Abstract
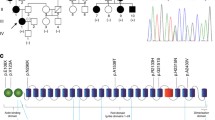
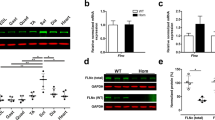
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) often leads to heart failure. Mutations in sarcomeric proteins are most frequently the cause of HCM but in many patients the gene defect is not known. Here we report on a young man who was diagnosed with HCM shortly after birth. Whole exome sequencing revealed a mutation in the FLNC gene (c.7289C > T; p.Ala2430Val) that was previously shown to cause aggregation of the mutant protein in transfected cells. Myocardial tissue from patients with this mutation has not been analyzed before and thus, the underlying etiology is not well understood. Myocardial tissue of our patient obtained during myectomy at the age of 23 years was analyzed in detail by histochemistry, immunofluorescence staining, electron microscopy and western blot analysis. Cardiac histology showed a pathology typical for myofibrillar myopathy with myofibril disarray and abnormal protein aggregates containing BAG3, desmin, HSPB5 and filamin C. Analysis of sarcomeric and intercalated disc proteins showed focally reduced expression of the gap junction protein connexin43 and Xin-positive sarcomeric lesions in the cardiomyocytes of our patient. In addition, autophagy pathways were altered with upregulation of LC3-II, WIPI1 and HSPB5, 6, 7 and 8. We conclude that the p.Ala2430Val mutation in FLNC most probably is associated with HCM characterized by abnormal intercalated discs, disarray of myofibrils and aggregates containing Z-disc proteins similar to myofibrillar myopathy, which supports the pathological effect of the mutation.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ader F et al (2019) FLNC pathogenic variants in patients with cardiomyopathies: prevalence and genotype-phenotype correlations. Clin Genet 96:317–329. https://doi.org/10.1111/cge.13594
Arndt V et al (2010) Chaperone-assisted selective autophagy is essential for muscle maintenance. Curr Biol 20:143–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2009.11.022
Baker J et al (2010) Identification of a Z-band associated protein complex involving KY, FLNC and IGFN1. Exp Cell Res 316:1856–1870. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2010.02.027
Beatham J, Romero R, Townsend SK, Hacker T, van der Ven PF, Blanco G (2004) Filamin C interacts with the muscular dystrophy KY protein and is abnormally distributed in mouse KY deficient muscle fibres. Hum Mol Genet 13:2863–2874. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddh308
Begay RL et al (2016) FLNC gene splice mutations cause dilated cardiomyopathy. JACC Basic Transl Sci 1:344–359. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacbts.2016.05.004
Brodehl A et al (2013) The novel desmin mutant p. A120D impairs filament formation, prevents intercalated disk localization, and causes sudden cardiac death. Circ Cardiovasc Genet 6:615–623. https://doi.org/10.1161/circgenetics.113.000103
Brodehl A et al (2016) Mutations in FLNC are associated with familial restrictive cardiomyopathy. Hum Mutat 37:269–279. https://doi.org/10.1002/humu.22942
Brodehl A, Gaertner-Rommel A, Milting H (2017) FLNC (filamin-C): a new(er) player in the field of genetic cardiomyopathies. Circ Cardiovasc Genet. https://doi.org/10.1161/circgenetics.117.001959
Carra S et al (2017) The growing world of small heat shock proteins: from structure to functions. Cell Stress Chaperones 22:601–611. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12192-017-0787-8
Chen Y, Lewis W, Diwan A, Cheng EH, Matkovich SJ, Dorn GW 2nd (2010) Dual autonomous mitochondrial cell death pathways are activated by Nix/BNip3L and induce cardiomyopathy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:9035–9042. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0914013107
Chevessier F et al (2015) Myofibrillar instability exacerbated by acute exercise in filaminopathy. Hum Mol Genet 24:7207–7220. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddv421
Claeys KG et al (2008) Electron microscopy in myofibrillar myopathies reveals clues to the mutated gene. Neuromuscul Disord 18:656–666. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nmd.2008.06.367
