Abstract
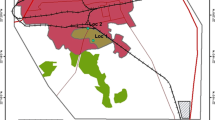
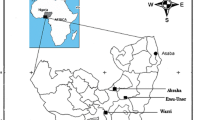
Dust deposited on residential and agricultural lands can have serious consequences for the ecosystem when toxic trace elements are present. This study aimed to assess the ecological risk of the trace elements found in the deposited dust around the Mehdi Abad Pb/Zn mine, Yazd, Iran, using several modified pollution indices. The dust samples were collected by the grid method and a Marble Dust Collector (MDCO) sampler to evaluate the concentration of thirty trace elements: nickel (Ni), lead (Pb), barium (Ba), beryllium (Be), chromium (Cr), copper (Cu), dysprosium (Dy), lanthanum (La), lithium (Li), niobium (Nb), tin (Sn), neodymium (Nd), praseodymium (Pr), rubidium (Rb), Ferrum (Fe), sulfur (S), selenium (Se), strontium (Sr), tantalum (Ta), terbium (Tb), zirconium (Zr), tellurium (Te), thorium (Th), titanium (Ti), uranium (U), vanadium (V), yttrium (Y), ytterbium (Yb), thulium (Tm), and cobalt (Co). This study employed multivariate statistical techniques, including Hierarchical cluster analysis (HCA) and the IDW interpolation technique, as well as modified pollution indices such as Enrichment Factor (EF), Modified Pollution Index (MPI), Modified Potential Ecological Risk Index (MRI), and Modified Hazard Quotient (mHQ). All the statistical data analyses were performed via SPSS Statistics, version 22.00. The HCA results showed that all of these trace elements, except Fe, form a group and had similar behavior. The average levels of all elements in the dust samples except for Cr, S, Sr, Ta, Tb, and Te exceeded the background value. The results confirmed that both anthropogenic activities and natural factors were responsible for the trace elements found in the dust. The average EF value for Pb (43.26) indicated its extremely high enrichment in the study area. The MPI, mHQ, and MRI results showed that 33%, 100%, and 33.33% of the dust samples were in the heavily polluted, extreme severity, and high risk categories, respectively. The IDW analysis results revealed that the highest value of the MRI and mHQ indices was in agricultural lands and residential areas; the predominant wind direction also played a role in transferring the elements from the mine to these areas. In general, the results indicated that mining activities increased the ecological risk in Mehdi Abad due to the presence of trace elements, especially Pb.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Roy S, Gupta SK, Prakash J, Habib G, Baudh K, Nasr M. Ecological and human health risk assessment of heavy metal contamination in road dust in the National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi, India. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2019;26(29):30413–25. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06216-5.
Cai K, Li C, Na S. Spatial distribution, pollution source, and health risk assessment of heavy metals in atmospheric depositions: a case study from the sustainable city of Shijiazhuang, China. Atmosphere. 2019;10(4):222. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10040222.
Fashola MO, Ngole-Jeme VM, Babalola OO. Heavy metal pollution from gold mines: environmental effects and bacterial strategies for resistance. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2016;13(11):1047. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph13111047.
Entwistle JA, Hursthouse AS, Reis PAM, Stewart AG. Metalliferous mine dust: human health impacts and the potential determinants of disease in mining communities. Curr Pollut Rep. 2019;5(3):67–83. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40726-019-00108-5.
Kamani H, Mahvi A, Seyedsalehi M, Jaafari J, Hoseini M, Safari G, et al. Contamination and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in street dust of Tehran, Iran. Int J Environ Sci Technol. 2017;14(12):2675–82. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-017-1327-x.
Alegre DAG, Peroni RL, Aquino ER. The impact of haulroad geometric parameters on open pit mine strip ratio. REM-Int Eng J. 2019;72(1):25–31. https://doi.org/10.1590/0370-44672018720136.
Obiora SC, Chukwu A, Toteu SF, Davies TC. Assessment of heavy metal contamination in soils around lead (Pb)-zinc (Zn) mining areas in Enyigba, southeastern Nigeria. J Geol Soc India. 2016;87(4):453–62. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-016-0413-x.
