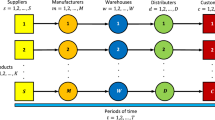
Abstract
Various studies have discussed the coordination of product and supply chain design decisions for global supply chain management. However, the impact of currency exchange rate uncertainty on the selection of product architectures and their suppliers has not been sufficiently addressed. As a response, this study proposes a two-stage stochastic optimization model in which the first stage determines the product architecture, and the second stage identifies suppliers for the modules and components in an optimal fashion based on the product architecture and uncertain currency exchange rates. The overall objective of two-stage stochastic programming is to determine the optimal product architecture that minimizes the expected total supply chain cost over uncertain currency exchange rate scenarios. The proposed model is applied to a bicycle supply chain case study for three global marketplaces associated with multiple currency exchange rates. The results demonstrate that optimal product architecture and its suppliers should be varied based on currency exchange rates and their uncertain fluctuation levels. Also, a product architecture for the supply chain of each marketplace maintains its optimality in the total supply chain cost, up to a specific exchange rate. The findings show the importance of joint integration between product and supply chain design when considering currency exchange rates. Additionally, the benefit of stochastic modelling is demonstrated by comparing the solution quality of the model with its deterministic counterpart.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bandaly D, Satir A, Shanker L (2014) Integrated supply chain risk management via operational methods and financial instruments. Int J Prod Res 52:2007–2025
Baud-Lavigne B, Bassetto S, Agard B (2016) A method for a robust optimization of joint product and supply chain design. J Intell Manuf 27:741–749
Bertsimas D, Gupta V, Kallus N (2018) Robust sample average approximation. Math Program 171:217–282
Blackhurst J, Wu T, O’Grady P (2005) PCDM: a decision support modeling methodology for supply chain, product and process design decisions. J Oper Manag 23:325–343
BLS (2016) Occupational outlook handbook 2016–2017. BLS (Bureau of Labor Statistics). https://www.bls.gov/ooh/production/assemblers-andfabricators.htm. Accessed 25 Sep 2017
Carter JR, Vickery SK (1989) Currency exchange rates: their impact on global sourcing. Journal of Purch Mater Manag 25:19–26
Chiu M-C (2010) A graph theory-based integration of product design and supply chain design. PhD Dissertation, The Pennsylvania State University, University Park
Chiu M-C, Okudan Kremer GE (2011) An integrative methodology for product and supply chain design decisions at the product design stage. J Mech Des 133:021008
Chiu M-C, Okudan Kremer GE (2014) An investigation on centralized and decentralized supply chain scenarios at the product design stage to increase performance. IEEE Trans Eng Manage 61:114–128
Christopher M (2016) Logistics & supply chain management, 5th edn. Financial Times Prentice Hall/Pearson, London
Christopher M, Mena C, Khan O, Yurt O (2011) Approaches to managing global sourcing risk. Supply Chain Manag Int J 16:67–81
Ding Q, Dong L, Kouvelis P (2007) On the integration of production and financial hedging decisions in global markets. Oper Res 55:470–489
Ellram LM, Tate WL, Carter CR (2007) Product-process-supply chain: an integrative approach to three-dimensional concurrent engineering. Int J Phys Distrib Log Manag 37:305–330
ElMaraghy HA, Mahmoudi N (2009) Concurrent design of product modules structure and global supply chain configurations. Int J Comput Integr Manuf 22:483–493
ERI (2017) Planning Global Compensation Budgets for 2018. Economic Research Institute (ERI). http://downloads.erieri.com/pdf/PlanningGlobalCompensationBudgetsfor2018.pdf. Accessed 20 Sep 2017
Eurostat (2017) Hourly labour costs. https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/statistics-explained/index.php/Hourly_labour_costs. Accessed 20 Sep 2017
Fine CH, Golany B, Naseraldin H (2005) Modeling tradeoffs in three-dimensional concurrent engineering: a goal programming approach. J Oper Manag 23:389–403
Fixson SK (2005) Product architecture assessment: a tool to link product, process, and supply chain design decisions. J Oper Manag 23:345–369
Frohlich MT, Westbrook R (2001) Arcs of integration: an international study of supply chain strategies. J Oper Manag 19:185–200
Goh M, Lim JY, Meng F (2007) A stochastic model for risk management in global supply chain networks. Eur J Oper Res 182:164–173
Günay EE, Kula U (2017) A stochastic programming model for resequencing buffer content optimisation in mixed-model assembly lines. Int J Prod Res 55(10):2897–2912
Günay EE, Okudan Kremer GE, Park K (2019) Effect of supplier selection regulations on new product design. Proc Manuf 39:1337–1345
Gylling M, Heikkilä J, Jussila K, Saarinen M (2015) Making decisions on offshore outsourcing and backshoring: A case study in the bicycle industry. Int J Prod Econ 162:92–100
Hammami R, Temponi C, Frein Y (2014) A scenario-based stochastic model for supplier selection in global context with multiple buyers, currency fluctuation uncertainties, and price discounts. Eur J Oper Res 233:159–170
