Abstract
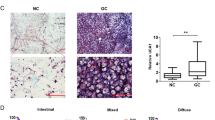
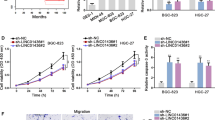
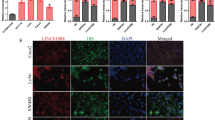
This study aimed to annotate the role of long intergenic non-coding RNA 152 (LINC00152) in CD8+ T cells mediated immune responses in gastric cancer (GC) and the underlying mechanism. LINC00152 expression levels were detected through RT-PCR. For tumor engraftment, HGC-27 cells that received LINC00152 shRNA, LINC00152 overexpression vectors, enhancer of zeste homolog 2 (EZH2) shRNA or combination transfection were injected into mice. Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) assay was used to explore the interaction between LINC00152, Cys-X-cys ligand 9 (CXCL9) and Cys-X-cys ligand 10 (CXCL10). Flow cytometry was adopted to measure the CD8+ T-cell infiltration in tumor issue. In this study, we found increased LINC00152 expression levels are positively associated with the poor prognosis of GC patients and negatively associated with the CD8 levels. ChIP assay verified that LINC00152 recruits EZH2 to the promoters of CXCL9 and CXCL10, thus the silencing of LINC00152 promoted the production of CXCL9 and CXCL10. Knockdown of LINC00152 suppressed tumor cells growth in vivo and in vitro, increased tumor-infiltrating CD8+ T cells numbers and promoted the expression of CXCL9, CXCL10 and C-X-C Motif Chemokine Receptor 3 (CXCR3) in xenograft tumors. While CD8+ T cell depletion reversed the tumor suppression effect of LINC00152 silence. Besides, the silencing of EZH2 partly inhibited the promotion effect LINC00152 on tumor growth. Our study indicated that LINC00152 inhibition suppressed the tumor progress may through promoting CD8+ T-cell infiltration.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Source data and reagents are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Aune TM, Spurlock CF III (2016) Long non-coding RNAs in innate and adaptive immunity. Virus Res 212:146–160
Cao R, Zhang Y (2004) The functions of E (Z)/EZH2-mediated methylation of lysine 27 in histone H3. CurrOpin Genet Dev 14:155–164
Cats A, Jansen EP, van Grieken NC, Sikorska K, Lind P, Nordsmark M, Kranenbarg EM-K, Boot H, Trip AK, Swellengrebel HM (2018) Chemotherapy versus chemoradiotherapy after surgery and preoperative chemotherapy for resectable gastric cancer (CRITICS): an international, open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 19:616–628
Chen Qn, Chen X, Chen Zy, Nie Fq, Wei Cc, Ma Hw, Wan L, Yan S, Ren Sn, Wang Zx (2017) Long intergenic non-coding RNA 00152 promotes lung adenocarcinoma proliferation via interacting with EZH2 and repressing IL24 expression. Mol Cancer 16:17
Chen Wm, D-pS MD, Kong R, Xu Tp, Xia R, Zhang Eb, Shu Y (2016) Long intergenic non-coding RNA 00152 promotes tumor cell cycle progression by binding to EZH2 and repressing p15 and p21 in gastric cancer. Oncotarget 7:9773
Chen X, Li D, Gao Y, Tang W, Lao I, Cao Y, Hao B (2018a) Long intergenic noncoding RNA 00152 promotes glioma cell proliferation and invasion by interacting with MiR-16. Cell PhysiolBiochem 46:1055–1064
Chen ZP, Wei JC, Wang Q, Yang P, Li WL, He F, Chen HC, Hu H, Zhong JB, Cao J (2018b) Long non-coding RNA 00152 functions as a competing endogenous RNA to regulate NRP1 expression by sponging with miRNA-206 in colorectal cancer. Int J Oncol 53:1227–1236
Cheng WC, Tsui YC, Ragusa S, Koelzer VH, Mina M, Franco F, Läubli H, Tschumi B, Speiser D, Romero P (2019) Uncoupling protein 2 reprograms the tumor microenvironment to support the anti-tumor immune cycle. Nat Immunol 20:206
Chheda ZS, Sharma RK, Jala VR, Luster AD, Haribabu B (2016) Chemoattractant receptors BLT1 and CXCR3 regulate antitumor immunity by facilitating CD8+ T cell migration into tumors. J Immunol 197(5):2016–2026
Christofides A, Karantanos T, Bardhan K, Boussiotis VA (2016) Epigenetic regulation of cancer biology and anti-tumor immunity by EZH2. Oncotarget 7:85624
Curran MA, Montalvo W, Yagita H, Allison JP (2010) PD-1 and CTLA-4 combination blockade expands infiltrating T cells and reduces regulatory T and myeloid cells within B16 melanoma tumors. ProcNatlAcadSci 107:4275–4280
Djebali S, Davis CA, Merkel A, Dobin A, Lassmann T, Mortazavi A, Tanzer A, Lagarde J, Lin W, Schlesinger F et al (2012) Landscape of transcription in human cells. Nature 489:101–108
Dolcetti R, De Re V, Canzonieri V (2018) Immunotherapy for gastric cancer: time for a personalized approach? Int J MolSci 19:1602
Fulton AM (2009) The chemokine receptors CXCR4 and CXCR3 in cancer. CurrOncol Rep 11:125–131