Baghaie AH, Aghili F. Investigation of heavy metals concentration in soil around a PbZn mine and ecological risk assessment. Environ Health Eng Manag J. 2019;6(3):151–6. https://doi.org/10.15171/EHEM.2019.17.
Bu Q, Li Q, Zhang H, Cao H, Gong W, Zhang X, et al. Concentrations, spatial distributions, and sources of heavy metals in surface soils of the coal Mining City Wuhai, China. J Cwhem. 2020;2020:10–1. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/4705954.
Li H, Xu W, Dai M, Wang Z, Dong X, Fang T. Assessing heavy metal pollution in paddy soil from coal mining area, Anhui, China. Environ Monitor Assess. 2019;191(8):518. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-7659-x.
Jahromi MA, Jamshidi-Zanjani A, Darban AK. Heavy metal pollution and human health risk assessment for exposure to surface soil of mining area: a comprehensive study. Environ Earth Sci. 2020;79(14):1–18. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-020-09110-3.
Kolawole TO, Olatunji AS, Jimoh MT, Fajemila OT. Heavy metal contamination and ecological risk assessment in soils and sediments of an industrial area in southwestern Nigeria. J Health Pollut. 2018;8(19):180906. https://doi.org/10.5696/2156-9614-8.19.
Mokhtarzadeh Z, Keshavarzi B, Moore F, Marsan FA, Padoan E. Potentially toxic elements in the Middle East oldest oil refinery zone soils: source apportionment, speciation, bioaccessibility and human health risk assessment. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2020;27:40573–91. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09895-7.
Ali Z, Malik R, Shinwari Z, Qadir A. Enrichment, risk assessment, and statistical apportionment of heavy metals in tannery-affected areas. Int J Environ Sci Technol. 2015;12(2):537–50. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-013-0428-4.
Keshavarzi A, Kumar V. Spatial distribution and potential ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in agricultural soils of northeastern Iran. Geol Ecol Landsc. 2020;4(2):87–103. https://doi.org/10.1080/24749508.2019.1587588.
Rayhan Khan M, Hosna Ara M, Kumar DP. Assessment of heavy metals concentrations in the soil of Mongla industrial area, Bangladesh. Environ Health Eng Manag J. 2019;6(3):191–202. https://doi.org/10.15171/EHEM.2019.22.
Yuan Q, Wang P, Wang C, Chen J, Wang X, Liu S, et al. Metals and metalloids distribution, source identification, and ecological risks in riverbed sediments of the Jinsha River, China. J Geochem Explor. 2019;205:106334. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2019.
Huang S, Yuan C, Li Q, Yang Y, Tang C, Ouyang K, et al. Distribution and risk assessment of heavy metals in soils from a typical Pb-Zn mining area. Pol J Environ Stud. 2017;26(3):1105–12. https://doi.org/10.15244/pjoes/68424.
Rajabi A, Rastad E, Canet C. Metallogeny of Cretaceous carbonate-hosted Zn–Pb deposits of Iran: geotectonic setting and data integration for future mineral exploration. Int Geol Rev. 2012;54(14):1649–72. https://doi.org/10.1080/00206814.2012.659110.
Santos-Francés F, Martínez-Graña A, Alonso Rojo P, García SA. Geochemical background and baseline values determination and spatial distribution of heavy metal pollution in soils of the Andes mountain range (Cajamarca-Huancavelica, Peru). Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2017;14(8):859. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph14080859.
Y-h L, Wan B, Xue D-s. Sample Digestion and Combined Preconcentration Methods for the Determination of Ultra-Low Gold Levels in Rocks. Molecules. 2019;24(9):1778. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24091778.
Konieczka P. Validation and regulatory issues for sample preparation in: comprehensive sampling and sample preparation. Chem Mol Sci Chem Eng. 2012;2:699–711.
