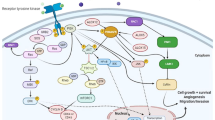
Abstract
Background
Oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) is a malignant oral cavity neoplasm that affects many people, especially in developing countries. Despite several advances that have been made in diagnosis and treatment, the morbidity and mortality rates due to OSCC remain high. Accumulating evidence indicates that aberrant activation of cellular signaling pathways, such as the Notch, Wnt and Hedgehog pathways, occurs during the development and metastasis of OSCC. In this review, we have articulated the roles of the Notch, Wnt and Hedgehog signaling pathways in OSCC and their crosstalk during tumor development and progression. We have also examined possible interactions and associations between these pathways and treatment regimens that could be employed to effectively tackle OSCC and/or prevent its recurrence.
Conclusions
Activation of the Notch signaling pathway upregulates the expression of several genes, including c-Myc, β-catenin, NF-κB and Shh. Associations between the Notch signaling pathway and other pathways have been shown to enhance OSCC tumor aggressiveness. Crosstalk between these pathways supports the maintenance of cancer stem cells (CSCs) and regulates OSCC cell motility. Thus, application of compounds that block these pathways may be a valid strategy to treat OSCC. Such compounds have already been employed in other types of cancer and could be repurposed for OSCC.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Ali, B. Sabiha, H. Ullah, S. Adnan, A. Ali, S.S. Ali, Genetic etiology of oral cancer. Oral Oncol. 70, 23–28 (2017)
J.D. Mcdowell, An overview of epidemiology and common risk factors for oral squamous cell carcinoma. Otolaryngol. Clin. North Am. 39, 277–294 (2006)
J.A. Nemes, L. Deli, Z. Nemes, I.J. Márton, Expression of p16 INK4A, p53, and Rb proteins are independent from the presence of human papillomavirus genes in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 102, 344–352 (2006)
J. Rautava, M. Luukkaa, K. Heikinheimo, J. Alin, R. Grenman, R.-P. Happonen, Squamous cell carcinomas arising from different types of oral epithelia differ in their tumor and patient characteristics and survival. Oral Oncol. 43, 911–919 (2007)
H. Mortazavi, Y. Safi, M. Baharvand, S. Rahmani, Diagnostic features of common oral ulcerative lesions: An updated decision tree. Int. J. Dent. 2016, 7278925 (2016)
A.C. Chi, T.A. Day, B.W. Neville, Oral cavity and oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma -an update. CA Cancer J. Clin. 65, 401–421 (2015)
L. Barnes, J.W. Eveson, P. Reichart, D. Sidransky, (eds) World health organization classification of tumours. pathology and genetics of head and neck tumours. (IARC Press, Lyon, 2005) pp 163–175
M. Umeda, S. Yokoo, Y. Take, A. Omori, K. Nakanishi, K. Shimada, Lymoh node metastasis in squamous cell carcinoma of the oral cavity: correlation between histologic features and the prevalence of metastasis. Head Neck 14, 263–272 (1992)
G.F. Huber, L. Züllig, A. Soltermann, M. Roessle, N. Graf, S.K. Haerle, G. Studer, W. Jochum, H. Moch, S.J. Stoeckli, Down regulation of E-Cadherin (ECAD) - a predictor for occult metastatic disease in sentinel node biopsy of early squamous cell carcinomas of the oral cavity and oropharynx. BMC Cancer 11, 1–8 (2011)
A. Jemal, R. Siegel, E. Ward, Y. Hao, J. Xu, T. Murray, M.J. Thun, C. Statistics, 2008. CA Cancer J. Clin. 58, 71–96 (2008)
J.K. Nagpal, B.R. Das, Oral cancer: reviewing the present understanding of its molecular mechanism and exploring the future directions for its effective management. Oral Oncol. 39, 213–221 (2003)
O. Dreesen, A.H. Brivanlou, Signaling pathways in cancer and embryonic stem cells. Stem Cell Rev. Rep. 3, 7–17 (2007)
J. Lei, J. Ma, Q. Ma, X. Li, H. Liu, Q. Xu, W. Duan, Q. Sun, J. Xu, Z. Wu, E. Wu, Hedgehog signaling regulates hypoxia induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition and invasion in pancreatic cancer cells via a ligand-independent manner. Mol. Cancer 12, 66 (2013)
J. Zhang, Pro-oncogenic and anti-oncogenic pathways: opportunities and challenges of cancer therapy. Future Oncol. 6, 587–603 (2010)
L. Miele, H. Miao, B.J. Nickoloff, NOTCH signaling as a novel cancer therapeutic target. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 6, 313–323 (2006)
M. Schwab (ed.), Encyclopedia of Cancer (Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg, 2017)
S. Artavanis-tsakonas, M.D. Rand, R.J. Lake, Notch signaling: Cell fate control and signal integration in development. JSTOR J. 284, 770–777 (1999)
I. Espinoza, L. Miele, Deadly crosstalk: Notch signaling at the intersection of EMT and cancer stem cells. Cancer Lett. 341, 1–5 (2013)
S. Zanotti, E. Canalis, Notch signaling and the skeleton. Endocrine Rev. 37, 223–253 (2016)
C. Lobry, P. Oh, M.R. Mansour, A.T. Look, I. Aifantis, Notch signaling: switching an oncogene to a tumor suppressor. Blood 123, 2451–2460 (2014)
C.R. Chillakuri, D. Sheppard, S.M. Lea, P.A. Handford, Seminars in cell & developmental biology Notch receptor – ligand binding and activation: Insights from molecular studies. Semin. Cell. Dev. Biol. 23, 421–428 (2012)
I. Rebay, R.J. Fleming, R.G. Fehon, L. Cherbas, P. Cherbas, S. Artavanis-Tsakonas, Specific EGF repeats of Notch mediate interactions with delta and serrate: Implications for Notch as a multifunctional receptor. Cell 67, 687–699 (1991)
M.B. Andrawes, X. Xu, H. Liu, S.B. Ficarro, J.A. Marto, J.C. Aster, S.C. Blacklow, Intrinsic selectivity of Notch 1 for Delta-like 4 over Delta-like 1. J. Biochem. 288, 25477–25489 (2013)
A.L. Parks, J.R. Stout, S.B. Shepard, K.M. Klueg, A.A. Santos, T.R. Dos, Parody, M. Vaskova, M.A.T. Muskavitch, Structure–function analysis of Delta trafficking, receptor binding and signaling in Drosophila. Genetics 174, 1947–1961 (2006)
K. Shimizu, S. Chiba, K. Kumano, N. Hosoya, T. Takahashi, Y. Kanda, Y. Hamada, Y. Yazaki, H. Hirai, Mouse Jagged1 physically interacts with Notch2 and other. J. Biochem. 274, 32961–32969 (1999)
Ma.X.G. Ilagan, R. Kopan, Notch signaling pathway. Cell 128, 1246.e1–1246.e2 (2007)
Y.-Y. Hu, M.-H. Zheng, R. Zhang, Y.-M. Liang, H. Han, Notch signaling pathway and cancer metastasis. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 727, 186–198 (2012)
S.J. Bray, Notch signalling: a simple pathway becomes complex. Nature Rev. 7, 678–689 (2006)
M.E. Fortini, γ-secretase-mediated proteolysis in cell-surface-receptor signalling. Mol. Cell. Biol. 3, 673–684 (2002)
D. Selkoe, R. Kopan, Notch and presenilin: Regulated intramembrane proteolysis links development and degeneration. Ann. Rev. Neurosci. 26, 565–597 (2003)
T. Borggrefe, F. Oswald, The Notch signaling pathway: Transcriptional regulation at Notch target genes. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 66, 1631–1646 (2009)
M. Katoh, M. Katoh, Identification and characterization of human HES2, HES3, and HES5 genes in silico. Int. J. Oncol. 25, 529–534 (2004)
T. Iso, L. Kedes, Y. Hamamori, HES and HERP families: Multiple effectors of the Notch signaling pathway. J. Cell. Physiol. 194, 237–255 (2003)
M. Eiraku, Y. Hirata, H. Takeshima, T. Hirano, M. Kengaku, Delta/Notch-like epidermal growth factor (EGF)-related receptor, a novel EGF-like repeat-containing protein targeted to dendrites of developing and adult central nervous system neurons. J. Biochem. 277, 25400–25407 (2002)