Hasani A, Khosrojerdi A (2016) Robust global supply chain network design under disruption and uncertainty considering resilience strategies: a parallel memetic algorithm for a real-life case study. Transport Res Part E Log Transport Rev 87:20–52
Hu X, Motwani JG (2014) Minimizing downside risks for global sourcing under price-sensitive stochastic demand, exchange rate uncertainties, and supplier capacity constraints. Int J Prod Econ 147:398–409. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2013.04.045
Khan O, Creazza A (2009) Managing the product design-supply chain interface: Towards a roadmap to the “design centric business.” Int J Phys Distrib Log Manag 39:301–319
Kim K-K, Park KS (2014) Transferring and sharing exchange-rate risk in a risk-averse supply chain of a multinational firm. Eur J Oper Res 237:634–648
Kleywegt AJ, Shapiro A, Homem-de-Mello T (2002) The sample average approximation method for stochastic discrete optimization. SIAM J Optim 12:479–502
Li L, Porteus EL, Zhang H (2001) Optimal operating policies for multiplant stochastic manufacturing systems in a changing environment. Manage Sci 47:1539–1551
Li H, Ma H, Xu Y (2015) How do exchange rate movements affect Chinese exports?—a firm-level investigation. J Int Econ 97:148–161
Mak W-K, Morton DP, Wood RK (1999) Monte Carlo bounding techniques for determining solution quality in stochastic programs. Oper Res Lett 24:47–56
Marsillac E, Roh JJ (2014) Connecting product design, process and supply chain decisions to strengthen global supply chain capabilities. Int J Prod Econ 147:317–329. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2013.04.011
Meixell MJ, Gargeya VB (2005) Global supply chain design: a literature review and critique. Transport Res Part E Log Transport Rev 41:531–550. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tre.2005.06.003
Nasiłowski M, Radzai R (1991) The hard road to the uniform exchange rate in poland. Soviet Eastern Eur Foreign Trade 27:83–96
NBC (2017) Forex: economics and streategy. https://www.nbc.ca/content/dam/bnc/en/rates-and-analysis/economic-analysis/forex.pdf. Accessed 20 Sep 2017
Nepal B, Monplaisir L, Famuyiwa O (2012) Matching product architecture with supply chain design. Eur J Oper Res 216:312–325. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejor.2011.07.041
Park K, Okudan Kremer GE, Ma J (2018) A regional information-based multi-attribute and multi-objective decision-making approach for sustainable supplier selection and order allocation. J Clean Prod 187:590–604
Pashaei S, Olhager J (2015) Product architecture and supply chain design: a systematic review and research agenda. Supply Chain Manag Int J 20:98–112. https://doi.org/10.1108/SCM-12-2013-0487
Petersen KJ, Handfield RB, Ragatz GL (2005) Supplier integration into new product development: coordinating product, process and supply chain design. J Oper Manag 23:371–388. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jom.2004.07.009
Rosenfield DB (1996) Global and variable cost manufacturing systems. Eur J Oper Res 95:325–343
Santoso T, Ahmed S, Goetschalckx M, Shapiro A (2005) A stochastic programming approach for supply chain network design under uncertainty. Eur J Oper Res 167:96–115
Schütz P, Tomasgard A, Ahmed S (2009) Supply chain design under uncertainty using sample average approximation and dual decomposition. Eur J Oper Res 199:409–419
Singh AR, Mishra PK, Jain R, Khurana MK (2012) Design of global supply chain network with operational risks. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 60:273–290
Tang O, Musa SN (2011) Identifying risk issues and research advancements in supply chain risk management. Int J Prod Econ 133:25–34
TE (2017a) Economic forcast. https://tradingeconomics.com/taiwan/forecast. Accessed 20 Sep 2017
TE (2017b) Japan munimum hourly wages. https://tradingeconomics.com/japan/minimum-wages. Accessed 20 Sep 2017
TE (2017c) Taiwan munimum hourly wages. https://tradingeconomics.com/japan/minimum-wages. Accessed 20 Sep 2017
Thomas DJ, Griffin PM (1996) Coordinated supply chain management. Eur J Oper Res 94:1–15
Ülkü S, Schmidt GM (2011) Matching product architecture and supply chain configuration. Prod Oper Manag 20:16–31
Wang G, Huang SH, Dismukes JP (2004) Product-driven supply chain selection using integrated multi-criteria decision-making methodology. Int J Prod Econ 91:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0925-5273(03)00221-4
Wang D, Du G, Jiao RJ, Wu R, Yu J, Yang D (2016) A Stackelberg game theoretic model for optimizing product family architecting with supply chain consideration. Int J Prod Econ 172:1–18
Ware NR, Singh SP, Banwet D (2014) Modeling flexible supplier selection framework. Glob J Flex Syst Manag 15:261–274
Acknowledgment
This work was partially supported by a TUBITAK (The Scientific and Technological Research Council of Turkey) Postdoctoral Research Fellowship. The authors would like to thank ICPR 25, which provided an opportunity to discuss and improve the preliminary work of this study (Günay et al. 2019).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Günay, E.E., Park, K. & Okudan Kremer, G.E. Integration of product architecture and supply chain under currency exchange rate fluctuation. Res Eng Design 32, 331–348 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00163-021-00361-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00163-021-00361-0