Taleuzzaman M. Limit of blank (LOB), limit of detection (LOD), and limit of quantification (LOQ). Org Med Chem. 2018;7(5):555722.
Brady JP, Ayoko GA, Martens WN, Goonetilleke A. Development of a hybrid pollution index for heavy metals in marine and estuarine sediments. Environ Monit Assess. 2015;187(5):306. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-015-4563-x.
Pandey B, Agrawal M, Singh S. Ecological risk assessment of soil contamination by trace elements around coal mining area. J Soils Sediments. 2016;16(1):159–68. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-015-1173-8.
Ma L, Sun J, Yang Z, Wang L. Heavy metal contamination of agricultural soils affected by mining activities around the Ganxi River in Chenzhou, Southern China. Environ Monit Assess. 2015;187(12):731. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-015-4966-8.
Duodu GO, Goonetilleke A, Ayoko GA. Comparison of pollution indices for the assessment of heavy metal in Brisbane River sediment. Environ Pollut. 2016;219:1077–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.09.008.
Shojaee Barjoee S, Azimzadeh H, Mosleh AA. Evaluation of Individual and Integrated Pollution Indices of Some Heavy Metals in Atmospheric Dust Deposition Around Khak-e-chini, Tile and Ceramic, Sand and Gravel and Glass in Ardakan County Industries in Winter 2018. J Environ Health Eng. 2020;7(3):314–37. https://doi.org/10.29252/jehe.7.3.314.
Bern CR, Walton-Day K, Naftz DL. Improved enrichment factor calculations through principal component analysis: examples from soils near breccia pipe uranium mines, Arizona, USA. Environ Pollut. 2019;248:90–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.01.122.
Kang Z, Wang S, Qin J, Wu R, Li H. Pollution characteristics and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in paddy fields of Fujian province, China. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-69165-x.
Nambiar R, Shah C, Kumar J, Shrivastav PS, Bhushan R. Assessment of contaminants in the northwestern Bay of Bengal. Environ Sci Pollut Res. 2020;27(27):34090–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09576-5.
Bay Ö, Akarsu T, Öztura E. Ecological risk assessment of surface sediments of Çardak lagoon along a human disturbance gradient. Environ Monit Assess. 2020;192:359. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-020-08336-9.
Rodríguez-Espinosa P, Shruti V, Jonathan M, Martinez-Tavera E. Metal concentrations and their potential ecological risks in fluvial sediments of Atoyac River basin, Central Mexico: Volcanic and anthropogenic influences. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2018;148:1020–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.11.068.
Benson NU, Adedapo AE, Fred-Ahmadu OH, Williams AB, Udosen ED, Ayejuyo OO, et al. A new method for assessment of sediment-associated contamination risks using multivariate statistical approach. MethodsX. 2018;5:268–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mex.2018.03.005.
Ustaoğlu F, Islam MS. Potential toxic elements in sediment of some rivers at Giresun, Northeast Turkey: A preliminary assessment for ecotoxicological status and health risk. Ecol Indic. 2020;113:106237. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2020.
Eker ÇS. Distinct contamination indices for evaluating potentially toxic element levels in stream sediments: a case study of the Harşit stream (NE Turkey). Arab J Geosci. 2020;13(22):1–18. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-020-06178-w.
Mortazavi S, Hatami-Manesh M, Joudaki F. Evaluation of toxicity and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments of Sezar River, Lorestan Province. Iran J Health Environ. 2019;11(4):487–504.
Xie Y, Chen T-b, Lei M, Yang J, Guo Q-j, Song B, et al. Spatial distribution of soil heavy metal pollution estimated by different interpolation methods: accuracy and uncertainty analysis. Chemosphere. 2011;82(3):468–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2010.09.053.
Antoniadis V, Shaheen SM, Levizou E, Shahid M, Niazi NK, Vithanage M, et al. A critical prospective analysis of the potential toxicity of trace element regulation limits in soils worldwide: are they protective concerning health risk assessment?-a review. Environ Int. 2019;127:819–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2019.03.039.
