Abstract
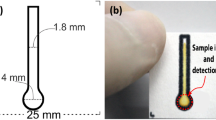
Main application of microfluidic paper-based analytical devices (µPADs) is for low-cost and portable assays. In order to reduce the cost, miniaturization seems to be an effective way to save reagents, samples, materials, etc. Present study demonstrates that mini-µPADs based on nitrocellulose membrane with only 2 main channels can perform sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA) for quantitative determination of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG). Moreover, the width and the length of these devices are only about 4.0 and 33.4 mm, respectively. Inkjet printing technology, having the advantages of simple and material-saving process, was used to create hydrophobic barrier. Colorimetric signals from ELISA captured by digital camera and measured by ImageJ software shows that these µPADs can quantitative determine of hCG in the range from 5 to 10 000 ng/mL. Furthermore, duration for each tests is only about 5 min. The success in fabricating miniaturized µPADs shows the potentials to reduce the size of µPADs as well as the amount of needed samples, time and reagents. For all these reasons, this miniaturization concept can be applied to many further applications of analytical biochemical assays.





Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Martinez, A.W., Phillips, S.T., Butte, M.J., and Whitesides, G.M., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2007, vol. 46, no. 8, pp. 1318–1320.
Li, X., Tian, J., and Shen, W., Anal. Bioanal. Chem., 2010, vol. 396, no. 1, pp. 495–501.
Apilux, A., Ukita, Y., Chikae, M., Chailapakul, O., and Takamura, Y., Lab Chip, 2013, vol. 13, pp. 126–135.
Xu, C., Cai, L., Zhong, M., and Zheng, S., RSC Adv., 2015, vol. 5, pp. 4770–4773.
Liang, L., Su, M., Li L., Lan, F., Yang, G., Ge, S., et al., Sens. Actuators B—Chem., 2016, vol. 229, pp. 347–354.
Lim, W.Y., Goh, B.T., and Khor, S.M., J. Chromatogr. B, 2017, vol. 1060, pp. 424–442.
Fu, L.M. and Wang, Y.N., Trends Anal. Chem., 2018, vol. 107, pp. 196–211.
Liu, C., Gomez, F.A., Miao, Y., Cui, P., and Lee, W., Talanta, 2019, vol. 194, pp. 171–176.
Liu, M.M., Lian, X., Liu, H., Guo, Z.Z., Huang, H.H., Lei, Y., et al., Talanta, 2019, vol. 200, pp. 511–517.
Cate, D.M., Adkins, J.A., Mettakoonpitak, J., and Henry, C.S., Anal. Chem., 2015, vol. 87, no. 1, pp. 19–41.
He, Y., Wu, W.B., and Fu, J.Z., RSC Adv., 2015, vol. 5, pp. 2694–2701.
Xia, Y., Si, J., and Li, Z., Biosens. Bioelectron., 2016, vol. 77, pp. 774–789.
He, Y., Gao, Q., Wu, W.B., Nie, J., and Fu, J.Z., Micromachines, 2016, vol. 7, no. 7, Article ID 108.
Strong, E.B., Schultz, S.A., Martinez, A.W., and Martinez, N.W., Sci. Rep., 2019, vol. 9, Article ID 7.
Yamada, K., Henares, T.G., Suzuki, K., and Citterio, D., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2015, vol. 54, no. 18, pp. 5294–5310.
Abe, K., Suzuki, K., and Citterio, D., Inkjet-printed microfluidic multianalyte chemical sensing paper, Anal. Chem., 2008, vol. 80, no. 18, pp. 6928–6934.
Li, X., Tian, J., Garnier, G., and Shen, W., Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces, 2010, vol. 76, pp. 564–570.
Wang, J., Monton, M.R.N., Zhang, X., Filipe, C.D.M., Pelton, R., and Brennan J.D., Lab Chip, 2014, vol. 14, no. 4, pp. 691–695.
Park, S., Kim, H., Paek, S.H., Hong, J.W., and Kim, J.K., Ultramicroscopy, 2008, vol. 108, pp. 1348–1351.
Kim, Y.K. and Kim, H., J. Ind. Eng. Chem., 2009, vol. 15, pp. 229–232.
Funding
The authors would like to appreciate Ministry of Science and Technology of Vietnam for funding this research under the grant no. 03/2019/HĐ-SPĐP.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. This article does not contain any studies involving animals or human participants performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Le, N.N., Phan, H.C., Dang, D.M. et al. Fabrication of Miniaturized Microfluidic Paper-Based Analytical Devices for Sandwich Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assays using INKJET Printing. Appl Biochem Microbiol 57, 257–261 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0003683821020071
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0003683821020071