Abstract
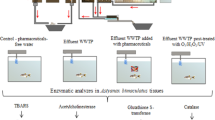
Anaerobically treated molasses-based distilleries spent wash is a major source of terrestrial and aquatic pollution due to the mixture of the various unknown organometallic compounds in discharged waste. The nature of pollutants present in effluent has to be characterized prior to the evaluation of their fate in the environment at various tropic levels. The absorption maxima (λmax) were obtained at 295 nm of pollutants present in spent wash which indicated that melanoidins are a major colorant along with other organic compounds. Abundantly identified compounds with GC–MS in effluent were found: 1,2,4,5-tetrahydro-2-methyl-3H-2-benzazepine-3-one, 6-(trifluoromethyl)-1H-imidazole [4,5-c] pyridine, 4,6-di-t-butyl-1H, 3H-thieno[3,4-c] thiophene, butanoic acid, trimethylsilyl ester, silane, (dodecyloxy)trimethylsilyl ester, 4-styryl [2,2] paracyclophane, 4-(p-cumylphenoxy) phthalonitrile, hexadecanoic acid, trimethylsilyl ester, butyl ester, and squalene. Some of these compounds are known with mutagenic and androgenic properties. The toxicity test of post-methanated distillery effluent (PMDE) showed direct toxic effects on catfish (Heteropneustes fossilis) even at 1% (v/v) concentration and caused degeneration of primary and secondary lamellae of the gill and the epithelial layer. Further, higher concentrations between 5 and 10% of PMDE showed loss of primary and secondary lamellae of gills, and liver catalase activity was also increased dramatically in H. fossilis, indicating the generation of oxidative free radicals. Similarly, inhibition of α-amylase activities in germinating Zea mays L. (Maize) seeds was also noted at 10% PMDE. This study confirmed the environmental toxicity of effluent with freshwater fish and Zea mays seeds.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
AIDA (All india distillers’ associations) (2016) Annual report. AIDA, New Delhi. http:// www.aidaindia.org/annual-report.html
Abdalla KZ, Hammam G (2014) Correlation between biochemical oxygen demand and chemical oxygen demand for various wastewater treatment plants in Egypt to obtain the biodegradability indices. Int J Sci Basic Appl Res 13(1):42–48
Alam MZ, Ahmad S, Malik A, Ahmad M (2010) Mutagenicity and genotoxicity of tannery effluents used for irrigation at Kanpur. India Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 73(7):1620–1628
Albretsen J (2006) The toxicity of iron, an essential element. Vet Med-Bonn Springs Edwardsville 101(2):82
American Public Health Association Vision/ Mission (2011) Available at http://www.apha.org/about/gov/execboard/executiveboardvisionmission.htm. Accessed 21 July 2011
Aniyikaiye TE, Oluseyi T, Odiyo JO, Edokpayi JN (2019) Physico-chemical analysis of wastewater discharge from selected paint industries in Lagos, Nigeria. Int J Environ Res Public Health 16(7):1235
Aoki KA, Harris CA, Katsiadaki I, Sumpter JP (2011) Evidence suggesting that di-n-butyl phthalate has antiandrogenic effects in fish. Environ Toxicol Chem 30(6):1338–1345
Asberry HB, Kuo CY, Gung CH, Conte ED, Suen SY (2014) Characterization of water bamboo husk biosorbents and their application in heavy metal ion trapping. Microchem J 113:59–63
Batista AH, Melo VF, Gilkes R, Roberts M (2018) Identification of heavy metals in crystals of sand and silt fractions of soils by scanning electron microscopy (SEM EDS/WD-EPMA). Rev Bras Ciênc Solo 42
Beri V, Gupta R (2007) Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors neostigmine and physostigmine inhibit induction of alpha-amylase activity during seed germination in barley, Hordeum vulgare var. Jyoti. Life Sci 80(24–25):2386–2388
Bezuneh TT (2016) The role of microorganisms in distillery wastewater treatment: a review. J Bioremediat Biodegrad 7(6)
