appl. Math. Model. 35, 1107–1123 (2011)
Choi, S.H., Wang, K.: Flexible flow shop scheduling with stochastic processing times: a decomposition-based approach. Comput. Ind. Eng. 63, 362–373 (2012)
Wang, K., Choi, S.H., Qin, H.: An estimation of distribution algorithm for hybrid flow shop scheduling under stochastic processing times. Int. J. Prod. Res. 52, 7360–7376 (2014)
Zhang, J., Qin, W., Song, D.L.: Hybrid flow shop rolling scheduling method considering uncertain working hours. J. Mech. Eng. 51, 99–108 (2015)
Gonzalez-Neira, E.M., Garcia-Caceres, R.G., Caballero-Villalobos, J.P., et al.: Stochastic flexible flow shop scheduling problem under quantitative and qualitative decision criteria. Comput. Ind. Eng. 101, 128–144 (2016)
Ahonen, H., Alvarenga, A.G.: Scheduling flexible flow shop with recirculation and machine sequence-dependent processing times: formulation and solution procedures. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 89, 765–777 (2017)
Qin, W., Zhang, J., Song, D.: An improved ant colony algorithm for dynamic hybrid flow shop scheduling with uncertain processing time. J. Intell. Manuf. 29, 891–904 (2018)
Zhou, B., Liu, W.: Energy-efficient multi-objective scheduling algorithm for hybrid flow shop with fuzzy processing time. P. I. Mech. Eng. I-J. Sys. 233, 1282–1297 (2019)
Yuan, F., Xu, X., Yin, M.: A novel fuzzy model for multi-objective permutation flow shop scheduling problem with fuzzy processing time. Adv. Mech. Eng. 11, 1687814019843699 (2019)
Zheng, J., Wang, L., Wang, J.: A cooperative coevolution algorithm for multi-objective fuzzy distributed hybrid flow shop. Knowl.-Based Syst. 194, 105536 (2020)
Melin, P., Castillo, O.: A review on type-2 fuzzy logic applications in clustering, classification and pattern recognition. Appl. Soft. Comput. 21, 568–577 (2014)
Wu, D., Mendel, J.: Similarity measures for closed general type-2 fuzzy sets: overview, comparisons, and a geometric approach. IEEE. Trans. Fuzzy. Syst. 27, 515–526 (2019)
Mendel, J., Liu, X.: Simplified interval type-2 fuzzy logic systems. IEEE. Trans. Fuzzy. Syst. 21, 1056–1069 (2013)
Mendel, J., Wu, H.: Type-2 fuzzistics for symmetric interval type-2 fuzzy sets: Part 1, forward problems. IEEE. Trans. Fuzzy. Syst. 14, 781–792 (2006)
Mendel, J., Wu, H.: Type-2 fuzzistics for nonsymmetric interval type-2 fuzzy sets: forward problems. IEEE. Trans. Fuzzy. Syst. 15, 916–930 (2007)
Figueroa-García, J., Hernández, G.: A method for solving linear programming models with interval type-2 fuzzy constraints. Pesquisa. Oper. 34, 73–89 (2014)
Li, C., Yi, J., Zhang, G.: On the monotonicity of interval type-2 fuzzy logic systems. IEEE. Trans. Fuzzy. Syst. 22, 1197–1212 (2014)
Li, C., Zhang, G., Yi, J., Shang, F., Gao, J.: A fast learning method for data-driven design of interval type-2 fuzzy logic system. J. Intell. Fuzzy. Syst. 32, 2705–2715 (2017)
Melin, P., Olivas, F., Castillo, O., Valdez, F., Soria, J., Valdez, M.: Optimal design of fuzzy classification systems using PSO with dynamic parameter adaptation through fuzzy logic. Expert. Syst. Appl. 40, 3196–3206 (2013)
Castillo, O., Amadorangulo, L.: A generalized type-2 fuzzy logic approach for dynamic parameter adaptation in bee colony optimization applied to fuzzy controller design. Inf. Sci. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2017.10.032
Olivas, F., Valdez, F., Melin, P., Sombra, A., Castillo, O.: Interval type-2 fuzzy logic for dynamic parameter adaptation in a modified gravitational search algorithm. Inf. Sci. 476, 159–175 (2019)
Melin, P., Gonzalez, C., Castro, J., Mendoza, O., Castillo, O.: Interval type-2 fuzzy logic for dynamic parameter adaptation in a modified gravitational search algorithm. IEEE. Trans. Fuzzy. Syst. 22, 1515–1525 (2014)
Shukla, A., Nath, R., Muhuri, P., Lohani, Q.: Energy efficient multi-objective scheduling of tasks with interval type-2 fuzzy timing constraints in an Industry 4.0 ecosystem. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 87, 103257 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engappai.2019.103257
Ontiverosrobles, E., Melin, P., Castillo, O.: Comparative analysis of noise robustness of type 2 fuzzy logic controllers. Kybernetika. 54, 175–201 (2018)
Li, C., Yi, J., Wang, H., Zhang, G., Li, J.: Interval data driven construction of shadowed sets with application to linguistic word modelling. Inf. Sci. 507, 503–521 (2020)
Soto, J., Melin, P., Castillo, O.: A new approach for time series prediction using ensembles of IT2FNN models with optimization of fuzzy integrators. Int. J. Fuzzy. Syst. 20, 701–728 (2018)
Li, J.Q., Liu, Z.M., Li, C.D., Zheng, Z.X.: Improved artificial immune system algorithm for type-2 fuzzy flexible job shop scheduling problem. IEEE. Trans. Fuzzy. Syst. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/TFUZZ.2020.3016225