Claeys KG et al (2009) Differential involvement of sarcomeric proteins in myofibrillar myopathies: a morphological and immunohistochemical study. Acta Neuropathol 117:293–307. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-008-0479-7
Cui H et al (2018) Mutation profile of FLNC gene and its prognostic relevance in patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Mol Genet Genomic Med 6:1104–1113. https://doi.org/10.1002/mgg3.488
Duff RM et al (2011) Mutations in the N-terminal actin-binding domain of filamin C cause a distal myopathy. Am J Hum Genet 88:729–740. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajhg.2011.04.021
Ehsan M, Jiang H, Thomson KL, Gehmlich K (2017) When signalling goes wrong: pathogenic variants in structural and signalling proteins causing cardiomyopathies. J Muscle Res Cell Motil 38:303–316. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10974-017-9487-3
Eulitz S et al (2013) Identification of Xin-repeat proteins as novel ligands of the SH3 domains of nebulin and nebulette and analysis of their interaction during myofibril formation and remodeling. Exp Cell Res 24:3215–3226. https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.E13-04-0202
Fidler LM, Wilson GJ, Liu F, Cui X, Scherer SW, Taylor GP, Hamilton RM (2009) Abnormal connexin43 in arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy caused by plakophilin-2 mutations. J Cell Mol Med 13:4219–4228. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1582-4934.2008.00438.x
Force T et al (2010) Research priorities in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: report of a Working Group of the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Circulation 122:1130–1133. https://doi.org/10.1161/circulationaha.110.950089
Fujita M et al (2012) Filamin C plays an essential role in the maintenance of the structural integrity of cardiac and skeletal muscles, revealed by the medaka mutant zacro. Dev Biol 361:79–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ydbio.2011.10.008
Fürst DO, Osborn M, Nave R, Weber K (1988) The organization of titin filaments in the half-sarcomere revealed by monoclonal antibodies in immunoelectron microscopy: a map of ten nonrepetitive epitopes starting at the Z line extends close to the M line. J Cell Biol 106:1563–1572. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.106.5.1563
Fürst DO, Goldfarb LG, Kley RA, Vorgerd M, Olive M, van der Ven PF (2013) Filamin C-related myopathies: pathology and mechanisms. Acta Neuropathol 125:33–46. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-012-1054-9
Gemelli C et al (2019) A novel mutation in the N-terminal acting-binding domain of filamin C protein causing a distal myofibrillar myopathy. J Neurol Sci 398:75–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jns.2019.01.019
Ghasemi Tahrir F, Gupta M, Myers V, Gordon J, Cheung JY, Feldman AM, Khalili K (2019) Role of Bcl2-associated athanogene 3 in turnover of gap junction protein, connexin 43, in neonatal cardiomyocytes. Sci Rep 9:7658. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-44139-w
Golenhofen N, Perng MD, Quinlan RA, Drenckhahn D (2004) Comparison of the small heat shock proteins alphaB-crystallin, MKBP, HSP25, HSP20, and cvHSP in heart and skeletal muscle. Histochem Cell Biol 122:415–425. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-004-0711-z
Gómez J et al (2017) Screening of the filamin C gene in a large cohort of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy patients. Circ Cardiovasc Genet. https://doi.org/10.1161/circgenetics.116.001584
Hall CL et al (2020) Filamin C variants are associated with a distinctive clinical and immunohistochemical arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy phenotype. Int J Cardiol 307:101–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijcard.2019.09.048
Hughes SE (2004) The pathology of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Histopathology 44:412–427. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2559.2004.01835.x