Bharagava RN, Chandra R (2010a) Effect of bacteria treated and untreated post-methanated distillery effluent (PMDE) on seed germination, seedling growth and amylase activity in Phaseolus mungo L. J Hazard Mater 180(1–3):730–734
Bharagava RN, Chandra R (2010b) Biodegradation of the major color containing compounds in distillery wastewater by an aerobic bacterial culture and characterization of their metabolites. Biodegradation 21(5):703–711
Bharagava RN, Chandra R, Rai V (2008) Phytoextraction of trace elements and physiological changes in Indian mustard plants (Brassica nigra L.) grown in post methanated distillery effluent (PMDE) irrigated soil. Bioresour Technol 99(17):8316–8324
Bharagava RN, Chandra R, Rai V (2009) Isolation and characterization of aerobic bacteria capable of the degradation of synthetic and natural melanoidins from distillery effluent. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 25(5):737–744
Billaud C, Brun-Merimee S, Louarme L, Nicolas J (2004) Effect of glutathione and maillard reaction products prepared from glucose or fructose with glutathione on polyphenoloxidase from apple—I: enzymatic browning and enzyme activity inhibition. Food Chem 84(2):223–233
Bloch ME (1794) Der malabarische hecht. In: Naturgeschichte des auslandische fische Berlin, 149–150
Bortoletto AM, Silvello GC, Alcarde AR (2018) Good manufacturing practices, hazard analysis and critical control point plan proposal for distilleries of cachaça. Sci Agricola 75(5):432–443
Causin V, Casamassima R, Marega C, Maida P, Schiavone S, Marigo A, Villari A (2008) The discrimination potential of ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometry, thin layer chromatography, and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy for the forensic analysis of black and blue ballpoint inks. J Forensic Sci 53(6):1468–1473
Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) (2003) Environmental management in selected industrial sectors status and needs, CPCB, ministry of environment and forest, New Delhi. PROBES/97/ 2002–03
Chandra R, Bharagava RN, Kapley A, Purohit HJ (2012) Characterization of phragmites cummunis rhizosphere bacterial communities and metabolic products during the two stage sequential treatment of post methanated distillery effluent by bacteria and wetland plants. Bioresour Technol 103(1):78–86
Chandra R, Bharagava RN, Yadav S, Mohan D (2009) Accumulation and distribution of toxic metals in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) and Indian mustard (Brassica campestris L.) irrigated with distillery and tannery effluents. J Hazard Mater 162(2–3):1514–1521
Chandra R, Castillo-Zacarias C, Delgado P, Parra-Saldívar R (2018) A biorefinery approach for dairy wastewater treatment and product recovery towards establishing a biorefinery complexity index. J Clean Prod 183:1184–1196
Chandra R, Pandey PK, Srivastava A (2004) Comparative toxicological evaluation of untreated and treated tannery effluent with Nostoc muscorum L. (algal assay) and microtox bioassay. Environ Monit Assess 95(1):287–294
Chandra R, Yadav S, Bharagava RN, Murthy RC (2008b) Bacterial pretreatment enhances removal of heavy metals during treatment of post-methanated distillery effluent by Typha angustata L. J Environ Manag 88(4):1016–1024
Chandra R, Yadav S, Mohan D (2008a) Effect of distillery sludge on seed germination and growth parameters of green gram (Phaseolus mungo L.). J Hazard Mater 152(1):431–439
Chandra R, Yadav S, Yadav S (2017) Phytoextraction potential of heavy metals by native wetland plants growing on chlorolignin containing sludge of pulp and paper industry. Ecol Eng 98:134–145
Chang TPY, Rangan C (2011) Iron poisoning: a literature-based review of epidemiology, diagnosis, and management. Pediatr Emerg Care 27(10):978–985