X. Cui, Q. Hu, M. Tekaya, Y. Shimoda, B. Ang, D. Nie, L. Sun, W. Hu, M. Karsak, T. Duka, Y. Takeda, L. Ou, G.S. Dawe, F. Yu, S. Ahmed, L. Jin, M. Schachner, K. Watanabe, Y. Arsenijevic, Z. Xiao, NB-3/Notch1 pathway via Deltex1 promotes neural progenitor cell differentiation into oligodendrocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 25858–25865 (2004)
R. Sanalkumar, S.B. Dhanesh, J. James, Non-canonical activation of Notch signaling/target genes in vertebrates. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 67, 2957–2968 (2010)
C.Y. Logan, R. Nusse, The Wnt signaling pathway in development and disease. Ann. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 20, 781–810 (2004)
Z. Steinhart, S. Angers, Wnt signaling in development and tissue homeostasis. Development 145, 1–8 (2018)
J. Wang, T. Sinha, A. Wynshaw-boris, Wnt signaling in mammalian development: Lessons from mouse genetics. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 4, 1–16 (2012)
S. Tanaka, K. Terada, T. Nohno, Canonical Wnt signaling is involved in switching from cell proliferation to myogenic differentiation of mouse myoblast cells Canonical Wnt signaling is involved in switching from cell proliferation to myogenic differentiation of mouse myoblast cells. J. Mol. Signal. 6, 12 (2011)
Y. Komiya, R. Habas, Wnt signal transduction pathways. Organogenesis 4, 68–75 (2008)
B.T. MacDonald, K. Tamai, X. He, Wnt/B-catenin signaling: components, mechanisms, and diseases. Dev. Cell 17, 9–26 (2009)
C. Niehrs, The complex world of WNT receptor signalling. Nature Rev. 13, 767–779 (2012)
C. Liu, Y. Kato, Z. Zhang, V.M. Do, B.A. Yankner, X. He, β-Trcp couples β-catenin phosphorylation-degradation and regulates Xenopus axis formation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96, 6273–6278 (1999)
H. Aberle, A. Bauer, A. Kispert, R. Kemler, β-catenin is a target for the ubiquitin proteasome pathway. EMBO J. 16, 3797–3804 (1997)
D. Hrckulak, M. Kolar, H. Strnad, V. Korinek, TCF/LEF Transcription factors: An update from the internet resources. Cancers 8, 1–18 (2016)
A. Bahrami, F. Amerizadeh, S. Shahidsales, M. Khazaei, M. Ghayour-mobarhan, H.R. Sadeghnia, M. Maftouh, S.M. Hassanian, A. Avan, Therapeutic potential of targeting Wnt/B-catenin pathway in treatment of colorectal cancer: Rational and progress. J. Cell. Biochem. 118, 1979–1983 (2017)
Q. Wang, Y. Zhou, P. Rychahou, J.W. Harris, Y.Y. Zaytseva, J. Liu, C. Wang, H.L. Weiss, C. Liu, E.Y. Lee, B.M. Evers, Deptor is a novel target of Wnt/β-catenin/c-Myc and contributes to colorectal cancer cell growth. Cancer Res. 78, 3163–3175 (2018)
J.L. Stamos, W.I. Weis, The B-catenin destruction complex. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 5, 1–16 (2013)
L.E. Olson, J. Tollkuhn, C. Scafoglio, A. Krones, J. Zhang, K.A. Ohgi, W. Wu, M.M. Taketo, R. Kemler, R. Grosschedl, D. Rose, X. Li, M.G. Rosenfeld, Homeodomain-mediated B-catenin-dependent switching events dictate cell-lineage determination. Cell 125, 593–605 (2006)
J.R.K. Seifert, M. Mlodzik, Frizzled/PCP signalling: a conserved mechanism regulating cell polarity and directed motility. Nature Rev. Genet. 8, 126–138 (2007)
C.R. Vinson, P.N. Adler, Directional non-cell autonomy and the transmission of polarity information by the frizzled gene of Drosophila. Nature 329, 549–551 (1987)
M. Mlodzik, Planar cell polarization: do the same mechanisms regulate Drosophila tissue polarity and vertebrate gastrulation ? Trends Genet. 18, 564–571 (2002)
Y. Wang, J. Nathans, Tissue/planar cell polarity in vertebrates: new insights and new questions. Development 134, 647–658 (2007)
A.M. Daulat, J. Borg, Wnt/planar cell polarity signaling: New opportunities for cancer treatment. Trends Cancer 3, 113–125 (2017)
I. Oishi, H. Suzuki, N. Onishi, R. Takada, S. Kani, H. Shibuya, S. Takada, Y. Minami, The receptor tyrosine kinase Ror2 is involved in non-canonical Wnt5a/JNK signalling pathway. Genes Cells 8, 645–654 (2003)
N. Sasai, Y. Nakazawa, T. Haraguchi, Y. Sasai, The neurotrophin-receptor-related protein NRH1 is essential for convergent extension movements. Nat. Cell Biol. 6, 741–748 (2004)
M. Nishita, S.K. Yoo, A. Kikuchi, N. Sougawa, Y. Ohta, S. Takada, A. Kikuchi, Y. Minami, Filopodia formation mediated by receptor tyrosine kinase Ror2 is required for Wnt5a-induced cell migration. J. Cell Biol. 175, 555–562 (2006)
W. Lu, V. Yamamoto, B. Ortega, D. Baltimore, Mammalian Ryk is a Wnt coreceptor required for stimulation of neurite outgrowth. Cell 119, 97–108 (2004)
J.B. Wallingford, R. Habas, The developmental biology of Dishevelled: an enigmatic protein governing cell fate and cell polarity. Development 132, 4421–4436 (2005)
M. Sebbagh, J. Borg, Insight into planar cell polarity. Exp. Cell Res. 328, 284–295 (2014)
A.D. Kohn, R.T. Moon, Wnt and calcium signaling: B-Catenin-independent pathways. Cell Calcium 38, 439–446 (2005)
D.C. Slusarski, Calcium signaling in vertebrate embryonic patterning and morphogenesis. Dev. Biol. 307, 1–13 (2007)
A. Mcquate, E. Latorre-esteves, A. Barria, A Wnt/calcium signaling cascade regulates neuronal excitability and trafficking of NMDARs. Cell Rep. 21, 60–69 (2017)
D.C. Slusarski, V.G. Corces, R.T. Moon, Interaction of Wnt and a Frizzled homologue triggers phosphatidylinositol signalling. Nature 390, 410–413 (1997)
S.K. Dissanayake, A.T. Weeraratna, Detecting PKC phosphorylation as part of the Wnt/calcium pathway in cutaneous melanoma. Methods Mol. Biol. 468, 1–16 (2008)
L.C. Sheldahl, D.C. Slusarski, P. Pandur, J.R. Miller, M. Kühl, R.T. Moon, Dishevelled activates Ca2 + flux, PKC, and CamKII in vertebrate embryos. J. Cell Biol. 161, 769–777 (2003)
A.E. Bale, Hedgehog signaling and human disease. Ann. Rev. Gen. Hum. Genet. 3, 47–65 (2002)
J.A. Porter, K.E. Young, P.A. Beachy, Cholesterol modification of Hedgehog signaling proteins in animal development. Science 274, 255–258 (1996)
R.B. Pepinsky, C. Zeng, D. Wen, P. Rayhorn, D.P. Baker, K.P. Williams, S.A. Bixler, C.M. Ambrose, E.A. Garber, K. Miatkowski, F.R. Taylor, E.A. Wang, A. Galdes, Identification of a palmitic acid-modified form of human Sonic hedgehog. J. Biochem. 273, 14037–14045 (1998)
M. Varjosalo, J. Taipale, Hedgehog signaling. J. Cell Sci. 120, 3–6 (2007)
E. Mart, P. Bovolenta, Sonic hedgehog in CNS development: one signal, multiple outputs. Trends Neurosci. 25, 89–96 (2002)
A. Abeliovich, R. Hammond, Midbrain dopamine neuron differentiation: Factors and fates. Dev. Biol. 304, 447–454 (2007)
W.A.O. Hara, W.J. Azar, R.R. Behringer, M.B. Renfree, A.J. Pask, Desert hedgehog is a mammal-specific gene expressed during testicular and ovarian development in a marsupial. BMC Dev. Biol. 11, 1–12 (2011)
L.P. Lai, J. Mitchell, I. Hedgehog, Its roles and regulation in endochondral bone development. J. Cell. Biochem. 96, 1163–1173 (2005)
B. St-jacques, M. Hammerschmidt, A.P. Mcmahon, Indian hedgehog signaling regulates proliferation and differentiation of chondrocytes and is essential for bone formation. Genes Dev. 13, 2072–2086 (1999)
F. Long, U. Chung, S. Ohba, J. Mcmahon, H.M. Kronenberg, Ihh signaling is directly required for the osteoblast lineage in the endochondral skeleton. Development 131, 1309–1318 (2004)
