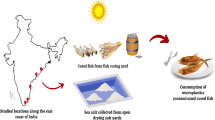
Abstract
Salted fish products provide essential nutrients and make a significant contribution to nutrition. Chemical composition, water activity (aw), sodium chloride content, pH, and microbiological analysis of five different salted fish products originating from Egypt and Spain were investigated. Chemical quality parameters such as free fatty acids (FFA), total volatile basic nitrogen (TVB-N) content, trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid (TNBS) content, peroxide value (PV), and thiobarbituric acid value (TBA) were also evaluated. The chemical composition varies greatly among different salted fish types. Analysis of salted fish samples showed high contents of TVB-N and PV, while TBA values of all samples were quite low, indicating the limited formation of secondary lipid oxidation products. The highest FFA value was recorded for Sardine, whereas Maruca recorded the lowest FFA value. Total bacterial count ranged from 3.68 to 6.92, Lactobacillus count 1.08–5.02, yeast and mold counts 0.98–3.78, Staphylococcus count 1.21–5.18, and halophilic bacteria count 2.87–6.35 log10 CFU/g. No coliforms group was detected in all samples, while enterococci count, with a less than 1.0 log10 CFU/g, was detected only in Fesseikh, Mugel, and Moloha samples. It could be concluded in the Egyptian and Spanish salted fish, the differences are meaningful, and this might be related to the different geographical origins of fishes and the different manufacturing processes used.
Graphic abstract



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adegunwa MO, Adebowale AA, Olisa ZG, Bakare HA (2013) Chemical and microbiological qualities of smoked herring (sardinella eba) in Odeda, Ogun State, Nigeria. Int J Microbiol Res 1:85–87
Ahmed EO, Ali ME, Hamed AA (2010) Quality changes of salted storage at ambient temperature (37±1°C). Pak J Nutr 9:877–881
Albertosa I, Martin-Dianaa AB, Cullenb PJ, Tiwaric BK, Shikha Ojhac K, Bourkeb P, Ricoa D (2019) Shelf-life extension of herring (Clupea harengus) using in-package atmospheric plasma technology. Innov Food Sci Emerg Technol 53:85–91
Aleksandar RP, Jasna MD, Dragana SD, Dubravka JR, Danijela VV, Milan PM, Lato LP (2018) Levels of toxic elements in canned fish from the Serbian markets and their health risks assessment. J Food Compos Anal 67:70–76
Anihouvi VB, Sakyi-Dawson E, Ayenor GS, Hounhouigan JB (2009) Biochemical changes and aroma development during the spontaneous fermentation of cassava fish into Lanhouin and their influence on product acceptability. J Aquat Food Prod Technol 18:370–384
Anihouvi VB, Kindossi JM, Hounhouigan JD (2012) Processing and quality characteristics of some major fermented fish products from Africa: a critical review. Int Res J Biol Sci 1:72–84
AOAC (2012) Official methods of analysis, 18th edn. AOAC International, Association of Official Analytical Chemists, Gaithersburg
Bimal PM, Arabinda M, Satabdi G, Tandrima M, Karunakaran D, Anandan R (2019) Nutritional composition of food fishes and their importance in providing food and nutritional security. Food Chem 293:561–570
Cadun A, Cakli S, Kisla D (2005) A study of marination of deep water pink shrimp (Parapenaeus longirostris, Lucas, 1846) and its shelf life. Food Chem 90:53–59
Chansuwan C, Chinachoti P (2015) Antioxidative properties and hydrolysis profile of Skipjack tuna dark muscle and skin. Int Food Res J 22(5):1968–1976
Chaudhry AS (2008) Forage based animal production systems and sustainability: an invited paper. Rev Bras de Zootec 37:78–84
Colin P, Robert D, Deborah F, Michael A, Dianne L (2008) Composition on non-protein nitrogen fraction of goat whole milk powder and goat milk-based infant and follow-on formulae. Int J Food Sci Nutr 59(2):123–133
Crettaz-Minaglia M, Juarez RA (2020) Fish diversity and biotic integrity in a small stream of a temperate plain. Rend Fis Acc Lincei 31:1027–1035. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12210-020-00947-1
Dieffenbacher A, Pocklington WD (1987) Standard methods for the analysis of oils, fats, and derivatives. International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry, 7th edn. Blackwell Scientific, Oxford
El-Lahamy AA, Khalil KI, El-Sherif SA, Mahmud AA (2018a) Effect of smoking methods (hot and cold) and refrigeration storage on the chemical composition of Catfish Fillets (Clarias Gariepinus). J Food Process Technol 9(10):759. https://doi.org/10.4172/2157-7110.1000759
El-Lahamy AA, Khalil KI, El-Sherif SA, Mahmud AA (2018b) Changes in quality attributes of sand smelt (Atherina hepsetus) fish burger and finger during frozen storage. J Fish Res 2(2):6–11
Farhat J, Abdul SC (2011) Chemical compositions and fatty acid profiles of three freshwater fish species. Food Chem 125:991–996
Gallart-Jornet LB (2007) A comparative study of brine salting of Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua) and Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). J Food Eng 79(1):261–270
Heliene LR, Antonio C, Victor EM, Gandhi R (2016) Evaluation of the chemical composition of fish species captured in the lower stretch of Itapecuru river Maranhão Brazil. Int J Adv Agric Environ Eng 3(1):181–186 (ISSN 2349-1523 EISSN 2349-1531)
Hirochi Y, Victor HP, Pedro LM, Valter U, Dolores RR, Ana CM, Daniel AR (2018) Physico-chemical characterization and biocompatibility of hydroxyapatite derived from fish waste. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater 80:137–142