Gajewski TF (2015) The next hurdle in cancer immunotherapy: overcoming the non–T-cell–inflamed tumor microenvironment. Semi Oncol 42:663–671
Gorbachev AV, Kobayashi H, Kudo D, Tannenbaum CS, Finke JH, Shu S, Farber JM, Fairchild RL (2007) CXC chemokine ligand 9/monokine induced by IFN-γ production by tumor cells is critical for T cell-mediated suppression of cutaneous tumors. J Immunol 178:2278–2286
Guan D, Zhang W, Zhang W, Liu GH, Belmonte JC (2013) Switching cell fate, ncRNAs coming to play. Cell Death Dis 4:e464
He W, Zhang H, Han F, Chen X, Lin R, Wang W, Qiu H, Zhuang Z, Liao Q, Zhang W (2017) CD155T/TIGIT signaling regulates CD8+ T-cell metabolism and promotes tumor progression in human gastric cancer. Can Res 77:6375–6388
Hu G, Tang Q, Sharma S, Yu F, Escobar TM, Muljo SA, Zhu J, Zhao K (2013) Expression and regulation of intergenic long noncoding RNAs during T cell development and differentiation. Nat Immunol 14:1190
Huarte M (2015) The emerging role of lncRNAs in cancer. Nat Med 21:1253
Kung JT, Colognori D, Lee JT (2013) Long noncoding RNAs: past, present, and future. Genetics 193:651–669
Li S, Wen D, Che S, Cui Z, Sun Y, Ren H, Hao J (2018) Knockdown of long noncoding RNA 00152 (LINC00152) inhibits human retinoblastoma progression. OncoTargetsTher 11:3215
Neves H, Kwok HF (2015) Recent advances in the field of anti-cancer immunotherapy. BBA Clin 3:280–288
Peng D, Kryczek I, Nagarsheth N, Zhao L, Wei S, Wang W, Sun Y, Zhao E, Vatan L, Szeliga W (2015) Epigenetic silencing of T H 1-type chemokines shapes tumour immunity and immunotherapy. Nature 527:249
Peng W, Liu C, Xu C, Lou Y, Chen J, Yang Y, Yagita H, Overwijk WW, Lizée G, Radvanyi L (2012) PD-1 blockade enhances T-cell migration to tumors by elevating IFN-γ inducible chemokines. Cancer Res 72:5209–5218
Ribas A, Wolchok JD (2018) Cancer immunotherapy using checkpoint blockade. Science 359:1350–1355
Sharma P, Hu-Lieskovan S, Wargo JA, Ribas A (2017) Primary, adaptive, and acquired resistance to cancer immunotherapy. Cell 168:707–723
Sitarz R, Skierucha M, Mielko J, Offerhaus GJA, Maciejewski R, Polkowski WP (2018) Gastric cancer: epidemiology, prevention, classification, and treatment. Cancer Manag Res 10:239
Tumeh PC, Harview CL, Yearley JH, Shintaku IP, Taylor EJ, Robert L, Chmielowski B, Spasic M, Henry G, Ciobanu V (2014) PD-1 blockade induces responses by inhibiting adaptive immune resistance. Nature 515:568
Wang Y, Liu J, Bai H, Dang Y, Lv P, Wu S (2017) Long intergenic non-coding RNA 00152 promotes renal cell carcinoma progression by epigenetically suppressing P16 and negatively regulates miR-205. Am J Cancer Res 7:312
Wu K, Zhao Z, Liu K, Zhang J, Li G, Wang L (2017) Long noncoding RNA lnc-sox5 modulates CRC tumorigenesis by unbalancing tumor microenvironment. Cell Cycle 16:1295–1301
Xue J, Yu X, Xue L, Ge X, Zhao W, Peng W (2019) Intrinsic β-catenin signaling suppresses CD8+ T-cell infiltration in colorectal cancer. Biomed Pharmacother 115:108921
Yang G, Lu X, Yuan L (2014) LncRNA: a link between RNA and cancer. BiochimetBiophysActa (BBA) 1839(11):1097–1109
Yang T, Zeng H, Chen W, Zheng R, Zhang Y, Li Z, Qi J, Wang M, Chen T, Lou J (2016) Helicobacter pylori infection, H19 and LINC00152 expression in serum and risk of gastric cancer in a Chinese population. Cancer Epidemiol 44:147–153
Yu WD, Wang H, He QF, Xu Y, Wang XC (2018) Long noncoding RNAs in cancer-immunity cycle. J Cell Physiol 233:6518–6523
Yu Y, Yang J, Li Q, Xu B, Lian Y, Miao L (2017) LINC 00152: a pivotal oncogenic long non-coding RNA in human cancers. Cell Prolif 50:e12349
Zhao E, Maj T, Kryczek I, Li W, Wu K, Zhao L, Wei S, Crespo J, Wan S, Vatan L et al (2016) Cancer mediates effector T cell dysfunction by targeting microRNAs and EZH2 via glycolysis restriction. Nat Immunol 17:95–103
Acknowledgements
The study was funded by Scientific Research Project of baoan district science and innovation bureau (2019JD254)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
GL and JH: designed the experiments. JO, PL, ZY, MY, LL and HM: performed the experiments. JO and PL: analyzed the data.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ou, J., Lei, P., Yang, Z. et al. LINC00152 mediates CD8+ T-cell infiltration in gastric cancer through binding to EZH2 and regulating the CXCL9, 10/CXCR3 axis. J Mol Histol 52, 611–620 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-021-09967-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-021-09967-z