Juo LY, Liao WC, Shih YL, Yang BY, Liu AB, Yan YT (2016) HSPB7 interacts with dimerized FLNC and its absence results in progressive myopathy in skeletal muscles. J Cell Sci 129:1661–1670. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.179887
Kabsch W, Sander C (1983) Dictionary of protein secondary structure: pattern recognition of hydrogen-bonded and geometrical features. Biopolymers 22:2577–2637. https://doi.org/10.1002/bip.360221211
Karmouch J, Protonotarios A, Syrris P (2018) Genetic basis of arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy. Curr Opin Cardiol 33:276–281. https://doi.org/10.1097/hco.0000000000000509
Kebir S et al (2016) Sarcomeric lesions and remodeling proximal to intercalated disks in overload-induced cardiac hypertrophy. Exp Cell Res 348:95–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2016.09.008
Kiselev A et al (2018) De novo mutations in FLNC leading to early-onset restrictive cardiomyopathy and congenital myopathy. Hum Mutat 39:1161–1172. https://doi.org/10.1002/humu.23559
Kley RA et al (2007) Clinical and morphological phenotype of the filamin myopathy: a study of 31 German patients. Brain 130:3250–3264. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awm271
Kley RA et al (2012) Pathophysiology of protein aggregation and extended phenotyping in filaminopathy. Brain 135:2642–2660. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/aws200
Kley RA et al (2013a) A combined laser microdissection and mass spectrometry approach reveals new disease relevant proteins accumulating in aggregates of filaminopathy patients. Mol Cell Proteomics 12:215–227. https://doi.org/10.1074/mcp.M112.023176
Kley RA, van der Ven PF, Olivé M, Höhfeld J, Goldfarb LG, Fürst DO, Vorgerd M (2013b) Impairment of protein degradation in myofibrillar myopathy caused by FLNC/filamin C mutations. Autophagy 9:422–423. https://doi.org/10.4161/auto.22921
Kley RA, Olivé M, Schröder R (2016) New aspects of myofibrillar myopathies. Curr Opin Neurol 29:628–634. https://doi.org/10.1097/wco.0000000000000357
Kunkel B, Lapp H, Kober G, Kaltenbach M (1978) Light-microscopic evaluation of myocardial biopsies. Cardiomyopathy and myocardial biopsy. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp 62–70
Labeit S et al (2006) Expression of distinct classes of titin isoforms in striated and smooth muscles by alternative splicing, and their conserved interaction with filamins. J Mol Biol 362:664–681. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2006.07.077
Leber Y et al (2016) Filamin C is a highly dynamic protein associated with fast repair of myofibrillar microdamage. Hum Mol Genet 25:2776–2788. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddw135
Levine B, Kroemer G (2008) Autophagy in the pathogenesis of disease. Cell 132:27–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2007.12.018
Lipshultz SE et al (2013) Risk stratification at diagnosis for children with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: an analysis of data from the Pediatric Cardiomyopathy Registry. Lancet 382:1889–1897. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(13)61685-2
Lipshultz SE et al (2019) Cardiomyopathy in children: classification and diagnosis: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 140(1):29-e68. https://doi.org/10.1161/cir.0000000000000682
Lu S, Carroll SL, Herrera AH, Ozanne B, Horowits R (2003) New N-RAP-binding partners alpha-actinin, filamin and Krp1 detected by yeast two-hybrid screening: implications for myofibril assembly. J Cell Sci 116:2169–2178. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.00425
Mao Z, Nakamura F (2020) Structure and function of filamin C in the muscle Z-disc. Int J Mol Sci 21(8):2696. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21082696
McKenna WJ, Maron BJ, Thiene G (2017) Classification, epidemiology, and global burden of cardiomyopathies. Circ Res 121:722–730. https://doi.org/10.1161/circresaha.117.309711
Miao J, Su FF, Liu XM, Wei XJ, Yuan Y, Yu XF (2018) A case report: a heterozygous deletion (2791_2805 del) in exon 18 of the filamin C gene causing filamin C-related myofibrillar myopathies in a Chinese family. BMC Neurol 18:79. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12883-018-1078-4