Chaudhary R, Arora M (2011) Study on distillery effluent: chemical analysis and impact on environment. Int J Adv Eng Technol 2(2):352–356
Chen X, Xu S, Tan T, Lee ST, Cheng SH, Lee FWF, Xu SJL, Ho KC (2014) Toxicity and estrogenic endocrine disrupting activity of phthalates and their mixtures. Int J Environ Res Public Health 11(3):3156–3168
Chhonkar PK, Datta SP, Joshi HC, Pathak H (2000) Impact of industrial effluents on soil health and agriculture-Indian experience: part I-distillery and paper mill effluents
Choi YY, Baek SR, Kim JI, Choi JW, Hur J, Lee TU, Park CJ, Lee BJ (2017) Characteristics and biodegradability of wastewater organic matter in municipal wastewater treatment plants collecting domestic wastewater and industrial discharge. Water 9(6):409
Chowdhary P, Raj A, Bharagava RN (2018) Environmental pollution and health hazards from distillery wastewater and treatment approaches to combat the environmental threats: a review. Chemosphere 194:229–246
Chowdhary P, Yadav A, Kaithwas G, Bharagava RN (2017) Distillery wastewater: a major source of environmental pollution and its biological treatment for environmental safety. Green technologies and environmental sustainability. Springer, Cham, pp 409–435
Clarkson PM, Tremblay ISABELLE (1988) Exercise-induced muscle damage, repair, and adaptation in humans. J Appl Physiol 65(1):1–6
David Noel S, Rajan MR (2015) Phytotoxic effect of dyeing industry effluent on seed germination and early growth of lady’s finger. J Pollut Eff Contr 2(126):10–4172
Echavarria-Pinto M, Escaned J, Macías E, Medina M, Gonzalo N, Petraco R, Sen S, Jimenez-Quevedo P, Hernandez R, Mila R, Ibañez B (2013) Disturbed coronary hemodynamics in vessels with intermediate stenoses evaluated with fractional flow reserve: a combined analysis of epicardial and microcirculatory involvement in ischemic heart disease. Circulation 128(24):2557–2566
Erhirhie EO, Ihekwereme CP, Ilodigwe EE (2018) Advances in acute toxicity testing: strengths, weaknesses and regulatory acceptance. Interdiscip Toxicol 11(1):5–12
Gomes CEM, Sousa AKD, Araujo MEDSO, Ferreira SB, Fontanini P (2019) Mechanical and microstructural properties of redispersible polymer-gypsum composites. Mater Res 22(3)
Gu FL, Kim JM, Abbas S, Zhang XM, Xia SQ, Chen ZX (2010) Structure and antioxidant activity of high molecular weight Maillard reaction products from casein–glucose. Food Chem 120(2):505–511
Hoffmann GF, McKiernan P (2017) Liver disease. Inherited metabolic diseases. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp 203–226
India (2010) Pollution control acts, rules and notifications issued thereunder. Central Pollution Control Board, New Delhi
Jain N, Bhatia A, Kaushik R, Kumar S, Joshi HC, Pathak H (2005) Impact of post-methanation distillery effluent irrigation on groundwater quality. Environ Monit Assess 110(1):243–255
Jaishankar M, Tseten T, Anbalagan N, Mathew BB, Beeregowda KN (2014) Toxicity, mechanism and health effects of some heavy metals. Interdiscip Toxicol 7(2):60–72
Juliano BO, Varner JE (1969) Enzymic degradation of starch granules in the cotyledons of germinating peas. Plant Physiol 44(6):886–892
Kabir ER, Rahman MS, Rahman I (2015) A review on endocrine disruptors and their possible impacts on human health. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 40(1):241–258
Kadam AA, Kamatkar JD, Khandare RV, Jadhav JP, Govindwar SP (2013) Solid-state fermentation: tool for bioremediation of adsorbed textile dyestuff on distillery industry waste-yeast biomass using isolated Bacillus cereus strain EBT1. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20(2):1009–1020
Kannan A, Upreti RK (2008) Influence of distillery effluent on germination and growth of mung bean (Vigna radiata) seeds. J Hazard Mater 153(1–2):609–615