A. Ruiz-gómez, C. Molnar, H. Holguín, F. Mayor, J.F. Celis, De, The cell biology of Smo signalling and its relationships with GPCRs. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1768, 901–912 (2007)
M.A. Stegman, J.A. Goetz, M. Ascano, S.K. Ogden, K.E. Nybakken, D.J. Robbins, The kinesin-related protein Costal2 associates with membranes in a Hedgehog-sensitive, Smoothened-independent manner. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 7064–7071 (2004)
R.A. Aikin, K.L. Ayers, P.P. Thérond, The role of kinases in the Hedgehog signalling pathway. EMBO Rep. 9, 330–336 (2008)
E.G. Huntzicker, I.S. Estay, H. Zhen, L.A. Lokteva, P.K. Jackson, A.E. Oro, Dual degradation signals control Gli protein stability and tumor formation. Genes Dev. 20, 276–281 (2006)
J. Jiang, Regulation of Hh/Gli signaling by dual ubiquitin pathways. Cell Cycle 5, 2457–2463 (2006)
M.F.S.D. Rodrigues, L. Miguita, N.P.D.E. Andrade, D. Heguedusch, C.O. Rodini, R.A. Moyses, T.N. Toporcov, R.R. Gama, E.E. Tajara, F.D. Nunes, GLI3 knockdown decreases stemness, cell proliferation and invasion in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Int. J. Oncol. 53, 2458–2472 (2018)
D. Jenkins, Hedgehog signalling: Emerging evidence for non-canonical pathways. Cell. Signal 21, 1023–1034 (2009)
G.B. Carballo, J.R. Honorato, G. Pinto, F. Lopes, T. De, Cristina, L. Sampaio, De, A highlight on Sonic hedgehog pathway. Cell Comm. Signal. 16, 1–15 (2018)
K.C. Corbit, P. Aanstad, V. Singla, A.R. Norman, D.Y.R. Stainier, J.F. Reiter, Vertebrate Smoothened functions at the primary cilium. Nature 437, 1018–1021 (2005)
A.M. Skoda, D. Simovic, V. Karin, V. Kardum, S. Vranic, L. Serman, The role of the Hedgehog signaling pathway in cancer: A comprehensive review. Bosnian J. Basic Med. Sci. 18, 8–20 (2018)
S. Pietrobono, S. Gagliardi, B. Stecca, Non-canonical Hedgehog signaling pathway in cancer: Activation of GLI transcription factors beyond Smoothened. Front. Genet. 10, 1–20 (2019)
H. Hijioka, T. Setoguchi, A. Miyawaki, H. Gao, T. Ishida, S. Komiya, N. Nakamura, Upregulation of Notch pathway molecules in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Int. J. Oncol. 36, 817–822 (2010)
T. Ishida, H. Hijioka, K. Kume, A. Miyawaki, N. Nakamura, Notch signaling induces EMT in OSCC cell lines in a hypoxic environment. Oncol. Lett. 5, 1201–1206 (2013)
T. Osathanon, N. Nowwarote, P. Pavasant, Expression and influence of Notch signaling in oral squamous cell carcinoma. J. Oral Sci. 58, 283–294 (2016)
X. Ding, Y. Zheng, Z. Wang, W. Zhang, Y. Dong, W. Chen, J. Li, W. Chu, W. Zhang, Y. Zhong, L. Mao, X. Song, Y. Wu, Expression and oncogenic properties of membranous Notch1 in oral leukoplakia and oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol. Rep. 39, 2584–2594 (2018)
J.P. Joseph, M.K. Harishankar, A.A. Pillai, A. Devi, Hypoxia induced EMT: A review on the mechanism of tumor progression and metastasis in OSCC. Oral Oncol. 80, 23–32 (2018)
R. Yoshida, M. Nagata, H. Nakayama, K. Niimori-kita, W. Hassan, T. Tanaka, M. Shinohara, T. Ito, The pathological significance of Notch1 in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Lab. Invest. 93, 1068–1081 (2013)
X. Song, R. Xia, J. Li, Z. Long, H. Ren, W. Chen, L. Mao, Common and complex Notch1 mutations in Chinese oral squamous cell carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 20, 701–711 (2014)
E. Izumchenko, K. Sun, S. Jones, M. Brait, N. Agrawal, W. Koch, C.L. Mccord, D.R. Riley, S.V. Angiuoli, V.E. Velculescu, W. Jiang, D. Sidransky, Notch1 mutations are drivers of oral tumorigenesis. Cancer Prev. Res. 8, 277–287 (2015)
C.R. Pickering, J. Zhang, S.Y. Yoo, L. Bengtsson, E. Cortez, T. Xie, D. Zhang, W. Chung, P.A. Zweidler-mckay, X. Wu, A.K. El-naggar, J.N. Weinstein, M.J. Frederick, Integrative genomic characterization of oral squamous cell carcinoma identifies frequent somatic drivers. Cancer Discov. 3, 1–21 (2013)
S.H. Lee, H.S. Hong, Z.X. Liu, R.H. Kim, M.K. Kang, N.-H. Park, K.-H. Shin, TNFa enhances cancer stem cell-like phenotype via Notch-Hes1 activation in oral squamous cell carcinoma cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm. 424, 58–64 (2012)
K. Kayamori, K.-I. Katsube, K. Sakamoto, Y. Ohyama, H. Hirai, A. Yukimori, Y. Ohata, T. Akashi, M. Saitoh, K. Harada, H. Harada, A. Yamaguchi, NOTCH3 is Iiduced in cancer-associated fibroblasts and promotes angiogenesis in oral squamous cell carcinoma. PLoS One 11, e0154112 (2016)
H. Mk, S. Prince, A.M. Mohan, K.V. Krishnan, A. Devi, Association of Notch4 with metastasis in human oral squamous cell carcinoma. Life Sci. 156, 38–46 (2016)
B. Li, M. Chen, M. Lu, J. Xin-Xiang, P. Meng-Xiong, M. Jun-Wu, Glutaredoxin 3 promotes migration and invasion via the Notch signalling pathway in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Free Radic. Res. 52, 390–401 (2018)
J. Zhang, G. Zheng, L. Zhou, P. Li, M. Yun, Q. Shi, T. Wang, X. Wu, Notch signalling induces epithelial–mesenchymal transition to promote metastasis in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Med. 42, 2276–2284 (2018)
W. Shi, F. Li, S. Li, J. Wang, Q. Wang, X. Yan, Q. Zhang, L. Chai, M. Li, Increased DCLK1 correlates with the malignant status and poor outcome in malignant tumors: a meta-analysis. Oncotarget 8, 100545–100557 (2017)
E.C. Broner, T. Subbannayya, A. Zhavoronkov, M. Korzinkin, A. Artemov, I. Ozerov, I. Sloma, D. Sidransky, A. Chatterjee, E. Izumchenko, Abstract 3443: Doublecortin-like kinase 1 (DCLK1) is novel Notch pathway signaling regulator in HNSCC. Cancer Res. 79, 3443–3443 (2019)
T. Zhan, N. Rindtorff, M. Boutros, Wnt signaling in cancer. Oncogene 36, 1461–1473 (2017)
S. Iwai, A. Yonekawa, C. Harada, M. Hamada, W. Katagiri, M. Nakazawa, Y. Yura, Involvement of the Wnt-β-catenin pathway in invasion and migration of oral squamous carcinoma cells. Int. J. Oncol. 37, 1095–1103 (2010)
J. Nwanze, C. Cohen, A.C. Schmitt, M.T. Siddiqui, β-Catenin expression in oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinomas: Comparison and correlation with p16 and human papillomavirus in situ hybridization. Acta Cytol. 59, 479–484 (2016)
F. Mahomed, M. Altini, S. Meer, Altered E-cadherin/B-catenin expression in oral squamous carcinoma with and without nodal metastasis. Oral Dis. 13, 386–392 (2007)
M. Uraguchi, M. Morikawa, M. Shirakawa, K. Sanada, K. Imai, Activation of WNT family expression and signaling in squamous cell carcinomas. J. Dent. Res. 83, 327–332 (2004)
S. Iwai, ÆW. Katagiri, ÆC. Kong, Mutations of the APC, beta-catenin, and axin1 genes and cytoplasmic accumulation of beta-catenin in oral squamous cell carcinoma. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 131, 773–782 (2005)
Z. Cui, Y. Cui, S. Yang, G. Luo, Y. Wang, Y. Lou, X. Sun, KLK4 silencing inhibits the growth of oral squamous cell carcinoma through Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway: KLK4 silencing inhibits OSCC cell growth. Cell Biol. Int. 41, 392–404 (2017)
Y. Bai, J. Sha, T. Kanno, The role of carcinogenesis-related biomarkers in the Wnt pathway and their effects on epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT) in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Cancers 12, 55 (2020)