Ney PA (2015) Mitochondrial autophagy: origins, significance, and role of BNIP3 and NIX. Biochim Biophys Acta 1853:2775–2783. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamcr.2015.02.022
Nilsson MI et al (2013) Xin is a marker of skeletal muscle damage severity in myopathies. Am J Pathol 183:1703–1709. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajpath.2013.08.010
Noorman M et al (2013) Remodeling of the cardiac sodium channel, connexin43, and plakoglobin at the intercalated disk in patients with arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy. Heart Rhythm 10:412–419. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hrthm.2012.11.018
Olivé M, Kley RA, Goldfarb LG (2013) Myofibrillar myopathies: new developments. Curr Opin Neurol 26:527–535. https://doi.org/10.1097/WCO.0b013e328364d6b1
Reimann J, Kunz WS, Vielhaber S, Kappes-Horn K, Schröder R (2003) Mitochondrial dysfunction in myofibrillar myopathy. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 29:45–51
Ruparelia AA, Zhao M, Currie PD, Bryson-Richardson RJ (2012) Characterization and investigation of zebrafish models of filamin-related myofibrillar myopathy. Hum Mol Genet 21:4073–4083. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/dds231
Ruparelia AA, Oorschot V, Ramm G, Bryson-Richardson RJ (2016) FLNC myofibrillar myopathy results from impaired autophagy and protein insufficiency. Hum Mol Genet 25:2131–2142. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddw080
Rupp S et al (2018) Genetic basis of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy in children. Clin Res Cardiol 108:282–289. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00392-018-1354-8
Saffitz JE, Laing JG, Yamada KA (2000) Connexin expression and turnover: implications for cardiac excitability. Circ Res 86:723–728. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.res.86.7.723
Schänzer A et al (2018) Dysregulated autophagy in restrictive cardiomyopathy due to Pro209Leu mutation in BAG3. Mol Genet Metabol 123:388–399. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymgme.2018.01.001
Schindelin J et al (2012) Fiji: an open-source platform for biological-image analysis. Nat Methods 9:676–682. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.2019
Schröder R, Schoser B (2009) Myofibrillar myopathies: a clinical and myopathological guide. Brain Pathol 19:483–492. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1750-3639.2009.00289.x
Schubert J, Tariq M, Geddes G, Kindel S, Miller EM, Ware SM (2018) Novel pathogenic variants in filamin C identified in pediatric restrictive cardiomyopathy. Hum Mutat 39:2083–2096. https://doi.org/10.1002/humu.23661
Schuld J et al (2020) Homozygous expression of the myofibrillar myopathy-associated p.W2710X filamin C variant reveals major pathomechanisms of sarcomeric lesion formation. Acta Neuropathol Commun 8:154. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40478-020-01001-9
Selcen D (2011) Myofibrillar myopathies. Neuromuscul Disord 21:161–171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nmd.2010.12.007
Severs NJ (2000) The cardiac muscle cell. BioEssays 22:188–199. https://doi.org/10.1002/(sici)1521-1878(200002)22:2%3c188::aid-bies10%3e3.0.co;2-t
Severs NJ et al (2006) Alterations in cardiac connexin expression in cardiomyopathies. Adv Cardiol 42:228–242. https://doi.org/10.1159/000092572
Sun Y, MacRae TH (2005) The small heat shock proteins and their role in human disease. FEBS J 272:2613–2627. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1742-4658.2005.04708.x
Tahrir FG, Knezevic T, Gupta MK, Gordon J, Cheung JY, Feldman AM, Khalili K (2017) Evidence for the role of BAG3 in mitochondrial quality control in cardiomyocytes. Cell Physiol 232:797–805. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.25476
Tahrir FG, Langford D, Amini S, Mohseni Ahooyi T, Khalili K (2019) Mitochondrial quality control in cardiac cells: mechanisms and role in cardiac cell injury and disease. J Cell Physiol 234:8122–8133. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.27597