Kaushik A, Nisha R, Jagjeeta K, Kaushik CP (2005) Impact of long and short term irrigation of a sodic soil with distillery effluent in combination with bioamendments. Biores Technol 96(17):1860–1866
Kavlock RJ, Daston GP, DeRosa C, Fenner-Crisp P, Gray LE, Kaattari S, Lucier G, Luster M, Mac MJ, Maczka C, Miller R (1996) Research needs for the risk assessment of health and environmental effects of endocrine disruptors: a report of the US EPA-sponsored workshop. Environ Health Perspect 104(suppl 4):715–740
Keramati V, Jamili S, Ramin M (2010) Effect of diazinon on catalase antioxidant enzyme activity in liver tissue of Rutilus rutilus. J Fish Aquat Sci 5(5):368–376
Kim HY (2014) Analysis of variance (ANOVA) comparing means of more than two groups. Restor Dent Endod 39(1):74
Kostich MS, Batt AL, Lazorchak JM (2014) Concentrations of prioritized pharmaceuticals in effluents from 50 large wastewater treatment plants in the US and implications for risk estimation. Environ Pollut 184:354–359
Kumar V, Chandra R (2018) Characterisation of manganese peroxidase and laccase producing bacteria capable for degradation of sucrose glutamic acid-Maillard reaction products at different nutritional and environmental conditions. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 34(2):1–18
Kumar S, Gopal K (2001) Impact of distillery effluent on physiological consequences in the freshwater teleost Channa punctatus. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 66(5):617–622
Kumaresan T, Begum KMS, Sivashanmugam P, Anantharaman N, Sundaram S (2003) Experimental studies on treatment of distillery effluent by liquid membrane extraction. Chem Eng J 95(1–3):199–204
MOEF (Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change) (2016) Environment (protection) amendment rules, 2015. Ministry of environment, forest, and climate change. The Gazette of India. New Delhi. Regd. No. D. L.-33004/99
Mahimairaja S, Bolan NS (2004) Problems and prospects of agricultural use of distillery spentwash in India. Magnesium 1715:2100
Martins SI, van Boekel MA (2003) Melanoidins extinction coefficient in the glucose/glycine Maillard reaction. Food Chem 83(1):135–142
Mishra S, Chaube R (2017) Distribution and localization of 3β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (3β-HSD) in the brain and its regions of the catfish Heteropneustes fossilis. Gen Comp Endocrinol 241:80–88
Nguyen TA, Juang RS (2013) Treatment of waters and wastewaters containing sulfur dyes: a review. Chem Eng J 219:109–117
OECD (2003) Guideline for testing of chemicals (2003 draft). Terrestrial plant tests: 208: seedling emergence and seedling growth test, pp 1–19
Oleszczuk P, Rycaj M, Lehmann J, Cornelissen G (2012) Influence of activated carbon and biochar on phytotoxicity of air-dried sewage sludges to Lepidium sativum. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 80:321–326
de Oliveira Silva J, Rodrigues Filho G, da Silva Meireles C, Ribeiro SD, Vieira JG, da Silva CV, Cerqueira DA (2012) Thermal analysis and FTIR studies of sewage sludge produced in treatment plants. The case of sludge in the city of Uberlândia-MG. Braz Thermochim Acta 528:72–75
Osweiler GD, Carson TL, Buck WB, Van Gelder GA (1985) Clinical and diagnostic veterinary toxicology. Kendall/Hunt Publishing Company, Dubuque
Phisut N, Jiraporn B (2013) Characteristics and antioxidant activity of Maillard reaction products derived from chitosan-sugar solution. Int Food Res J 20(3):1077
Quaratino D, D’Annibale A, Federici F, Cereti CF, Rossini F, Fenice M (2007) Enzyme and fungal treatments and a combination thereof reduce olive mill wastewater phytotoxicity on Zea mays L. seeds. Chemosphere 66(9):1627–1633
Rai PK, Lee SS, Zhang M, Tsang YF, Kim KH (2019) Heavy metals in food crops: Health risks, fate, mechanisms, and management. Environ Int 125:365–385