J. Paluszczak, The significance of the dysregulation of canonical Wnt signaling in head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. Cells 9, 723 (2020)
J.K. Strzelczyk, Ł Krakowczyk, A.J. Owczarek, Methylation status of SFRP1, SFRP2, RASSF1A, RARβ and DAPK1 genes in patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma. Arch. Oral Biol. 98, 265–272 (2019)
S. Liang, S. Zhang, P. Wang, C. Yang, C. Shang, J. Yang, J. Wang, LncRNA, TUG1 regulates the oral squamous cell carcinoma progression possibly via interacting with Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Gene 608, 49–57 (2017)
C. Li, W. Jiang, Y. Zhou, X. Huang, N. Zhou, PF4V1 affects the progression of oral squamous cell carcinoma by regulating Wnt/β-catenin pathway and angiogenesis. Appl. Biol. Chem. 63, 18 (2020)
A. Almangush, A.A. Mäkitie, A. Triantafyllou, R. de Bree, P. Strojan, A. Rinaldo, J.C. Hernandez-Prera, C. Suárez, L.P. Kowalski, A. Ferlito, I. Leivo, Staging and grading of oral squamous cell carcinoma: An update. Oral Oncol. 107, 104799 (2020)
B.-W. Dai, Z.-M. Yang, P. Deng, Y.-R. Chen, Z.-J. He, X. Yang, S. Zhang, H.-J. Wu, Z.-H. Ren, HOXC10 promotes migration and invasion via the WNT-EMT signaling pathway in oral squamous cell carcinoma. J. Cancer 10, 4540–4551 (2019)
A. Ebrahimi, R. Murali, K. Gao, M.S. Elliott, J.R. Clark, The prognostic and staging implications of bone invasion in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer 117, 4460–4467 (2011)
J. Park, X. Zhang, S.K. Lee, N.-Y. Song, S.H. Son, K.R. Kim, J.H. Shim, K.-K. Park, W.-Y. Chung, CCL28-induced RARβ expression inhibits oral squamous cell carcinoma bone invasion. J. Clin. Invest. 129, 5381–5399 (2019)
S. Srinath, A.R. Iyengar, V. Mysorekar, Sonic hedgehog in oral squamous cell carcinoma: An immunohistochemical study. J. Oral Maxillofac. Pathol. 20, 377–383 (2016)
M.E.C. Buim, C.A.S. Gurgel, E.A.G. Ramos, S.V. Lourenco, F.A. Soares, Activation of sonic hedgehog signaling in oral squamous cell carcinomas: a preliminary study. Hum. Pathol. 42, 1484–1490 (2011)
Y.-F. Wang, C.-J. Chang, C.-P. Lin, S.-Y. Chang, P.-Y. Chu, S.-K. Tai, W.-Y. Li, K.S.C. Chao, Y.-J. Chen, Expression of hedgehog signaling molecules as a prognostic indicator of oral squamous cell carcinoma. Head Neck 34, 1556–1561 (2012)
M. Yan, L. Wang, H. Zuo, Z. Zhang, W. Chen, L. Mao, P. Zhang, HH/GLI signalling as a new therapeutic target for patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Oncol. 47, 504–509 (2011)
H. Kuroda, N. Kurio, T. Shimo, K. Matsumoto, M. Masui, K. Takabatake, T. Okui, S. Ibaragi, Y. Kunisada, K. Obata, N. Yoshioka, K. Kishimoto, H. Nagatsuka, A. Sasaki, Oral squamous cell carcinoma-derived sonic hedgehog promotes angiogenesis. Anticancer Res. 37, 6731–6737 (2017)
H.X. Fan, S. Wang, H. Zhao, N. Liu, D. Chen, M. Sun, J.H. Zheng, Sonic hedgehog signaling may promote invasion and metastasis of oral squamous cell carcinoma by activating MMP-9 and E-cadherin expression. Med. Oncol. 31, 1–8 (2014)
M.F.S.D. Rodrigues, L. Miguita, N.P. De Andrade, D. Heguedusch, C.O. Rodini, R.A. Moyses, T.N. Toporcov, R.R. Gama, E.E. Tajara, F.D. Nunes, GLI3 knockdown decreases stemness, cell proliferation and invasion in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Int. J. Oncol. 53, 2458–2472 (2018)
T. Honami, T. Shimo, T. Okui, N. Kurio, N. Mohammad, M. Hassan, M. Iwamoto, A. Sasaki, Sonic hedgehog signaling promotes growth of oral squamous cell carcinoma cells associated with bone destruction. Oral Oncol. 48, 49–55 (2012)
K. Takabatake, T. Shimo, J. Murakami, C. Anqi, H. Kawai, S. Yoshida, M. Wathone Oo, O. Haruka, S. Sukegawa, H. Tsujigiwa, K. Nakano, H. Nagatsuka, The role of sonic hedgehog signaling in the tumor microenvironment of oral squamous cell carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 20, 5779 (2019)
W. Yan, Y. Deng, Y. Zhang, J. Luo, D. Lu, Q. Wan, L. Mao, Y. chen, DZIP1 promotes proliferation, migration, and invasion of oral squamous carcinoma through the GLI1/3 pathway. Transl. Oncol. 12, 1504–1515 (2019)
Q. Song, B. Wang, M. Liu, Z. Ren, Y. Fu, P. Zhang, M. Yang, MTA1 promotes the invasion and migration of oral squamous carcinoma by inducing epithelial-mesenchymal transition via the hedgehog signaling pathway. Exp. Cell Res. 382, 111450 (2019)
A. Dumortier, A.-D. Durham, M. Di Piazza, S. Vauclair, U. Koch, G. Ferrand, I. Ferrero, S. Demehri, L.L. Song, A.G. Farr, W.J. Leonard, R. Kopan, L. Miele, D. Hohl, D. Finke, F. Radtke, Atopic dermatitis-like disease and associated lethal myeloproliferative disorder arise from loss of Notch signaling in the murine skin. PLoS One 5, e9258 (2010)
P. Rizzo, C. Osipo, K. Foreman, T. Golde, B. Osborne, L. Miele, Rational targeting of Notch signaling in cancer. Oncogene 27, 5124–5131 (2008)
B. Cohen, M. Shimizu, J. Izrailit, N.F.L. Ng, Y. Buchman, J.G. Pan, J. Dering, M. Reedijk, Cyclin D1 is a direct target of JAG1-mediated Notch signaling in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 123, 113–124 (2010)
I. Joshi, L.M. Minter, J. Telfer, R.M. Demarest, A.J. Capobianco, J.C. Aster, P. Sicinski, A. Fauq, T.E. Golde, B.A. Osborne, Notch signaling mediates G1/S cell-cycle progression in T cells via cyclin D3 and its dependent kinases. Blood 113, 1689–1698 (2009)
L.M. Sarmento, H. Huang, A. Limon, W. Gordon, J. Fernandes, M.J. Tavares, L. Miele, A.A. Cardoso, M. Classon, N. Carlesso, Notch1 modulates timing of G1-S progression by inducing SKP2 transcription and p27 Kip1 degradation. J. Exp. Med. 202, 157–168 (2005)
R. Qi, H. An, Y. Yu, M. Zhang, S. Liu, H. Xu, Z. Guo, T. Cheng, X. Cao, Notch1 signaling inhibits growth of human hepatocellular carcinoma through induction of cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. Cancer Res. 63, 8323–8329 (2003)
K.-W. Hsu, R.-H. Hsieh, Y.-H.W. Lee, C.-H. Chao, K.-J. Wu, M.-J. Tseng, T.-S. Yeh, The activated Notch1 receptor cooperates with alpha-enolase and MBP-1 in modulating c-myc activity. Mol. Cell. Biol. 28, 4829–4842 (2008)
T.D. Allen, E.M. Rodriguez, K.D. Jones, J.M. Bishop, Activated Notch1 induces lung adenomas in mice and cooperates with Myc in the generation of lung adenocarcinoma. Cancer Res. 71, 6010–6018 (2011)
X. Guo, X.-F. Wang, Signaling cross-talk between TGF-β/BMP and other pathways. Cell Res. 19, 71–88 (2009)
X. Zeng, D. Ju, Hedgehog signaling pathway and autophagy in cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 19, 2279 (2018)
J.A. McCubrey, D. Rakus, A. Gizak, L.S. Steelman, S.L. Abrams, K. Lertpiriyapong, T.L. Fitzgerald, L.V. Yang, G. Montalto, M. Cervello, M. Libra, F. Nicoletti, A. Scalisi, F. Torino, C. Fenga, L.M. Neri, S. Marmiroli, L. Cocco, A.M. Martelli, Effects of mutations in Wnt/β-catenin, hedgehog, Notch and PI3K pathways on GSK-3 activity—Diverse effects on cell growth, metabolism and cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta - Mol. Cell Res. 1863, 2942–2976 (2016)
M. Pelullo, S. Zema, F. Nardozza, S. Checquolo, I. Screpanti, D. Bellavia, Wnt, Notch, and TGF-β pathways impinge on Hedgehog signaling complexity: An open window on cancer. Front. Genet. 10, 711 (2019)
C. Lobry, P. Oh, I. Aifantis, Oncogenic and tumor suppressor functions of Notch in cancer: it’s NOTCH what you think. J. Exp. Med. 208, 1931–1935 (2011)