Zhang S, Liu Y, Yang Y, Ni X, Arif M, Charles W, et al. Trace elements in soils of a typical Industrial District in Ningxia, Northwest China: pollution, source, and risk evaluation. Sustain. 2020;12(5):1868. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12051868.
Maghfouri S, Hosseinzadeh MR, Rajabi A, Choulet F. A review of major non-sulfide zinc deposits in Iran. Geosci Front. 2018;9(1):249–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsf.2017.04.003.
Ghasemi M, Momenzadeh M, Yaghubpur A, Mirshokraei AA. Mineralogy and textural studies of Mehdiabad zinc-Lead deposit-Yazd, Central Iran. Mineral Explor Sustain Dev. 2008;16(3):404–389.
Maghfouri S, Hosseinzadeh M, RAJABI R, Azimzadeh A. Facies analysis and stratighraphy position of carbonate-clastic hosted Zn-Pb-Ba mineralization horizons in the early cretaceous sedimentary sequence, Southern Yazd Basin. J Geosci. 2017;26(102):233–46.
Kianpor M, Payandeh K, Ghanavati N. Environmental assessment of some heavy metals pollution in street dust in the industrial areas of Ahvaz. Jundishapur J Health Sci. 2019;11(3):e87212. https://doi.org/10.5812/jjhs.
Rout TK, Masto R, Ram L, George J, Padhy PK. Assessment of human health risks from heavy metals in outdoor dust samples in a coal mining area. Environ Geochem Health. 2013;35(3):347–56. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-012-9499-2.
Hu J, Lin B, Yuan M, Lao Z, Wu K, Zeng Y, et al. Trace metal pollution and ecological risk assessment in agricultural soil in Dexing Pb/Zn mining area, China. Environ Geochem Health. 2019;41(2):967–80. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-018-0193-x.
Keshavarzi A, Kumar V. Ecological risk assessment and source apportionment of heavy metal contamination in agricultural soils of northeastern Iran. Int J Environ Health Res. 2019;29(5):544–60. https://doi.org/10.1080/09603123.2018.1555638.
Hadzi GY, Ayoko GA, Essumang DK, Osae SK. Contamination impact and human health risk assessment of heavy metals in surface soils from selected major mining areas in Ghana. Environ Geochem Health. 2019;41(6):2821–43. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-019-00332-4.
Zhu H-n, X-z Y, G-m Z, Jiang M, Liang J, Zhang C, et al. Ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments of Xiawan Port based on modified potential ecological risk index. Trans Nonferrous Metals Soc China. 2012;22(6):1470–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/S003-6326(11)61343-5.
Traczyk P, Gruszecka-Kosowska A. The condition of air pollution in Kraków, Poland, in 2005–2020, with health risk assessment. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020;17(17):6063. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17176063.
Benson NU, Adedapo AE, Fred-Ahmadu OH, Williams AB, Udosen ED, Ayejuyo OO, et al. New ecological risk indices for evaluating heavy metals contamination in aquatic sediment: a case study of the Gulf of Guinea. Reg Stud Mar Sci. 2018;18:44–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rsma.2018.01.004.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank office of Health, Safety and Environment (HSE) of Mehdi Abad Pb/Zn mine for support of this research project.
Code availability
Not applicable.
Funding
All sources of this study were supported by the authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SSB work concept, conducted the data collection, ecological risk calculations, preparation of inverse distance weighting maps of mHQ and MRI, manuscript writing, proofreading, results and discussion, tables and figures. SZMA, MRE, VTV and MN Analysis (ICP-MS), ecological risk calculations, results and discussion, implementation of HCA, tables, figures, proofreading and references. The author(s) read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest/competing interests
There are no competing interests.
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barjoee, S.S., Abadi, S.Z.M., Elmi, M.R. et al. Evaluation of trace elements pollution in deposited dust on residential areas and agricultural lands around Pb/Zn mineral areas using modified pollution indices. J Environ Health Sci Engineer 19, 753–769 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40201-021-00643-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40201-021-00643-8