Ramakritinan CM, Kumaraguru AK, Balasubramanian MP (2005) Impact of distillery effluent on carbohydrate metabolism of freshwater fish. Cyprinus Carpio Ecotoxicol 14(7):693–707
Ramana S, Biswas AK, Singh AB (2002) Effect of distillery effluents on some physiological aspects in maize. Bioresour Technol 84(3):295–297
Rocha OP, De Oliveira DP (2017) Investigation of a Brazilian tannery effluent by means of zebra fish (Danio rerio) embryo acute toxicity (FET) test. J Toxicol Environ Health A 80(19–21):1078–1085
Saha NK, Balakrishnan M, Batra VS (2005) Improving industrial water use: case study for an Indian distillery. Resour Conserv Recycl 43(2):163–174
Sangave PC, Pandit AB (2006) Enhancement in biodegradability of distillery wastewater using enzymatic pretreatment. J Environ Manag 78(1):77–85
Sankaran K, Premalatha M, Vijayasekaran M, Somasundaram VT (2014) DEPHY project: distillery wastewater treatment through anaerobic digestion and phycoremediation—a green industrial approach. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 37:634–643
Saxena G, Chandra R, Bharagava RN (2016) Environmental pollution, toxicity profile and treatment approaches for tannery wastewater and its chemical pollutants. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol 240:31–69
Shon HK, Vigneswaran S, Snyder SA (2006) Effluent organic matter (EfOM) in wastewater: constituents, effects, and treatment. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 36(4):327–374
USEPA (2002) The environment protection rules, 3A, Schedule- II, III. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Office of research and development, Cincinnati
USEPA, US Environmental Protection Agency, 2012. Endocrine Disruptor Screening Program, Universe of Chemicals for Potential Endocrine Disruptor Screening and Testing. Jointly developed by the Office of Chemical Safety & Pollution Prevention, the Office of Water and the Office of Research and Development, pp 1–176
Vuori KM (1995) Direct and indirect effects of iron on river ecosystems. In: Annales zoologici fennici. Finnish Zoological and Botanical Publishing Board, pp 317–329
Yadav S, Chandra R (2019) Environmental health hazards of post-methanated distillery effluent and its biodegradation and decolorization. Environmental biotechnology: for sustainable future. Springer, Singapore, pp 73–101
Yan N, Marschner P, Cao W, Zuo C, Qin W (2015) Influence of salinity and water content on soil microorganisms. Int Soil Water Conserv Res 3(4):316–323
Zayneb C, Lamia K, Olfa E, Naïma J, Grubb CD, Bassem K, Hafedh M, Amine E (2015) Morphological, physiological and biochemical impact of ink industry effluent on germination of maize (Zea mays), Barley (Hordeum vulgare) and Sorghum (Sorghum bicolor). Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 95(5):687–693
Acknowledgements
This research was financially supported by the Department of Biotechnology, Government of India. Vide Letter No. BT/PR13922/BCE/8/1129/2015
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors assert no conflicting, contending, and fiscal interests in any capacity.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors. However, the toxicity text using freshwater fish (Heteropneustes fossilis) was done as per national ethical committee guidelines and approval through the departmental ethical committee of the university.
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: S. Mirkia.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tripathi, S., Singh, K., Singh, A. et al. Organo-metallic pollutants of distillery effluent and their toxicity on freshwater fish and germinating Zea mays seeds. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 19, 2025–2038 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-021-03233-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-021-03233-1