A.Q. Khan, E.I. Ahmed, N.R. Elareer, K. Junejo, M. Steinhoff, S. Uddin, Role of miRNA-regulated cancer stem cells in the pathogenesis of human malignancies. Cells 8, 840 (2019)
S. Chatterjee, P.C. Sil, Targeting the crosstalks of Wnt pathway with Hedgehog and Notch for cancer therapy. Pharmacol. Res. 142, 251–261 (2019)
P. Hayward, T. Kalmar, A.M. Arias, Wnt/Notch signalling and information processing during development. Development 135, 411–424 (2008)
S.K. Kay, H.A. Harrington, S. Shepherd, K. Brennan, T. Dale, J.M. Osborne, D.J. Gavaghan, H.M. Byrne, The role of the Hes1 crosstalk hub in Notch-Wnt interactions of the intestinal crypt. PLoS Comp. Biol. 13, e1005400 (2017)
L. Ma, Y. Wang, Y. Hui, Y. Du, Z. Chen, H. Feng, S. Zhang, N. Li, J. Song, Y. Fang, X. Xu, L. Shi, B. Zhang, J. Cheng, S. Zhou, L. Liu, X. Zhang, WNT/NOTCH pathway is essential for the maintenance and expansion of human MGE progenitors. Stem Cell Rep. 12, 934–949 (2019)
V. Rodilla, A. Villanueva, A. Obrador-Hevia, A. Robert-Moreno, V. Fernández-Majada, A. Grilli, N. López-Bigas, N. Bellora, M.M. Albà, F. Torres, M. Duñach, X. Sanjuan, S. Gonzalez, T. Gridley, G. Capella, A. Bigas, L. Espinosa, Jagged1 is the pathological link between Wnt and Notch pathways in colorectal cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 106, 6315–6320 (2009)
C. Gekas, T. D’Altri, R. Aligué, J. González, L. Espinosa, A. Bigas, β-Catenin is required for T-cell leukemia initiation and MYC transcription downstream of Notch1. Leukemia 30, 2002–2010 (2016)
Y.-F. Xiao, X. Yong, B. Tang, Y. Qin, J.-W. Zhang, D. Zhang, R. Xie, S.-M. Yang, Notch and Wnt signaling pathway in cancer: Crucial role and potential therapeutic targets (Review). Int. J. Oncol. 48, 437–449 (2016)
S. Yokogi, T. Tsubota, K. Kanki, J. Azumi, N. Itaba, H. Oka, M. Morimoto, K. Ryoke, G. Shiota, Wnt/beta-catenin signal inhibitor HC-1 sensitizes oral squamous cell carcinoma cells to 5-fluorouracil through reduction of CD44-positive population. Yonago Acta Med. 59, 93–99 (2016)
J. Camps, J.J. Pitt, G. Emons, A.B. Hummon, C.M. Case, M. Grade, T.L. Jones, Q.T. Nguyen, B.M. Ghadimi, T. Beissbarth, M.J. Difilippantonio, N.J. Caplen, T. Ried, Genetic amplification of the NOTCH modulator LNX2 upregulates the WNT/β-catenin pathway in colorectal cancer. Cancer Res. 73, 2003–2013 (2013)
M. Moghbeli, M.R. Abbaszadegan, E. Golmakani, M.M. Forghanifard, Correlation of Wnt and NOTCH pathways in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J. Cell. Comm. Signal. 10, 129–135 (2016)
C. Porcheri, C.T. Meisel, T. Mitsiadis, Multifactorial contribution of Notch signaling in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 20, 1520 (2019)
J.H. Es, M.E. Van, Gijn, O. Van, Riccio, M. Born, M. Van Den, Vooijs, H. Begthel, M. Cozijnsen, S. Robine, D.J. Winton, F. Radtke, H. Clevers, Notch/gamma-secretase inhibition turns proliferative cells in intestinal crypts and adenomas into goblet cells. Nature 435, 959–963 (2005)
M.R. Abbaszadegan, A. Riahi, M.M. Forghanifard, M. Moghbeli, WNT and NOTCH signaling pathways as activators for epidermal growth factor receptor in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 23, 42 (2018)
A. Gulino, L. Di Marcotullio, I. Screpanti, The multiple functions of Numb. Exp. Cell Res. 316, 900–906 (2010)
S. Pece, S. Confalonieri, R. Romano, P.P. Di Fiore, NUMB-ing down cancer by more than just a NOTCH. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1815, 26–43 (2011)
L. Di Marcotullio, E. Ferretti, A. Greco, E. De Smaele, A. Po, M.A. Sico, M. Alimandi, G. Giannini, M. Maroder, I. Screpanti, A. Gulino, Numb is a suppressor of Hedgehog signalling and targets Gli1 for Itch-dependent ubiquitination. Nat. Cell Biol. 8, 1415–1423 (2006)
H. Kim, Z.A. Ronai, Rewired Notch/p53 by Numb’ing Mdm2. J. Cell Biol. 217, 445–446 (2018)
M.A. McGill, C.J. McGlade, Mammalian numb proteins promote Notch1 receptor ubiquitination and degradation of the Notch1 intracellular domain. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 23196–23203 (2003)
N. Takebe, L. Miele, P.J. Harris, W. Jeong, H. Bando, M. Kahn, S.X. Yang, S.P. Ivy, Targeting Notch, Hedgehog, and Wnt pathways in cancer stem cells: clinical update. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 12, 445–464 (2015)
J. Koury, L. Zhong, J. Hao, Targeting signaling pathways in cancer stem cells for cancer treatment. Stem Cells Int. 2017, 2925869 (2017)
M.A. Burns, Z.W. Liao, N. Yamagata, G.P. Pouliot, K.E. Stevenson, D.S. Neuberg, A.R. Thorner, M. Ducar, E.A. Silverman, S.P. Hunger, M.L. Loh, S.S. Winter, K.P. Dunsmore, B. Wood, M. Devidas, M.H. Harris, L.B. Silverman, S.E. Sallan, A. Gutierrez, Hedgehog pathway mutations drive oncogenic transformation in high-risk T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia 32, 2126–2137 (2018)
A.S.W. Oak, G. Bocheva, T.-K. Kim, A.A. Brożyna, Z. Janjetovic, M. Athar, R.C. Tuckey, A.T. Slominski, Noncalcemic vitamin D hydroxyderivatives inhibit human oral squamous cell carcinoma and down-regulate Hedgehog and WNT/β-catenin pathways. Anticancer Res. 40, 2467–2474 (2020)
A. Bakshi, S.C. Chaudhary, M. Rana, C.A. Elmets, M. Athar, Basal cell carcinoma pathogenesis and therapy involving hedgehog signaling and beyond. Mol. Carcinog. 56, 2543–2557 (2017)
M. Nicolas, A. Wolfer, K. Raj, J. Kummer, P. Mill, M. Noort, C. Hui, H. Clevers, G.P. Dotto, F. Radtke, Notch1 functions as a tumor suppressor in mouse skin. Nature Genet. 33, 416–421 (2003)
Z. Wang, Y. Li, S. Banerjee, F.H. Sarkar, Exploitation of the Notch signaling pathway as a novel target for cancer therapy. Anticancer Res. 28, 3621–3630 (2008)
J. Domingo-Domenech, S.J. Vidal, V. Rodriguez-Bravo, M. Castillo-Martin, S.A. Quinn, R. Rodriguez-Barrueco, D.M. Bonal, E. Charytonowicz, N. Gladoun, J. de la Iglesia-Vicente, D.P. Petrylak, M.C. Benson, J.M. Silva, C. Cordon-Cardo, Suppression of acquired docetaxel resistance in prostate cancer through depletion of Notch-and Hedgehog-dependent tumor-initiating cells. Cancer Cell 22, 373–388 (2012)
M.P. Yavropoulou, A. Maladaki, J.G. Yovos, The role of Notch and Hedgehog signaling pathways in pituitary development and pathogenesis of pituitary adenomas. Hormones (Athens) 14, 5–18 (2015)
M.P. Steinbuck, S. Winandy, A review of Notch processing with new insights into ligand-independent Notch signaling in T-cells. Front Immunol 9, 1230 (2018)
W.J. Ingram, K.I. McCue, T.H. Tran, A.R. Hallahan, B.J. Wainwright, Sonic Hedgehog regulates Hes1 through a novel mechanism that is independent of canonical Notch pathway signalling. Oncogene 27, 1489–1500 (2008)
D.S. Wall, A.J. Mears, B. McNeill, C. Mazerolle, S. Thurig, Y. Wang, R. Kageyama, V.A. Wallace, Progenitor cell proliferation in the retina is dependent on Notch-independent Sonic hedgehog/Hes1 activity. J. Cell Biol. 184, 101–112 (2009)
C.L. Curry, L.L. Reed, B.J. Nickoloff, L. Miele, K.E. Foreman, Notch-independent regulation of Hes-1 expression by c-Jun N-terminal kinase signaling in human endothelial cells. Lab. Invest. 86, 842–852 (2006)
J.W. Kim, M.J. Kim, K.J. Kim, H.J. Yun, J.S. Chae, S.G. Hwang, T.-S. Chang, H.-S. Park, K.-W. Lee, P.-L. Han, S.-G. Cho, T.-W. Kim, E.-J. Choi, Notch interferes with the scaffold function of JNK-interacting protein 1 to inhibit the JNK signaling pathway. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 102, 14308–14313 (2005)
