Abstract
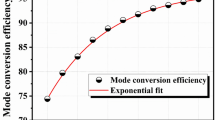
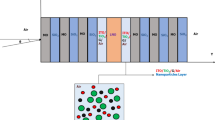
In this work, a kind of magnetic photonic crystal fiber (MPCF) design based on yttrium iron garnet (YIG) structure filled with magnetic fluid (MF) is presented. In order to improve the magneto-optical (MO) properties of isolator devices, a numerical study has been developed to investigate the non-reciprocal TE-TM mode conversion. This technique consists in producing, under the influence of a magnetic field parallel to the direction of propagation, a coupling between the modes. The influence of gyrotropy and MF infiltration at different magnetic nanoparticle volume fraction concentrations is investigated. The results revealed that the mode conversion efficiency (Rm) increases with the increase of the MF concentration, while modal birefringence (∆n) is inversely proportional to its increase. Thus, the higher concentration provides the best results. For MF concentration and gyrotropy equal respectively to 1.75% and 0.0125, Rm is improved to over 93%, and ∆n is reduced to close to 10–6. Whereas, Rm decreases to 89.59 and ∆n increases to 6 × 10–6 for MF concentration equal to 0.25%. From these results, it can be seen that this MPCF filled with MF concentration equal to 1.75% is well suited to the design of MO isolators.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shoji, Y., Mizumoto, T.: Magneto-optical non-reciprocal devices in silicon photonics. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 15, 014605 (2014)
Bahlmann, N., Zhuromskyy, O., Hammer, M., Wilkens, L., Gerhardt, R., Hertel, P.: Applications of magneto-optical waveguides in integrated optics : review. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 22, 240 (2005)
P. Dulal, T. E. Gage, A. D. Block, E. Cofell, D. C. Hutchings, and B. J. H. Stadler, Sputter-deposited seedlayer-free cerium-doped terbium iron garnets for SOI waveguide isolators, IEEE Photonics Conf. IPC (2016) 773.
Srinivasan, K., Stadler, B.J.H.: Magneto-optical materials and designs for integrated TE- and TM-mode planar waveguide isolators : a review [Invited ]. Opt. Mater. Express 8, 3307 (2018)
Liu, J., Wang, S., Deng, S., Wang, Y., Zhang, J.: Polarization research of YIG based two-dimensional magneto photonic crystals. Opt. Commun. 402, 319 (2017)
Khokhlov, N.E., et al.: Photonic crystals with plasmonic patterns: Novel type of the heterostructures for enhanced magneto-optical activity. J. Phys. D. Appl. Phys. 48, 095001 (2015)
Akhtar, M.N., et al.: Structural and magnetic properties of yttrium iron garnet (YIG) and yttrium aluminum iron garnet (YAIG) nanoferrites prepared by microemulsion method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 401, 425 (2015)
Tu, S., Białek, M., Zhang, Y., Zhao, W., Yu, H., Ansermet, J.P.: Bolometric detection of ferromagnetic resonance in YIG slab. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 439, 53 (2017)
Pan, L., Zhang, X., Wang, J., Liu, Q.: Structural and magnetic properties of electrospun yttrium iron garnet (YIG) nanofibers. Ceram. Int. 43, 1 (2017)
Saker, K., Bouchemat, T., Lahoubi, M., Bouchemat, M.: Enhancement of magneto-optical properties in magnetic photonic crystal slab waveguide based on yttrium iron garnet. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1310, 012019 (2019)
Gevorgyan, A.H.: On some optical properties of magnetic photonic crystals. J. Mod. Opt. 65, 2160 (2018)
Dong, Y., et al.: Magnetic field and temperature sensor based on D-shaped fiber modal interferometer and magnetic fluid. Opt. Laser Technol. 107, 169 (2018)
Saker, K., Bouchemat, T., Lahoubi, M., Bouchemat, M., Pu, S.: Magnetic field sensor based on a magnetic-fluid-infiltrated photonic crystal L4 nanocavity and broadband W1 waveguide. J. Comput. Electron. 18, 619 (2019)
Pu, S., Mao, L., Yao, T., Gu, J., Lahoubi, M., Zeng, X.: Microfiber coupling structures for magnetic field sensing with enhanced sensitivity. IEEE Sens. J. 17, 5857 (2017)