Shi, Y.H.: Brain storm optimization algorithm. International Conference in Swarm Intelligence, pp. 303–309. Springer, Berlin (2011)
Jia, Z.X., Duan, H.B., Shi, Y.H.: Hybrid brain storm optimisation and simulated annealing algorithm for continuous optimisation problems. Int. J. Bio Inspir. Comput. 8, 109–121 (2016)
Yu, Y., Gao, S.C., Cheng, S., Wang, Y.R., Song, S.Y., Yuan, F.G.: CBSO: a memetic brain storm optimization with chaotic local search. Memetic. Comput. 10, 353–367 (2017)
Shi, Y.H., Xue, J.Q., Wu, Y.L.: Multi-objective optimization based on brain storm optimization algorithm. IJSIR. 4, 1–21 (2013)
Duan, H., Li, S., Shi, Y.: Predator–prey brain storm optimization for DC brushless motor. IEEE. Trans. Magn. 49, 5336–5340 (2013)
Sun, C., Duan, H., Shi, Y.: Optimal satellite formation reconfiguration based on closed-loop brain storm optimization. IEEE. Comput. Intell. Mag. 8, 39–51 (2013)
Ma, X., Jin, Y., Dong, Q.: A generalized dynamic fuzzy neural network based on singular spectrum analysis optimized by brain storm optimization for short-term wind speed forecasting. Appl. Soft. Comput. 54, 296–312 (2017)
Ke, L.: A brain storm optimization approach for the cumulative capacitated vehicle routing problem. Memet. Comput. 10, 411–421 (2018)
Nawaz, M., Enscore Jr., E.E., Ham, I.: A heuristic algorithm for the m-machine, n-job flow-shop sequencing problem. Omega 11, 91–95 (1983)
Revathi, S.T., Ramaraj, N., Chithra, S.: Brain storm-based Whale Optimization Algorithm for privacy-protected data publishing in cloud computing. Clust. Comput. 22, 3521–3530 (2019)
Yan, X., Zhu, Z., Wu, Q., Gong, W., Wang, L.: Elastic parameter inversion problem based on brain storm optimization algorithm. Memetic. Comput. 11, 143–153 (2019)
Arai, K., Fukuyama, Y., Iizaka, T., Matsui, T.: Dependable multi-population improved brain storm optimization with differential evolution for optimal operational planning of energy plants. Electr. Eng. Jpn. 207, 25–35 (2019)
Liang, X.P., Guo, Z.J., Zhu, C.H., Guo, Z.J.: BP neural network fuzzy image restoration based on brain storming optimization algorithm. J. Electron. Inf. Technol. 41, 2980–2986 (2019)
Kumar, T.D., Venkatesan, P.: Performance estimation of multicarrier CDMA using adaptive brain storm optimization for 5G communication system in frequency selective fading channel. Trans. Emerg. Telecommun. Technol. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1002/ett.3829
Guo, Y., Yang, H., Chen, M., Gong, D., Cheng, S.: Grid-based dynamic robust multi-objective brain storm optimization algorithm. Soft. Comput. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-019-04365-w
Cervantes-Castillo, A., Mezura-Montes, E.: A modified brain storm optimization algorithm with a special operator to solve constrained optimization problems. Appl. Intell. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-020-01763-8
Li, J.Q., Han, Y.Q., Duan, P.Y., Han, Y.Y., Niu, B., Li, C.D., Zheng, Z.X., Liu, Y.P.: Meta-heuristic algorithm for solving vehicle routing problems with time windows and synchronized visit constraints in prefabricated systems. J. Clean Prod. 250, 119464 (2020)
Acknowledgements
This research is partially supported by National Science Foundation of China under Grant 61773192, 61803192, 61773246.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix
Appendix
The list of acronyms used in this study is given as follows:
-
FSP: flowshop scheduling problem
-
HFS: hybrid flowshop scheduling
-
FJSP: flexible job shop scheduling problem
-
DFSP: distributed flow shop scheduling problems
-
DAPFSP: distributed assembly permutation flowshop scheduling problems
-
DFJSP: distributed flexible job shop scheduling problems
-
TFN: triangular fuzzy number
-
T1FLS: type-1 fuzzy logic system
-
T2FS: type-2 fuzzy logic system
-
BSO: brain storm optimization
-
VNS: variable neighborhood search
-
ILS: iterated local search
-
SA: simulated annealing
-
IG: iterated greedy
-
FOA: fruit fly optimization algorithm
-
TS: tabu search
-
PSO: particle swarm optimization
-
ABC: artificial bee colony
-
GA: genetic algorithm
-
TLBO: teaching-learning-based optimization
-
SS: scatter search
-
CRO: chemical reaction optimization
-
EDA: estimation of distribution algorithm
-
ANOVA: analysis of variance
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, J., Li, J., Zhang, L. et al. Solving Type-2 Fuzzy Distributed Hybrid Flowshop Scheduling Using an Improved Brain Storm Optimization Algorithm. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 23, 1194–1212 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-021-01050-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-021-01050-9