M.-T. Stockhausen, J. Sjölund, H. Axelson, Regulation of the Notch target gene Hes-1 by TGFalpha induced Ras/MAPK signaling in human neuroblastoma cells. Exp. Cell Res. 310, 218–228 (2005)
X.-Y. Huang, R.-H. Gan, J. Xie, L. She, Y. Zhao, L.-C. Ding, B.-H. Su, D.-L. Zheng, Y.-G. Lu, The oncogenic effects of HES1 on salivary adenoid cystic carcinoma cell growth and metastasis. BMC Cancer 18, 436 (2018)
J.H. Kong, L. Yang, E. Dessaud, K. Chuang, D.M. Moore, R. Rohatgi, J. Briscoe, B.G. Novitch, Notch activity modulates the responsiveness of neural progenitors to sonic hedgehog signaling. Dev. Cell 33, 373–387 (2015)
E. Ezratty, N. Stokes, S. Chai, A. Shah, S. Williams, E. Fuchs, A role for the primary cilium in Notch signaling and epidermal differentiation during skin development. Cell 145, 1129–1141 (2011)
M. Stasiulewicz, S.D. Gray, I. Mastromina, J.C. Silva, M. Björklund, P.A. Seymour, D. Booth, C. Thompson, R.J. Green, E.A. Hall, P. Serup, J.K. Dale, A conserved role for Notch signaling in priming the cellular response to Shh through ciliary localisation of the key Shh transducer Smo. Development 142, 2291–2303 (2015)
N. Oikawa, J. Walter, Presenilins and γ-secretase in membrane proteostasis. Cells 8, 209 (2019)
K. Dimitrova, M. Stoehr, F. Dehghani, A. Dietz, G. Wichmann, J. Bertolini, C. Mozet, Overexpression of the Hedgehog signalling pathway in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Onkologie 36, 279–286 (2013)
T. Ishida, H. Hijioka, K. Kume, A. Miyawaki, N. Nakamura, Notch signaling induces EMT in OSCC cell lines in a hypoxic environment. Oncol. Lett. 6, 1201–1206 (2013)
M. Yan, L. Wang, H. Zuo, Z. Zhang, W. Chen, L. Mao, P. Zhang, HH / GLI signalling as a new therapeutic target for patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Oncol. 47, 504–509 (2011)
J. Qu, Y. Wang, Y. Yang, J. Liu, Targeting Notch-1 reverses cisplatin chemosensitivity in ovarian cancer cells by upregulation of PUMA. Int. J. Exp. Med. 10, 7785–7795 (2017)
L. Li, H.-C. Liu, C. Wang, X. Liu, F.-C. Hu, N. Xie, L. Lü, X. Chen, H.-Z. Huang, Overexpression of β-catenin induces cisplatin resistance in oral squamous cell carcinoma. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 1–11 (2016)
J. Tian, X. Cui, Y. Feng, L. Gu, Inhibition of WNT7A-β-catenin signaling pathway sensitizes oral squamous cell carcinoma to cisplatin. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 11, 4926–4933 (2018)
F. Huang, C. Xin, K. Lei, H. Bai, J. Li, Q. Chen, Noncoding RNAs in oral premalignant disorders and oral squamous cell carcinoma. Cell. Oncol. 43, 763–777 (2020)
J. Manokawinchoke, T. Osathanon, P. Pavasant, Regulation of osteoprotegerin expression by Notch signaling in human oral squamous cell carcinoma cell line. Asian Pacific J. Tropical Biomed. 6, 692–697 (2016)
H. Inoue, Y. Ohnishi, Y. Shoju, M. Nakajima, K. Kakudo, Effects of a gamma secretase inhibitor on the proliferation and invasiveness of oral squamous cell carcinoma cell lines. Asian J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 23, 1–6 (2011)
Z.-L. Zhao, L. Zhang, C.-F. Huang, S.-R. Ma, L.-L. Bu, J.-F. Liu, G.-T. Yu, B. Liu, J.S. Gutkind, A.B. Kulkarni, W.-F. Zhang, Z.-J. Sun, NOTCH1 inhibition enhances the efficacy of conventional chemotherapeutic agents by targeting head neck cancer stem cell. Sci. Rep. 6, 24704 (2016)
J.-P. Ou, H.-Y. Lin, K.-Y. Su, S.-L. Yu, I.-H. Tseng, C.-J. Chen, H.-C. Hsu, D.-C. Chan, S. Chen, Y.-L., Potential therapeutic role of Z-isochaihulactone in lung cancer through induction of apoptosis via Notch signaling. Evid. Based Compl. Alternat. Med. 2012, 809204 (2012)
J. Yao, L. Duan, M. Fan, X. Wu, γ-secretase inhibitors exerts antitumor activity via down-regulation of Notch and Nuclear factor kappa B in human tongue carcinoma cells. Oral Dis. 13, 555–563 (2007)
A. Greife, S. Jankowiak, J. Steinbring, P. Nikpour, G. Niegisch, M.J. Hoffmann, W.A. Schulz, Canonical Notch signalling is inactive in urothelial carcinoma. BMC Cancer 14, 628 (2014)
C.-K. Kim, P. He, A.B. Bialkowska, V.W. Yang, SP and KLF Transcription factors in digestive physiology and diseases. Gastroenterology 152, 1845–1875 (2017)
T.-H. Kim, R.A. Shivdasani, Genetic evidence that intestinal Notch functions vary regionally and operate through a common mechanism of Math1 repression. J. Biol. Chem. 286, 11427–11433 (2011)
Y. Hayakawa, H. Ariyama, J. Stancikova, K. Sakitani, S. Asfaha, B.W. Renz, Z.A. Dubeykovskaya, W. Shibata, H. Wang, C.B. Westphalen, X. Chen, Y. Takemoto, W. Kim, S.S. Khurana, Y. Tailor, K. Nagar, H. Tomita, A. Hara, A.R. Sepulveda, W. Setlik, M.D. Gershon, S. Saha, L. Ding, Z. Shen, J.G. Fox, R.A. Friedman, S.F. Konieczny, D.L. Worthley, V. Korinek, T.C. Wang, Mist1 expressing gastric stem cells maintain the normal and neoplastic gastric epithelium and are supported by a perivascular stem cell niche. Cancer Cell 28, 800–814 (2015)
G. Ferrari-Toninelli, S.A. Bonini, D. Uberti, L. Buizza, P. Bettinsoli, P.L. Poliani, F. Facchetti, M. Memo, Targeting Notch pathway induces growth inhibition and differentiation of neuroblastoma cells. Neuro Oncol. 12, 1231–1243 (2010)
C. Dantas-Barbosa, G. Bergthold, E. Daudigeos-Dubus, H. Blockus, J.F. Boylan, C. Ferreira, S. Puget, M. Abely, G. Vassal, J. Grill, B. Geoerger, Inhibition of the NOTCH pathway using γ-secretase inhibitor RO4929097 has limited antitumor activity in established glial tumors. Anticancer Drugs 26, 272–283 (2015)
A. De Jesus-Acosta, D. Laheru, A. Maitra, J. Arcaroli, M.A. Rudek, A. Dasari, P.J. Blatchford, K. Quackenbush, W. Messersmith, A phase II study of the gamma secretase inhibitor RO4929097 in patients with previously treated metastatic pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Invest. New Drugs 32, 739–745 (2014)
R. Gan, L. Lin, J. Xie, L. Huang, L. Ding, B. Su, X. Peng, D. Zheng, Y. Lu, FLI-06 intercepts Notch signaling and suppresses the proliferation and self-renewal of tongue cancer cells. Onco. Targets. Ther. 12, 7663–7674 (2019)
N. Cook, B. Basu, D.-M. Smith, A. Gopinathan, J. Evans, W.P. Steward, D. Palmer, D. Propper, B. Venugopal, M. Hategan, D.A. Anthoney, L.V. Hampson, M. Nebozhyn, D. Tuveson, H. Farmer-Hall, H. Turner, R. McLeod, S. Halford, D. Jodrell, A phase I trial of the γ-secretase inhibitor MK-0752 in combination with gemcitabine in patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Brit. J. Cancer 118, 793–801 (2018)
S. Liao, J. Xia, Z. Chen, S. Zhang, A. Ahmad, L. Miele, F.H. Sarkar, Z. Wang, Inhibitory effect of curcumin on oral carcinoma CAL-27 cells via suppression of Notch-1 and NF-κB signaling pathways. J. Cell. Biochem. 112, 1055–1065 (2011)
L. Zeng, A. Nikolaev, C. Xing, D.L. Della Manna, E.S. Yang, CHK1/2 Inhibitor Prexasertib suppresses NOTCH signaling and enhances cytotoxicity of cisplatin and radiation in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Mol. Cancer Ther. 19, 1279–1288 (2020)
C. Braicu, A.I. Irimie, O. Zanoaga, C. Gherman, I. Berindan-Neagoe, R.S. Campian, V. Pileczki, Epigallocatechin-3-gallate suppresses cell proliferation and promotes apoptosis and autophagy in oral cancer SSC-4 cells. Onco. Targets. Ther. 8, 461–470 (2015)