Pu, S., Dong, S., Huang, J.: Tunable slow light based on magnetic-fluid-infiltrated photonic crystal waveguides. J. Opt. 16, 045102 (2014)
Choueikani, F., et al.: Magneto-optical waveguides made of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles embedded in silica/zirconia organic-inorganic matrix. Appl. Phys. Lett. 94, 51113 (2009)
Wolfe, R., Lieberman, R.A., Fratello, V.J., Scotti, R.E., Kopylov, N.: Etch-tuned ridged waveguide magneto-optic isolator. Appl. Phys. Lett. 56, 426 (1990)
Dulal, P., et al.: Optimized magneto-optical isolator designs inspired by seedlayer-free terbium iron garnets with opposite chirality. ACS Photonics 3, 1818 (2016)
Alcantara, L.D.S., Teixeira, F.L., Member, S., César, A.C., Borges, B.V.: A new full-vectorial FD-BPM scheme : application to the analysis of magnetooptic and nonlinear saturable media. J. Light. Technol. 23, 2579 (2005)
Choueikani, F., et al.: Low birefringent magneto-optical waveguides fabricated via organic-inorganic sol-gel process. Eur. Phys. J. Appl. Phys. 47, 30401 (2009)
Otmani, H., Bouchemat, M., Bouchemat, T., Lahoubi, M., Wang, W., Pu, S.: Nonreciprocal TE – TM mode conversion based on photonic crystal fiber of air holes filled with magnetic fluid into a terbium gallium garnet fiber. IEEE Trans. Magn. 51, 4004604 (2015)
Mondal, S.K., Stadler, B.J.H.: Novel designs for integrating YIG / air photonic crystal slab polarizers with waveguide Faraday rotators. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 17, 127 (2005)
Otmani, H., Bouchemat, M., Bouchemat, T., Lahoubi, M., Pu, S., Deghdak, R.: Magneto-optical properties of magnetic photonic crystal fiber of terbium gallium garnet filled with magnetic fluid. Photonics Nanostruct. 22, 24 (2016)
Pu, S., Bai, X., Wang, L.: Temperature dependence of photonic crystals based on thermoresponsive magnetic fluids. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 323, 2866 (2011)
Horng, H.E., Hong, C., Yang, S.Y., Yang, H.C.: Designing the refractive indices by using magnetic fluids. Appl. Phys. Lett. 82, 2434 (2003)
Zhao, Y., Wu, D., Lv, R.-Q., Ying, Y.: Tunable characteristics and mechanism analysis of the magnetic fluid refractive index with applied magnetic field. IEEE Trans. Magn. 50, 4600205 (2014)
Hong, C.Y., Yang, S.Y., Horng, H.E., Yang, H.C.: Control parameters for the tunable refractive index of magnetic fluid films. J. Appl. Phys. 94, 3849 (2003)
Chen, Y.F., Yang, S.Y., Tse, W.S., Horng, H.E., Hong, C.Y., Yang, H.C.: Thermal effect on the field-dependent refractive index of the magnetic fluid film. Appl. Phys. Lett. 82, 3481 (2003)
Yusuf, N.A., Abu-Aljarayesh, I., Rousan, A.A., El-Ghanem, H.M.: On the concentration dependence of faraday rotation in magnetic fluids. IEEE Trans. Magn. 26, 2852 (1990)
Zvezdin, A.K., Kotov, V.A.: Modern Magnetooptics and Magnetooptical Materials. IOP Publis, London (1997)
Saker, K., Bouchemat, T., Lahoubi, M., Bouchemat, M., Pu, S.: Design of non-reciprocal device based on magnetic photonic crystal fiber with enhanced birefringence. Microelectronics J. 100, 104786 (2020)
Acknowledgments
A part of this work was presented at the poster section of the Fourth International Conference on Energy, Materials, Applied Energetics and Pollution. ICEMAEP2018, April29-30, 2018, Constantine, Algeria. Authors (K Saker, T Bouchemat, M Lahoubi, M Bouchemat). It was supported in part by the Algerian Ministry of Higher Education and Scientific Research and partly by a joined cooperation project between the Laboratory L.P.S. of the Department of Physics, Badji-Mokhtar Annaba University, Annaba, Algeria and the Photonics Research Laboratory of the College of Science, University of Shanghai for Science and Technology, Shanghai, China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saker, K., Lahoubi, M. & Pu, S. Gyrotropy and magnetic fluid dependences of magneto-optical properties in YIG-magnetic photonic crystal fiber. J Comput Electron 20, 1326–1331 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10825-021-01679-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10825-021-01679-7