Abstract
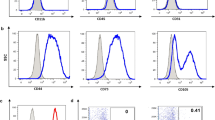
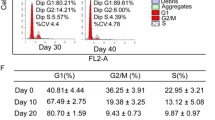
The use of mesenchymal stem cells is an effective treatment strategy for a number of retinal degenerative diseases. The poor survival of these cells after transplantation is the limiting factor of this approach. It was shown previously that the cultivation of mesenchymal stem cells under hypoxia can increase their proliferative activity. We assumed that this method of cultivation will improve the viability of these cells after their transplantation into the subretinal space. To this end, we isolated mesenchymal stem cells from the red bone marrow of mice, characterized their phenotype, their ability to differentiate in the chondrogenic, osteogenic, and adipogenic directions, as well as their proliferative activity after cultivation under hypoxia (5% oxygen in the atmosphere) and normoxia (21% oxygen in the atmosphere). Red bone marrow cells were obtained in the same way from C57 Black mice carrying the GFP gene. These cells were loaded with magnetic microparticles after preliminary cultivation under normoxia (the control) and hypoxia (the experiment) and injected subretinally to rabbits. The cells were held at the injection site using a magnetic implant that prevented their migration. Cell survival was evaluated on the 3rd, 5th, 9th, 12th, and 15th days using fluorescence microscopy and optical coherence tomography. According to the obtained data, the cells grown under hypoxic conditions remained viable in the subretinal space for 9 days, while the cells that grew under normoxia conditions died after 6 days. Thus, pre-cultivation of mesenchymal stem cells under hypoxic conditions can increase their viability after transplantation into the subretinal space, which can be used in the treatment of degenerative diseases of the retina.







Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
E. J. Duh, J. K. Sun, and A. W. Stitt, JCI Insight 2 (14), e93751 (2017).
B. Yu, X. Zhang, and X. Li, Int. J. Mol. Sci. 15 (3), 4142 (2014).
H. J. Kim and J. S. Park, Dev. Reprod. 21 (1), 1 (2017).
B. Mathew, J. N. Poston, J. C. Dreixler, et al., Ophthalmologie 255 (8), 1581 (2017).
D. Sacks, B. Baxter, C. V. Campbell, et al., Int. J. Stroke 13 (6), 612 (2018)
X. Hu, S. P. Yu, and J. L. Fraser, J. Thoracic Cardiovasc. Surg. 135 (4), 799 (2008)
X. Liu and N. Quan, Bio Protoc. 5 (20), e1631 (2015)
M. Kheirandish, S. P. Gavgani, and S. Samiee, Transfus. Apher. Sci. 56, 392 (2017)
L. Liu, J. Gao, Y. Yuan, et al., Cell Biol. Int. 37, 551 (2013)
A. M. Bader, K. Klose, K. Bieback, et al., PLoS One 10, e0138477 (2015)
J. R. Choi, B. Pingguan-Murphy, W. A. Wan Abas, et al., Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 448, 218 (2014).
J. Liu, H. Hao, H. Huang, et al., Int. J. Low Extrem. Wounds 14, 63 (2015)
L. B. Boyette, O. A. Creasey, L. Guzik, et al., Stem Cells Transl. Med. 3, 241 (2014).
I. Datta, S. Mishra, L. Mohanty, et al., Cytotherapy 13 (8), 918 (2011).
J. Liang, S. Wu, H. Zhao, et al., Neurosci. Lett. 532, 59 (2013).
J. Peng, Y. Wang, L. Zhang, et al., Brain Res. Bull. 84 (3), 235 (2011).
E. Mikaeili Agah, K. Parivar, M. Nabiuni, et al., J. Mol. Neurosci. 51 (2), 328 (2013).
W. Liao, J. Xie, J. Zhong, et al., Transplantation 87 (3), 350 (2009).
A. Kicic, W. Y. Shen, A. S. Wilson, et al., J. Neurosci. 23 (21), 7742 (2003).
C. Huang, J. Zhang, M. Ao, et al., J. Cell. Biochem. 113 (2), 590–598 (2012).
J. Y. Hsieh, H. W. Wang, S. J. Chang, et al., PLoS One 8 (8), e72604 (2013).
Funding
This work was supported by a grant under the agreement dated 28.10.2018, no. 14.575.21.0179 (unique project ID RFMEFI57518X0179), concluded between the Ministry of Science and Higher Education of the Russian Federation and the Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
COMPLIANCE WITH ETHICAL STANDARDS
All applicable international, national and institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals in the performance of work were followed. The animals were kept in accordance with Directive 2010/63/EU on the protection of animals used for scientific purpose
Additional information
Translated by E. Puchkov
Abbreviations: VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor; MSCs, mesenchymal stem cells; GFP, green fluorescent protein; PBS, phosphate buffered saline.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Plakhotniy, M.A., Kodunov, A.M., Gorina, E.V. et al. The Effect of the Cultivation Conditions of Mesenchymal Stem Cells on Their Viability upon Being Transplanted into the Subretinal Space. BIOPHYSICS 65, 958–965 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006350920060160
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006350920060160