V.K. Kartha, K.A. Alamoud, K. Sadykov, B.-C. Nguyen, F. Laroche, H. Feng, J. Lee, S.I. Pai, X. Varelas, A.M. Egloff, J.E. Snyder-Cappione, A.C. Belkina, M.V. Bais, S. Monti, M.A. Kukuruzinska, Functional and genomic analyses reveal therapeutic potential of targeting β-catenin/CBP activity in head and neck cancer. Genome Med. 10, 54 (2018)
L.-H. Wang, M. Xu, L.-Q. Fu, X.-Y. Chen, F. Yang, The antihelminthic Niclosamide inhibits cancer stemness, extracellular matrix remodeling, and metastasis through dysregulation of the nuclear β-catenin/c-Myc axis in OSCC. Sci. Rep. 8, 12776 (2018)
S. Maji, O. Shriwas, S.K. Samal, M. Priyadarshini, R. Rath, S. Panda, S.K. Das Majumdar, D.K. Muduly, R. Dash, STAT3- and GSK3β-mediated Mcl-1 regulation modulates TPF resistance in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Carcinogenesis 40, 173–183 (2019)
C. Xiao, L. Wang, L. Zhu, C. Zhang, J. Zhou, Curcumin inhibits oral squamous cell carcinoma SCC-9 cells proliferation by regulating miR-9 expression. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm. 454, 576–580 (2014)
M. Giefing, M. Wierzbicka, K. Szyfter, J.C. Brenner, B.J. Braakhuis, R.H. Brakenhoff, C.R. Bradford, J.A. Sorensen, A. Rinaldo, J.P. Rodrigo, R.P. Takes, A. Ferlito, Moving towards personalised therapy in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma through analysis of next generation sequencing data. Eur. J. Cancer 55, 147–157 (2016)
C.-J. Yao, G.-M. Lai, C.-T. Yeh, M.-T. Lai, P.-H. Shih, W.-J. Chao, J. Whang-Peng, S.-E. Chuang, T.-Y. Lai, Honokiol eliminates human oral cancer stem-like cells accompanied with suppression of Wnt/β-catenin signaling and apoptosis induction. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med.. 2013, 1–10 (2013)
C. Zhang, Y. Hao, Y. Sun, P. Liu, Quercetin suppresses the tumorigenesis of oral squamous cell carcinoma by regulating microRNA-22/WNT1/β-catenin axis. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 140, 128–136 (2019)
J. Sophia, J. Kowshik, A. Dwivedi, S.K. Bhutia, B. Manavathi, R. Mishra, S. Nagini, Nimbolide, a neem limonoid inhibits cytoprotective autophagy to activate apoptosis via modulation of the PI3K/Akt/GSK-3β signalling pathway in oral cancer. Cell Death Dis. 9, 1087 (2018)
J. Sophia, T.K. Kiran Kishore, J. Kowshik, R. Mishra, S. Nagini, Nimbolide, a neem limonoid inhibits Phosphatidyl Inositol-3 Kinase to activate Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3β in a hamster model of oral oncogenesis. Sci. Rep. 6, 22192 (2016)
K.L. Hamilton, S.A. Sheehan, E.P. Retzbach, C.A. Timmerman, G.B. Gianneschi, P.J. Tempera, P. Balachandran, G.S. Goldberg, Effects of Maackia amurensis seed lectin (MASL) on oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) gene expression and transcriptional signaling pathways. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 147, 445–457 (2021)
H. Fan, H. Li, G. Liu, W. Cong, H. Zhao, W. Cao, J. Zheng, Doxorubicin combined with low intensity ultrasound suppresses the growth of oral squamous cell carcinoma in culture and in xenografts. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 36, 163 (2017)
S. Hehlgans, P. Booms, Ö Güllülü, R. Sader, C. Rödel, P. Balermpas, F. Rödel, S. Ghanaati, Radiation sensitization of basal cell and head and neck squamous cell carcinoma by the Hedgehog pathway inhibitor Vismodegib. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 19, 2485 (2018)
H. Kuroda, N. Kurio, T. Shimo, K. Matsumoto, M. Masui, K. Takabatake, T. Okui, S. Ibaragi, Y. Kunisada, K. Obata, N. Yoshioka, K. Kishimoto, H. Nagatsuka, A. Sasaki, Oral squamous cell carcinoma-derived Sonic Hedgehog promotes angiogenesis. Anticancer Res. 37, 6731–6737 (2017)
S. Kasiri, C. Shao, B. Chen, A.N. Wilson, P. Yenerall, B.C. Timmons, L. Girard, H. Tian, C. Behrens, I.I. Wistuba, A.F. Gazdar, J. Kim, GLI1 blockade potentiates the antitumor activity of PI3K antagonists in lung squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Res. 77, 4448–4459 (2017)
J. Kim, B.T. Aftab, J.Y. Tang, D. Kim, A.H. Lee, M. Rezaee, J. Kim, B. Chen, E.M. King, A. Borodovsky, G.J. Riggins, E.H. Epstein, P.A. Beachy, C.M. Rudin, Itraconazole and arsenic trioxide inhibit hedgehog pathway activation and tumor growth associated with acquired resistance to smoothened antagonists. Cancer Cell 23, 23–34 (2013)
X. Cai, K. Yu, L. Zhang, Y. Li, Q. Li, Z. Yang, T. Shen, L. Duan, W. Xiong, W. Wang, Synergistic inhibition of colon carcinoma cell growth by Hedgehog-Gli1 inhibitor arsenic trioxide and phosphoinositide 3-kinase inhibitor LY294002. Onco. Targets. Ther. 8, 877–883 (2015)
A. Almazán-Moga, P. Zarzosa, I. Vidal, C. Molist, I. Giralt, N. Navarro, A. Soriano, M.F. Segura, A. Alfranca, J. Garcia-Castro, Sánchez de Toledo, J., J. Roma, S. Gallego, Hedgehog pathway inhibition hampers sphere and holoclone formation in rhabdomyosarcoma. Stem Cells Int. 2017, 7507380 (2017)
M.C. Pietanza, A.M. Litvak, A.M. Varghese, L.M. Krug, M. Fleisher, J.B. Teitcher, A.I. Holodny, C.S. Sima, K.M. Woo, K.K. Ng, H.H. Won, M.F. Berger, M.G. Kris, C.M. Rudin, A phase I trial of the Hedgehog inhibitor, sonidegib (LDE225), in combination with etoposide and cisplatin for the initial treatment of extensive stage small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 99, 23–30 (2016)
S.A. Cannonier, C.B. Gonzales, K. Ely, S.A. Guelcher, J.A. Sterling, Hedgehog and TGFβ signaling converge on Gli2 to control bony invasion and bone destruction in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oncotarget 7, 76062–76075 (2016)
Q. Gao, Y. Yuan, H.-Z. Gan, Q. Peng, Resveratrol inhibits the hedgehog signaling pathway and epithelial-mesenchymal transition and suppresses gastric cancer invasion and metastasis. Oncol. Lett. 9, 2381–2387 (2015)
X.-D. Yu, J. Yang, W.-L. Zhang, D.-X. Liu, Resveratrol inhibits oral squamous cell carcinoma through induction of apoptosis and G2/M phase cell cycle arrest. Tumor Biol. 37, 2871–2877 (2016)
H. Xie, B.D. Paradise, W.W. Ma, M.E. Fernandez-Zapico, Recent advances in the clinical targeting of Hedgehog/GLI signaling in cancer. Cells 8, 394 (2019)
C.H. Choi, J.-Y. Ryu, Y.-J. Cho, H.-K. Jeon, J.-J. Choi, K. Ylaya, Y.-Y. Lee, T.-J. Kim, J.-Y. Chung, S.M. Hewitt, B.-G. Kim, D.-S. Bae, J.-W. Lee, The anti-cancer effects of itraconazole in epithelial ovarian cancer. Sci. Rep. 7, 6552 (2017)
R.D. Freitas, R.B. Dias, M.T.A. Vidal, L. Valverde, de F.Gomes Alves Costa, R. Damasceno, A.K.A. Sales, C.B.S., Siquara da Rocha, L. de O.Dos Reis, M.G. Soares, M.B.P. Coletta, R.D. Pereira, T.A. Bezerra, D.P.,G. Rocha, C.A., Inhibition of CAL27 oral squamous carcinoma cell by targeting Hedgehog pathway with Vismodegib or Itraconazole. Front. Oncol. 10, 563838 (2020)
Y. Guo, Y. Chen, H. Liu, W. Yan, Alpinetin inhibits oral squamous cell carcinoma proliferation via miR-211-5p upregulation and Notch pathway deactivation. Nutr. Cancer 72, 757–767 (2020)
Z. Liu, H. Li, S. Fan, H. Lin, W. Lian, STAT3-induced upregulation of long noncoding RNA HNF1A-AS1 promotes the progression of oral squamous cell carcinoma via activating Notch signaling pathway. Cancer Biol. Ther. 20, 444–453 (2019)
F. Liu, H.-X. Chu, J.-S. Han, X. Sun, J. Chen, X.-L. Qiu, X.-H. Zheng, B. Jia, J.-J. Zhao, Inhibitory effect of the Notch pathway-inhibitor DAPT on invasion and metastasis of tongue cancer via lncRNA-KAT14 regulation. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 24, 189–199 (2020)