Thompson TG et al (2000) Filamin 2 (FLN2): a muscle-specific sarcoglycan interacting protein. J Cell Biol 148:115–126. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.148.1.115
Touw WG, Baakman C, Black J, te Beek TA, Krieger E, Joosten RP, Vriend G (2015) A series of PDB-related databanks for everyday needs. Nucleic Acids Res 43:D364-368. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gku1028
Towbin JA (2014) Inherited cardiomyopathies. Circ J 78:2347–2356
Traub O et al (1994) Immunochemical and electrophysiological characterization of murine connexin40 and -43 in mouse tissues and transfected human cells. Eur J Cell Biol 64:101–112
Tucker NR et al (2017) Novel mutation in FLNC (filamin C) causes familial restrictive cardiomyopathy. Circ Cardiovasc Genet. https://doi.org/10.1161/circgenetics.117.001780
Valdés-Mas R et al (2014) Mutations in filamin C cause a new form of familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Nat Commun 5:5326. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms6326
van der Ven PF, Obermann WM, Lemke B, Gautel M, Weber K, Fürst DO (2000a) Characterization of muscle filamin isoforms suggests a possible role of gamma-filamin/ABP-L in sarcomeric Z-disc formation. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton 45:149–162. https://doi.org/10.1002/(sici)1097-0169(200002)45:2%3c149::aid-cm6%3e3.0.co;2-g
van der Ven PF et al (2000b) Indications for a novel muscular dystrophy pathway. Gamma-filamin, the muscle-specific filamin isoform, interacts with myotilin. J Cell Biol 151:235–248. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.151.2.235
van der Ven PF et al (2006) Unusual splicing events result in distinct Xin isoforms that associate differentially with filamin c and Mena/VASP. Exp Cell Res 312:2154–2167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2006.03.015
Verdonschot JAJ et al (2020) A mutation update for the FLNC gene in myopathies and cardiomyopathies. Hum Mutat 41:1091–1111. https://doi.org/10.1002/humu.24004
Vincent AE et al (2016) Mitochondrial dysfunction in myofibrillar myopathy. Neuromuscul Disord 26:691–701. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nmd.2016.08.004
Vorgerd M et al (2005) A mutation in the dimerization domain of filamin c causes a novel type of autosomal dominant myofibrillar myopathy. Am J Hum Genet 77:297–304. https://doi.org/10.1086/431959
Yacoub MH (2014) Decade in review—cardiomyopathies: cardiomyopathy on the move. Nat Rev Cardiol 11:628–629. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrcardio.2014.157
Yussman MG et al (2002) Mitochondrial death protein Nix is induced in cardiac hypertrophy and triggers apoptotic cardiomyopathy. Nat Med 8:725–730. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm719
Zhang YT, Pu CQ, Ban R, Liu HX, Shi Q, Lu XH (2018) Clinical, pathological, and genetic features of two Chinese cases with filamin C myopathy. Chin Med J 131:2986–2988. https://doi.org/10.4103/0366-6999.247208
Zhou Y et al (2020) Loss of filamin C is catastrophic for heart function. Circulation 141:869–871. https://doi.org/10.1161/circulationaha.119.044061
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the patients for their cooperation and permission to publish the data. The authors thank Hannah Schlierbach, Kerstin Leib and Babette Bockmühl for excellent technical assistance. This work was funded by the Deutsche Gesellschaft für Muskelkranke (DGM) e.V. (Sc22/11) and the German Research Foundation (DFG, FOR2473 to D.O.F.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
This work was approved by the ethical committee of the University of Giessen, and written informed consent was obtained from all patients.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schänzer, A., Schumann, E., Zengeler, D. et al. The p.Ala2430Val mutation in filamin C causes a "hypertrophic myofibrillar cardiomyopathy". J Muscle Res Cell Motil 42, 381–397 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10974-021-09601-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10974-021-09601-1