Kawarazuka N, Bene C (2013) The potential role of small fish species in improving micronutrient deficiencies in developing countries: building evidence. Public Health Nutr 14(11):1927–1938
Koffi-Nevry R, Ouina TS, Koussememon M, Broi K (2011) Chemical composition and lactic acid microflora of Adjuevan, traditional Ivorian fermented fish condiment. Pak J Nutr 10:332–337
Köse S (2010) Evaluation of seafood safety health hazards for traditional fish products: preventive measures and monitoring Issues. Turk J Fish Aquat Sci 10:139–160
Kristín AP (2010) The influence of salting procedures, on the characteristics of heavy salted cod Ph.D. Thesis. Department of Food Technology, Engineering, and Nutrition, Faculty of Engineering, LTH, Lund University, LTH
Manat C, Soottawat B, Wonnop V, Cameron F (2006) Changes of lipids in sardine (Sardinella gibbosa) muscle during iced storage. Food Chem 99:83–91
Marco C, Margherita A, Massimo P, Nicola F, Gabriele S, Giovanni P, Gavino S (2018) Physico-chemical, colorimetric, rheological parameters and chemometric discrimination of the origin of Mugil cephalus’ roes during the manufacturing process of Bottarga. Food Res Int 108:128–135
Maria HL, Brais M, Stina F, Flemming J (2018) The influence of processing conditions on the weight change of single herring (Clupea herengus) fillets during marinating. Food Res Int 108:331–338
Mitsutoshi N, Yoshimasa S, Ryosuke K, Yozo N, Masao Y, Toshihiro W, Katsumi T, Hiroaki S (2018) Chemical properties and colors of fermenting materials in salmon fish sauce production. Data Brief 16:483–488
Mohammed HM (2010) Nutritive value of fresh and salted fermented fish (aleste dentex) Terkin. B.Sc. Thesis, Food Science and Technology Department, Ed. Khartoum. Sudan
Mohanty BP, Sankar TV, Ganguly S, Mahanty A, Anandan R, Chakrabarty K et al (2016) DHA, EPA content and fatty acid profile of 39 food fishes from India. Biomed Res Int. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/4027437
Mustafa AG (2019) Microbiological and chemical quality of a traditional salted-fermented fish (Hout-Kasef) product of Jazan Region, Saudi Arabia. Saudi J Biol Sci 26(137):140
Nuwanthi SGL, Madage SSK, Hewajulige IGN, Wijesekera RGS (2016) Comparative study on organoleptic, microbiological and chemical qualities of dried fish, Goldstripe Sardinella (Sardinella gibbosa) with low salt levels and spices. Procedia Food Sci 6:356–361
Oishi D, Sanath HK, Binaya BN (2020) Relative abundance of halophilic archaea and bacteria in diverse salt fermented fish products. LWT Food Sci Technol 117:108688
Osman OA, Sulieman AE, Elkhalifa EA, Mustafa WA (2012) Chemical and microbiological characteristic of fermented fish product, Fassiekh. Food Public Health 2:213–218
Paul YI, Charles AN, Mamudu HB, David IG (2016) Total volatile base nitrogen (TVBN) and trimethylamine (TMA) content of “Bunyi youri” as influenced by the addition of glucose and clove during storage. Int J Biotechnol Food Sci 4(5):81–85
Petrus PH, Suprayitno E (2013) Physicochemical characteristics, sensory acceptability and microbial quality of WadiBetok a traditional fermented fish from South Kalimantan, Indonesia. Int Food Res J 20(2):933–939
Roy D, Majumbar RK, Maurya SK, Tripathi DB, Priyadarshini MB (2014) Understanding of traditional knowledge and characterization of Telesech-a fermented fish product of Tripura state. Indian J Nat Prod Resour 5:351–358
Ruan G, Nico JS, Johan HJ, Victor W (2016) Metal concentrations in Hydrocynus vittatus (Castelnau 1861) populations from a premier conservation area: relationships with environmental concentrations. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 129:91–102
Serkan K, Bekir T, Andrej S, Drago K, Matevz P, Sevim K (2013) Investigation of the contents of biogenic amines and some food safety parameters of various commercially salted fish products. Food Control 32:597–606
United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) (2016) National nutrient database for standard database. http://ndb.nal.usda.gov/ndb/search/list?qlookup=16108&format=Full
Yanshun X, Lin L, Joe M, Pei G, Jinhong Z, Wenshui X, Qixing J (2018) The contribution of autochthonous microflora on free fatty acids release and flavor development in low-salt fermented fish. Food Chem 256:259–267
Yuesheng Q, Jie-Hua C, Weijun Y, Pei W, Minxian R, Hong D (2017) Contamination of Chinese salted fish with volatile N-nitrosamines as determined by QuEChERS and gas chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Food Chem 232:763–769
Zang J, Xu Y, Xia W, Regenstein JM (2019) Quality, functionality, and microbiology of fermented fish: A review. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2019.1565491
Zied K, Beth M (2018) Comparative dynamics of fish by-catch hydrolysis through chemical and microbial methods. LWT Food Sci Technol 97:135–143
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AAAM, AAM, MER, MHHR performed the examination of the fish products and all authors involved in the article writing. MFR analyzed the results and edited the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mohdaly, A.A.A., Mahmoud, A.A., Ramadan, M.F. et al. Biochemical and microbiological characteristics of some Mediterranean salted fish products. Rend. Fis. Acc. Lincei 32, 343–355 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12210-021-00984-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12210-021-00984-4