K. He, Z.-B. Zhu, R. Shu, A. Hong, LncRNA NEAT1 mediates progression of oral squamous cell carcinoma via VEGF-A and Notch signaling pathway. World J. Surg. Oncol. 18, 261 (2020)
K.-L. Tang, H.-Y. Tang, Y. Du, T. Tian, S.-J. Xiong, MiR-638 suppresses the progression of oral squamous cell carcinoma through wnt/β-catenin pathway by targeting phospholipase D1. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 47, 3278–3285 (2019)
C. Huang, L. Wang, H. Song, C. Wu, MiR-29a inhibits the progression of oral squamous cell carcinoma by targeting Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 47, 3037–3042 (2019)
B. Liu, W. Chen, G. Cao, Z. Dong, J. Xu, T. Luo, S. Zhang, MicroRNA-27b inhibits cell proliferation in oral squamous cell carcinoma by targeting FZD7 and Wnt signaling pathway. Arch. Oral Biol. 83, 92–96 (2017)
B. Qiao, B.-X. He, J.-H. Cai, Q. Tao, A. King-Yin Lam, MicroRNA-27a-3p modulates the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway to promote epithelial-mesenchymal transition in oral squamous carcinoma stem cells by targeting SFRP1. Sci. Rep. 7, 44688 (2017)
J. Weng, H. Zhang, C. Wang, J. Liang, G. Chen, W. Li, H. Tang, J. Hou, miR-373-3p Targets DKK1 to promote EMT-induced metastasis via the Wnt/β-catenin pathway in tongue squamous cell carcinoma. Biomed. Res. Int. 2017, 6010926 (2017)
T.-R. Shao, Z.-N. Zheng, Y.-C. Chen, Q.-Q. Wu, G.-Z. Huang, F. Li, W.-S. Zeng, X.-Z. Lv, LncRNA AC007271.3 promotes cell proliferation, invasion, migration and inhibits cell apoptosis of OSCC via the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Life Sci. 239, 117087 (2019)
F. Chen, S. Qi, X. Zhang, J. Wu, X. Yang, R. Wang, lncRNA PLAC2 activated by H3K27 acetylation promotes cell proliferation and invasion via the activation of Wnt/β-catenin pathway in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Int. J. Oncol. 54, 1183–1194 (2019)
Y. Zhou, S. Sinha, J.L. Schwartz, G.R. Adami, A subtype of oral, laryngeal, esophageal, and lung, squamous cell carcinoma with high levels of TrkB-T1 neurotrophin receptor mRNA. BMC Cancer 19, 607 (2019)
H. Ma, L. Li, L. Jia, A. Gong, A. Wang, L. Zhang, M. Gu, G. Tang, POM121 is identified as a novel prognostic marker of oral squamous cell carcinoma. J. Cancer 10, 4473–4480 (2019)
S.M. De carvalho lyra, A.B. Moleri, R.S. Dezonne, De sampaio e spohr, T.C.L., De Queiroz chaves lourenço, S. Moura-neto, V. Pereira, C.M., Evaluation of microRNAs related to the Sonic Hedgehog pathway in oral cancer. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 129, e133 (2020)
Z. Wei, Y. Wang, L. Jiang, N. Ji, Y. Wang, F. Chen, T. Li, J. Li, H. Xu, X. Zeng, Q. Chen, miR-223 regulates oral squamous cell carcinoma metastasis through the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Oral Oncol. 109, 104941 (2020)
G.-H. Li, Z.-H. Ma, X. Wang, Long non-coding RNA CCAT1 is a prognostic biomarker for the progression of oral squamous cell carcinoma via miR-181a-mediated Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Cell Cycle 18, 2902–2913 (2019)
Y. Ai, S. Wu, C. Zou, H. Wei, LINC00941 promotes oral squamous cell carcinoma progression via activating CAPRIN2 and canonical WNT/β-catenin signaling pathway. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 24, 10512–10524 (2020)
J. Vermonken, E. Remenar, A. Kawecki, S. Rottey, J. Erfan, D. Zabolotnyy, H.-R. Keinzer, D. Cupissol, F. Peyrade, M. Benasso, I. Vynnychenko, D. Raucourt, C. De, Bokemeyer, A. Schueler, N. Amellal, R. Hitt, Platinum-based chemotherapy plus cetuximab in head and neck cancer. New Engl. J. Med. 359, 1116–1127 (2008)
B. Burtness, M.A. Goldwasser, W. Flood, B. Mattar, A.A. Forastiere, Phase III randomized trial of cisplatin plus placebo compared with cisplatin plus cetuximab in metastatic / recurrent head and neck cancer: An eastern cooperative oncology group study. J. Clin. Oncol. 23, 8646–8654 (2017)
S.A. Kono, M.H. Jr, S.S. Yom, N. Saba, EGFR monoclonal antibodies in the treatment of squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck: A view beyond cetuximab. Chemother. Res. Pract. 2012, 1–10 (2012)
P. Bonomo, I. Desideri, M. Loi, M. Mangoni, M. Sottili, L. Marrazzo, C. Talamonti, D. Greto, S. Pallotta, L. Livi, Anti PD-L1 DUrvalumab combined with Cetuximab and RadiOtherapy in locally advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck: A phase I/II study (DUCRO). Clin. Transl. Radiat. Oncol. 9, 42–47 (2018)
C. Xiao, L. Wang, L. Zhu, C. Zhang, J. Zhou, Curcumin inhibits oral squamous cell carcinoma SCC-9 cells proliferation by regulating miR-9 expression. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm. 454, 576–580 (2014)
S. Liao, J. Xia, Z. Chen, S. Zhang, A. Ahmad, L. Miele, F.H. Sarkar, Z. Wang, Inhibitory effect of curcumin on oral carcinoma CAL-27 cells via suppression of Notch-1 and NF-kB signaling pathways. J. Cell. Biochem. 1065, 1055–1065 (2011)
W. Pathway, X. Li, J. Wu, S. Geng, C. Zhong, H. Han, (–)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate inhibits colorectal cancer stem cells by suppressing Wnt/ β-catenin pathway. Nutrients 9, 1–11 (2017)
J. Kim, X. Zhang, K.M. Rieger-christ, I.C. Summerhayes, D.E. Wazer, K.E. Paulson, A.S. Yee, Suppression of Wnt signaling by the green tea compound (؊) -epigallocatechin 3-gallate (EGCG) in invasive breast cancer cells. J. Biol. Chem. 281, 10865–10875 (2006)
J. Zhu, Y. Jiang, X. Yang, S. Wang, C. Xie, X. Li, Y. Li, Y. Chen, X. Wang, Y. Meng, M. Zhu, R. Wu, C. Huang, X. Ma, S. Geng, J. Wu, C. Zhong, Wnt/β-catenin pathway mediates (-)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) inhibition of lung cancer stem cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 482, 15–21 (2017)
Y. Chen, X. Wang, (–) -Epigallocatechin gallate targets Notch to attenuate the inflammatory response in the immediate early stage in human macrophages. Front. Immunol. 8, 1–21 (2017)
E.J. Allenspach, I. Maillard, J.C. Aster, W.S. Pear, Notch signaling in cancer. Cancer Biol. Ther. 1, 466–476 (2002)
L.L. Rubin, F.J. de Sauvage, Targeting the Hedgehog pathway in cancer. Nature Rev. Drug Discov. 5, 1026–1033 (2006)
P. Polakis, Wnt signaling and cancer. Genes Dev. 14, 1837–1851 (2000)
M. Dvorakova, T. Vanek, Histone deacetylase inhibitors for the treatment of cancer. Stem Cells 7, 2217–2231 (2016)
Acknowledgements
Work on OSCC Notch signaling has been performed in the lab through an Indo-Africa project sanctioned by the Government of India. The authors thank the Department of Science and Technology (DST), Government of India, for the support.
Funding
Funded through an Indo South Africa project sanctioned by the Department of Science and Technology (DST), Government of India, under the Bilateral Programme (DST/INT/SOUTH Africa/P-12/2016).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Consent for publication
All authors agreed to publish the article.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Patni, A.P., Harishankar, M.K., Joseph, J.P. et al. Comprehending the crosstalk between Notch, Wnt and Hedgehog signaling pathways in oral squamous cell carcinoma - clinical implications. Cell Oncol. 44, 473–494 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13402-021-00591-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13402-021-00591-3